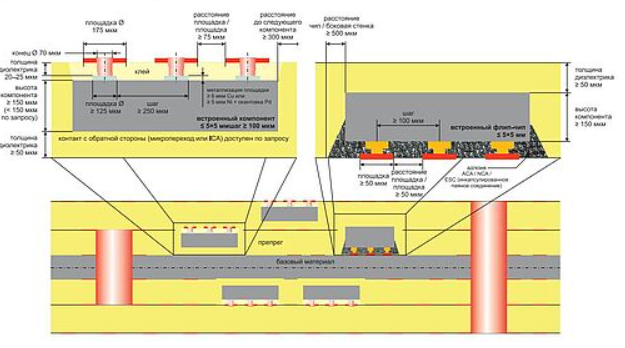
As electronic devices become faster and more complex, maintaining the quality of electrical signals on a PCB is critical. Signal Integrity PCBs are designed to preserve signal quality, minimize noise, and reduce data errors in high-speed circuits. Proper design and manufacturing of these boards are essential for reliable high-performance electronics, from telecommunications and computing to...
HomeTag
PCB Design - KKPCB
Modern electronics often require boards capable of handling high currents safely and efficiently. High Current PCBs are specially designed to manage large amounts of electrical current while maintaining thermal stability, signal integrity, and mechanical reliability. These PCBs are widely used in power electronics, automotive systems, industrial machinery, and energy storage applications. What is a High...
In today’s rapidly evolving electronics market, devices are becoming smaller, faster, and more complex. To meet these demands, Microvia PCBs have become a critical solution in HDI PCB and high-speed PCB design. Microvias are extremely small vias that create precise interlayer connections, allowing for high-density routing, improved signal integrity, and reliable performance in modern electronic...
1. Why Thermal Conductivity of Metals Matters in PCB Applications Metals are widely used in electronic devices and printed circuit boards (PCBs) due to their excellent electrical and thermal properties. However, not all metals conduct heat equally. High thermal conductivity metals rapidly transfer heat and are ideal for heat dissipation Low thermal conductivity metals restrict...
Introduction: Why PCB Prototype Engineering Defines Modern Electronics A PCB Prototype is no longer just a pre-production sample—it is the central engineering stage that determines product performance, manufacturability, reliability, and cost.In advanced electronics such as 5G, IoT, robotics, automotive, aerospace, AI edge computing, and industrial automation, a well-engineered PCB Prototype ensures signal integrity, thermal stability,...
The Evolution of Embedded Component Technology in Modern Electronics Looking back at the evolution of computing—from Apollo workstations and early mainframes to ultrathin laptops and smartphones—the miniaturization of electronic components has always been central to technological progress. As devices become smaller and more powerful, engineers must balance form factor, functionality, PCB materials, signal integrity, power...
Medical PCB Manufacturing: Technologies, Design, and the Future of Electronic Healthcare As medical technology continues to evolve, diagnostics and treatments increasingly depend on sophisticated automated systems. These systems rely on high-precision PCBs (Printed Circuit Boards)—miniaturized, high-density circuit assemblies that integrate numerous components within limited space. To guarantee performance, medical PCB assemblies incorporate advanced design features...
Single Layer PCBs: A Comprehensive and Technical Guide Introduction Single-layer printed circuit boards (PCBs)—often referred to as single-sided or 1-layer PCBs—represent the most fundamental yet enduring form of PCB technology. Despite the fast-growing adoption of multilayer, HDI, and advanced substrate solutions, single-layer boards continue to dominate large segments of consumer electronics, industrial instrumentation, IoT nodes,...
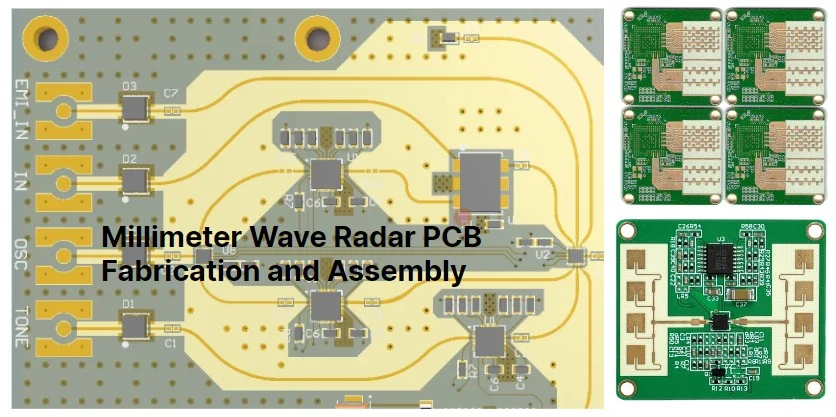
ADAS PCB Layout Guidelines for Automotive Radar Systems In the rapidly advancing world of automotive technology, Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) are revolutionizing how we drive, enhancing safety and intelligence in vehicles. At the heart of many ADAS features lies the automotive radar system, which relies on precise and effective printed circuit board (PCB) design...
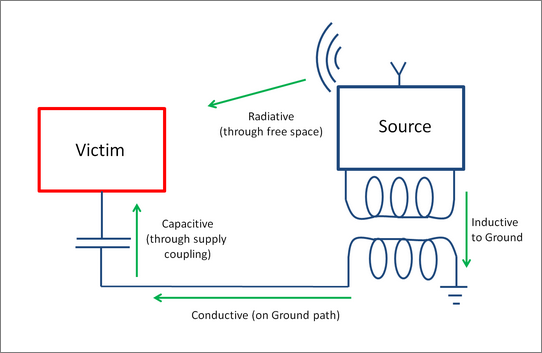
Why EMC Matters in PCB Design Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) is a key requirement in modern PCB design, ensuring that electronic systems operate reliably without generating or being affected by electromagnetic interference (EMI). Proper PCB layout—especially GND routing, trace spacing, and layer design—plays a decisive role in reducing ESD (Electrostatic Discharge) and improving overall signal integrity....