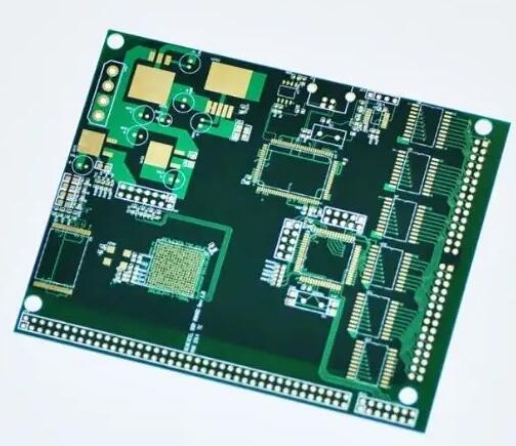
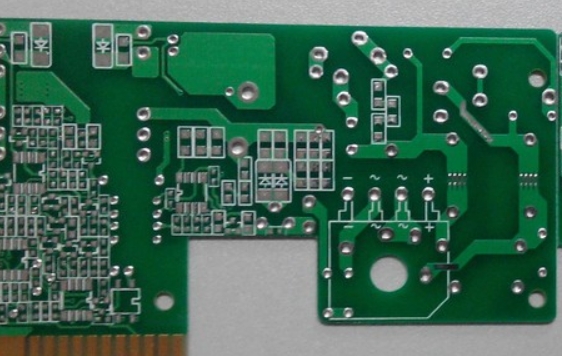
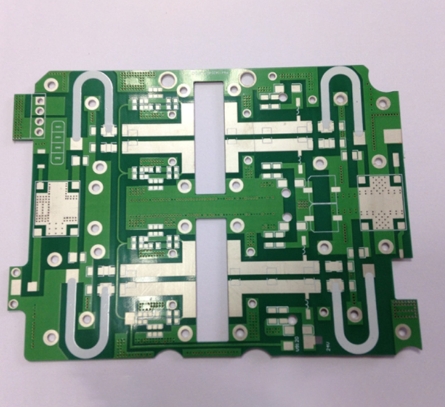
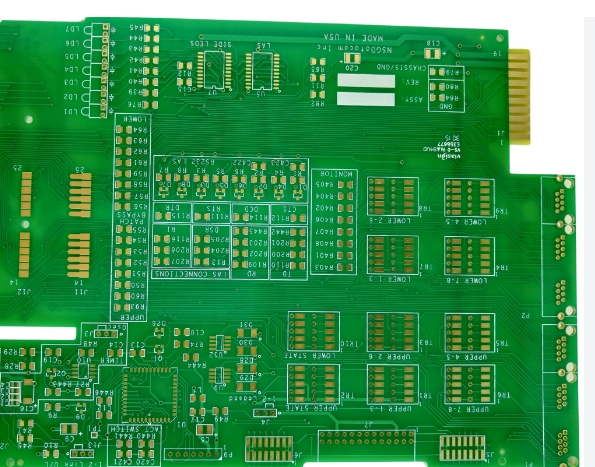
Designing mixed-signal systems requires attention to placement, trace layout, and protection elements. Today’s SOCs necessitate expertise in digital, analog, and thermal design, pushing system designers to mitigate common pitfalls such as noise, ground bounce, and latch-up. 1. Challenges in Mixed-Signal Systems High-Speed Trends The drive for higher performance in systems like PCs and servers has...
HomeAuthor
kkpcba-Cindy - KKPCB - Page 48 of 75
When designing high-speed PCBs, understanding the core concepts is crucial for ensuring efficiency and functionality. This guide introduces key elements such as layers, vias, pads, and more to help beginners and professionals alike. 1. The Concept of “Layer” PCB layers represent the actual copper foil layers within the board material, unlike virtual layers in software. Modern...
Impedance plays a critical role in the functionality, reliability, and performance of printed circuit boards (PCBs). Understanding and managing impedance is essential for ensuring proper signal transmission and maintaining the integrity of the electronic devices that rely on these boards. Below is a detailed analysis of impedance and its importance in PCB design and manufacturing. 1. What...
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) play a crucial role in supporting and connecting electronic components, while interference can significantly impact their performance. This guide explores anti-interference design principles for PCBs and microcontrollers (MCUs) to ensure reliable operation in high-noise environments. Key Principles of PCB Anti-Interference Design 1. Ground Wire Layout Separate Digital and Analog Ground: Isolate digital and...
Copper coating, also known as copper filling, is an essential aspect of PCB design that plays a key role in reducing impedance, improving anti-interference capabilities, and enhancing the overall efficiency of power delivery. However, there are several factors to consider when applying copper coating, and the effectiveness depends on how well it is executed. Let’s explore the...
High-quality PCB production begins with high-quality design. Huaqiang PCB manufacturing heavily relies on the cooperation of the design process. Engineers, please design your PCBs according to the detailed explanation of the conventional production process below. Design Parameters for PCB Manufacturing 1. Via (Conductive Hole) Minimum hole diameter: 0.3mm (12mil) The minimum via hole diameter is 0.3mm, and...
PCB design is a critical, time-consuming task. Any errors require engineers to meticulously check the entire design, analyzing each network and component. This process requires a level of carefulness comparable to chip design. Typical PCB Design Process The typical PCB design process consists of several steps, with the first three steps taking the most time. Schematic...
PCB layout in mobile phone design requires meticulous attention to minimize risks and ensure optimal performance. With multiple layers dedicated to various functions, specific guidelines help maintain signal integrity and reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI). Below are the detailed issues and wiring principles to consider in mobile phone PCB layout, especially for complex components like RF circuits...
Power supply noise interference is a critical challenge in PCB design, particularly in high-frequency circuits. Noise from the power supply can significantly impact signal integrity and overall circuit performance. This article provides an in-depth analysis of power supply noise, its causes, and practical strategies to mitigate interference in PCB design. Understanding Power Supply Noise Power supply...
I. Component Layout Rules Module-Based Layout: Group related components that serve the same function into a module. Separate digital and analog circuits to minimize interference. Clearance Around Holes: Non-mounting holes (e.g., positioning holes): Keep a 1.27mm clearance around them. Mounting holes (e.g., screw holes): Maintain 3.5mm clearance for M2.5 screws and 4mm for M3 screws. Avoid Vias Under Components: Do not place vias under horizontal...