Introduction With the rapid advancement of modern technology, high-frequency electronic systems such as RF, microwave, and radar equipment are increasingly prevalent. At the core of these systems lies the Printed Circuit Board (PCB) — the foundation upon which signal integrity and overall device performance depend. Among the materials used for PCB fabrication, Teflon (PTFE) stands...
HomeTag
PCB manufacturing - KKPCB
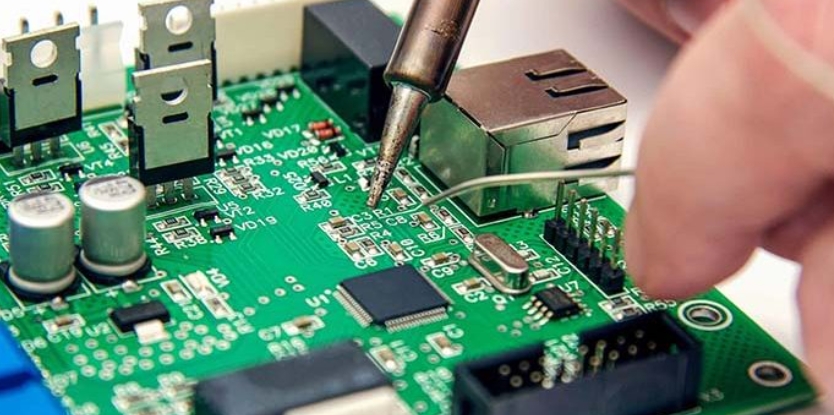
Mastering High-Speed PCB Test Point Design: Precision, Performance, and Signal Integrity In high-speed printed circuit board (PCB) design, test point placement is far more than a routine step—it’s a science of balance. The miniature metal pads scattered across a PCB may look simple, but their position, size, and electrical behavior can determine whether a product...
Ensuring PCB Reliability Through Burn-in Testing — How KKPCB Guarantees Long-Term Performance In high-performance electronics, reliability isn’t a luxury — it’s a requirement. At KKPCB, every printed circuit board that leaves our production line is expected to perform consistently under demanding real-world conditions. One of the most critical steps in achieving that standard is our...
Blind and Buried Vias in PCB Design — Structure, Function, and Manufacturing Insights As the miniaturization of electronic components continues to accelerate, PCB designs must accommodate finer pitch components and higher circuit densities, especially in advanced mobile, communication, and computing applications. One of the critical technologies enabling this evolution is the use of blind and...
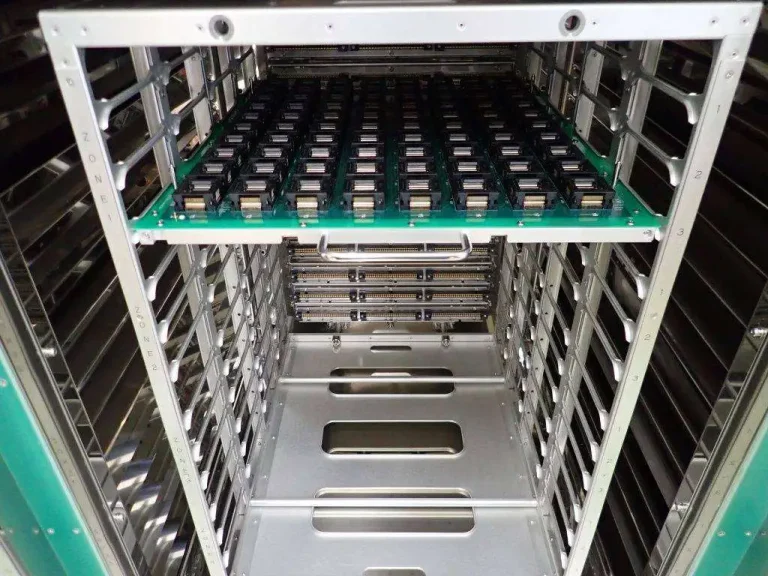
Radar PCB Overview Radar PCBs represent the pinnacle of high-frequency circuit design, bridging advanced RF engineering and precise manufacturing. These specialized boards operate in the 1 GHz – 77 GHz range, demanding exceptional signal integrity, low loss materials, and extreme reliability — especially in mission-critical applications like automotive radar, aerospace, and defense. KKPCB has extensive...
KKPCB provides expert PCB stackup design and multilayer PCB manufacturing. Ensure impedance control, EMI performance, and reliable high-speed circuit performance.
Electronic devices have transformed our lives, from smartphones to electric vehicles, all thanks to continuous innovation and advancements in technology. At the heart of these devices are printed circuit boards (PCBs) that are meticulously manufactured, assembled, and packaged to deliver the final products we rely on. This article explores the PCB Surface Mount Technology (SMT) assembly process,...
When it comes to assembling Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs), there are two primary technologies: Surface Mount Technology (SMT) assembly and Through-Hole Technology (PTH) assembly. Understanding their differences, advantages, and disadvantages is crucial for selecting the best option for your PCB-based project. This guide by Viasion experts provides a comprehensive comparison to help you make an informed decision. What...
Manufacturers use flux to solder components on PCBs. Depending on the PCB components, flux also varies and is used to fix them on the board. It ensures uninterrupted and strong electrical connections between devices. However, it is crucial to remove excess flux so as not to blur signal traces or damage connections. In this article,...
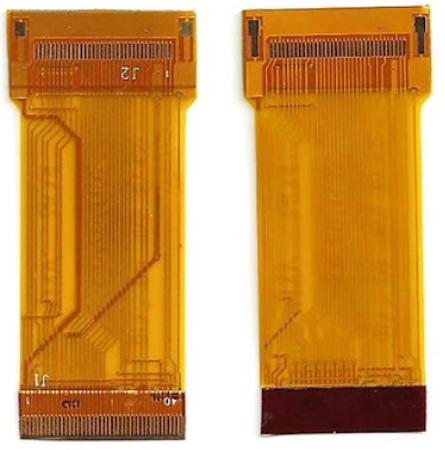
Differences between single-layer FPC, double-layer FPC and multi-layer FPC Multi-layer FPC Multi-layer FPC is to stack three or more layers of single-sided or double-sided flexible circuits together, and make metallized holes through drilling, electroplating and other processes to achieve conductive paths between different layers, so no complex welding process is required. Multi-layer circuits have great functional...