Why PCB Turnkey Matters in Modern Electronics Manufacturing As electronic systems become more complex, managing separate suppliers for PCB fabrication, component sourcing, assembly, and testing introduces cost risk, schedule delays, and quality uncertainty. This is especially true for products involving high-speed digital signals, RF circuits, power electronics, or mixed-technology assemblies. PCB turnkey solutions address this...
HomeCategory
PCB Materials | FR-4, High-Frequency, Low-Loss & Heavy Copper - KKPCB
Introduction: Why Controlled Impedance Defines High-Speed Reliability As high-speed electronics push into multi-gigabit data rates and high-frequency RF domains, signal behavior is no longer dominated by logic thresholds—it is governed by transmission line physics. In these systems, every PCB trace behaves as a controlled impedance structure, and any deviation can introduce reflections, timing skew, and...
Balancing Electrical Performance and Manufacturability in Buried Via PCB Structures Buried vias are often introduced into PCB designs to improve electrical performance.Shorter signal paths, reduced stub effects, and higher routing density make buried via PCB structures attractive for high-speed and high-density applications. In practice, however, electrical optimization and manufacturing stability do not always move in...
Engineering High Layer Count PCBs: Why “More Layers” Isn’t the Answer As electronic systems evolve toward higher speeds, higher integration, and smaller form factors, high layer count PCBs—typically 16 layers and above—have become standard in data centers, telecommunications, aerospace electronics, and advanced industrial systems. However, many multilayer PCBs fail not because of schematic errors, but...
Electronics Industry NewsCustomer CaseEngineering TechnologiesPCB DesignPCB ManufacturingPCB Materials
Small Batch PCB Manufacturing for High-Mix, Engineering-Driven Electronics Development
Small Batch PCB manufacturing refers to low-volume PCB production typically ranging from a few pieces to several hundred units, designed to support prototype validation, pilot runs, and early-stage product commercialization. Unlike mass production, Small Batch PCB emphasizes engineering accuracy, process flexibility, and rapid iteration over scale efficiency. For modern electronics development, Small Batch PCB is...
Electronics Industry NewsCustomer CaseEngineering TechnologiesPCB DesignPCB ManufacturingPCB Materials
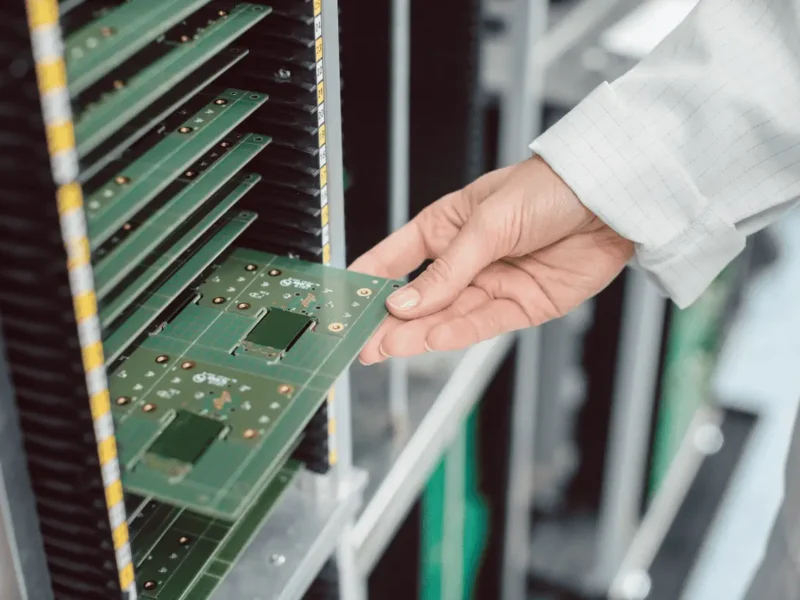
PCB Turnkey Solutions for Integrated Design, Fabrication, Assembly, and Supply Chain Management
PCB Turnkey: A Complete Engineering-Driven Manufacturing Model PCB Turnkey refers to a fully integrated manufacturing solution that covers PCB fabrication, component sourcing, PCB assembly, functional testing, and logistics delivery under a single engineering-managed workflow. Unlike fragmented outsourcing models, PCB Turnkey services eliminate interface risk between suppliers and significantly improve quality consistency, lead time predictability, and...
High Layer Count PCB: The Backbone of Complex Electronic Systems A High Layer Count PCB refers to a multilayer printed circuit board typically featuring 16 layers, 24 layers, 32 layers, or more, designed to support complex signal routing, dense interconnections, and advanced power distribution. As electronic systems continue to integrate higher data rates, tighter form...
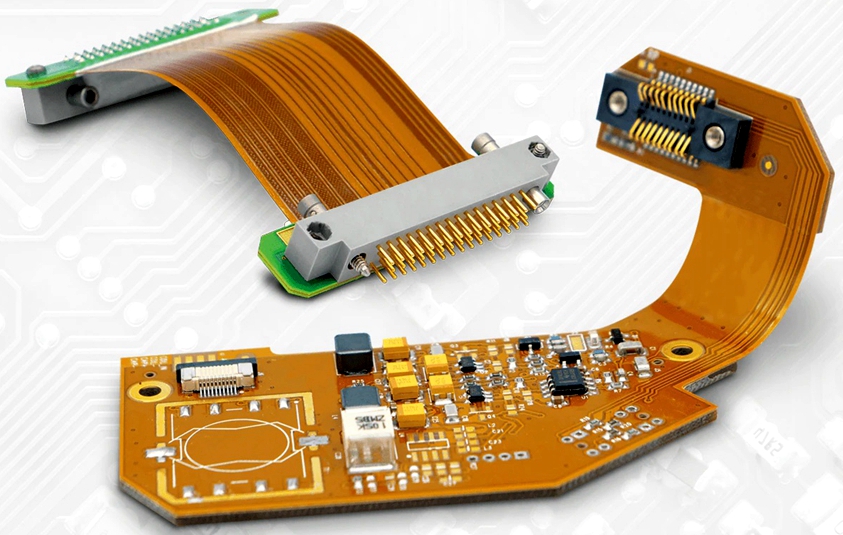
Rigid-Flex PCB: Integrating Mechanical Flexibility with Rigid PCB Performance A Rigid-Flex PCB is a hybrid printed circuit board that combines rigid PCB sections and flexible circuits into a single integrated structure. By embedding flexible polyimide layers between rigid FR-4 or high-performance laminates, Rigid-Flex PCB architectures eliminate connectors, reduce interconnect failures, and enable compact three-dimensional electronic...
Buried Via PCB: Enabling High-Density Interconnection Beyond Conventional Multilayer Boards A Buried Via PCB is a multilayer printed circuit board in which vias connect only internal layers and do not extend to the outer layers. Unlike through-hole vias, buried vias are completely embedded within the PCB stackup, enabling higher routing density, improved signal integrity, and...
High Layer Count PCB: The Backbone of Ultra-Complex Electronic Integration A High Layer Count PCB refers to a multilayer printed circuit board typically exceeding 12 layers and extending to 20, 30, or even 60+ layers for advanced electronic systems. High layer count PCB designs are essential for applications requiring dense routing, high-speed signal transmission, controlled...