KKPCB specializes in high-performance Aluminum PCBs (MCPCBs) with 1–8 W/m·K thermal conductivity for LED lighting, power converters, motor drivers, and industrial electronics. Fast quote & high reliability.
HomeCategory
PCB Manufacturing Services | High-Quality PCB & PCBA - KKPCB
Printed circuit board (PCB) Prototyping allows engineers to check whether the design will perform as their expectations. At the same time, your PCB prototyping manufacturer would like to check if your circuit boards can be manufactured efficiently. Multiple prototyping runs can be used to test the PCB design variations or to perfect a single function before moving on to the...
Copper in Printed Circuit Boards Printed circuit boards (PCBs), or called printed wiring boards (PWBs), have become basic parts in almost all areas of modern technologies. Copper trace is a crucial element on circuit boards. The copper always plays a role of carrying electrical signals to different components across the board assembly. Without traces, the...
Printed circuit boards (PCBs) are the core of most electronics today, determining basic functions through combinations of components and wiring mechanisms. Most PCBs of the past were relatively simple and limited by manufacturing techniques, while today’s PCBs are much more complex. From advanced flexible options to odd-shaped varieties, PCBs are much more varied in nowadays’ world...
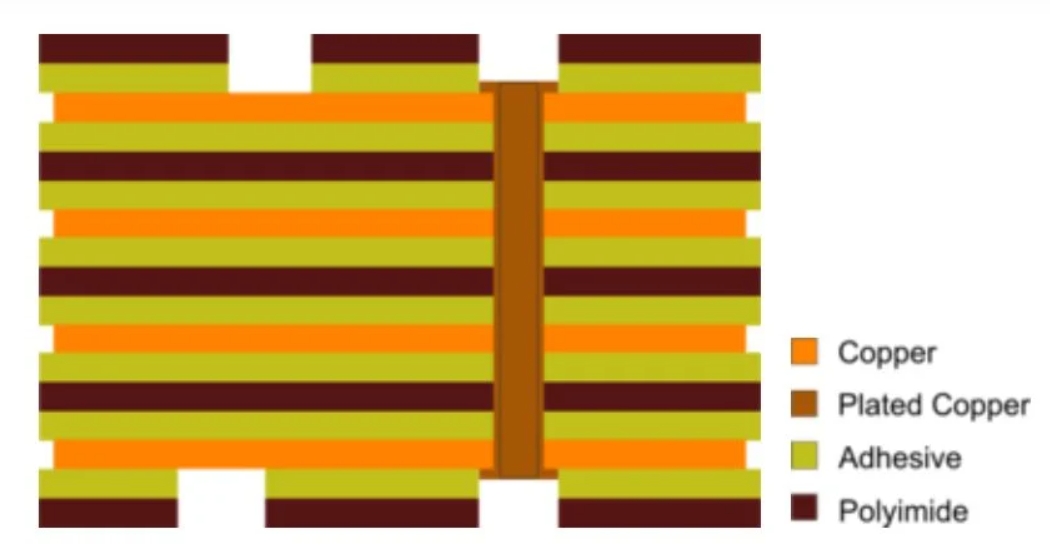
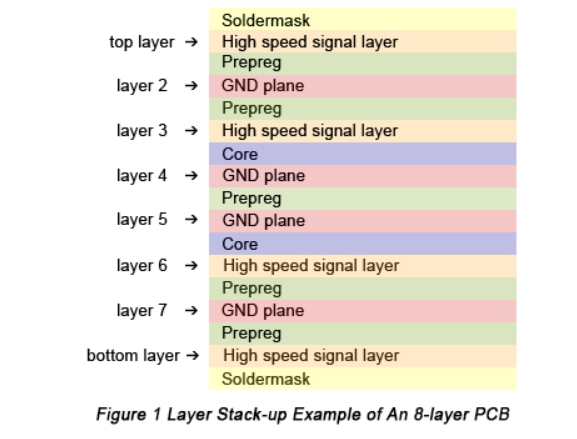
Stack-up refers to the arrangement of copper layers and insulating layers that make up a PCB prior to board layout design. While a layer stack-up allows you to get more circuitry on a single board through the various PCB board layers, the structure of PCB stackup design confers many other advantages: • A PCB layer stack...
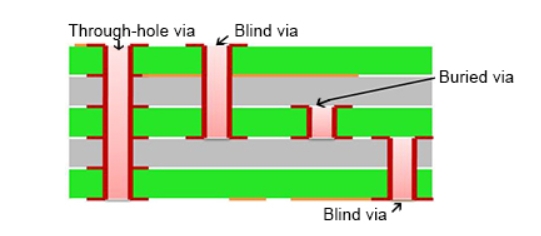
What is a Via? Vias are the copper-plated holes in the PCB that allows the layers to connect. The standard via is called a through-hole via, but there are several disadvantages to using through-hole vias in Surface Mount Technology (SMT). For this reason, we often use a blind via or buried via instead. A blind...
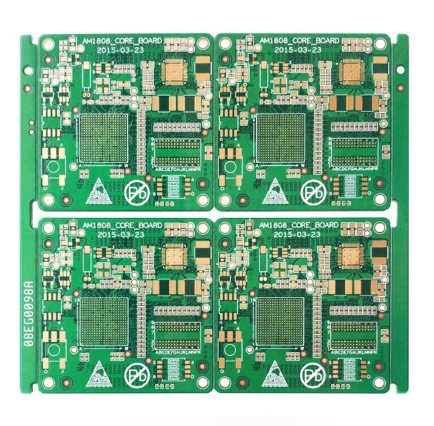
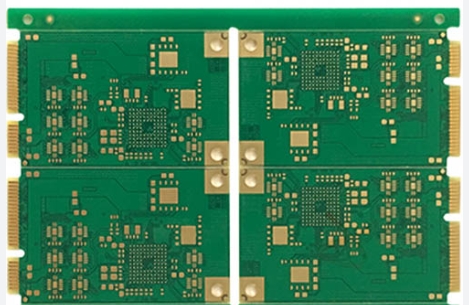
Multilayer PCBs (Printed Circuit Boards) are integral to modern electronics, offering unparalleled performance in compact designs. While they come with several benefits, they also present unique challenges. This article delves into the advantages and disadvantages of multilayer PCBs, providing insight into their role in electronic design and manufacturing. Advantages of Multilayer PCBs 1. Higher Density and Efficiency...
In the evolution of printed circuit boards (PCBs), the transition from single-sided to double-sided to multilayer PCBs has been pivotal. This shift addresses the growing demand for compact, efficient, and high-performance electronic devices. Here’s a detailed look at what multilayer PCBs are, how they work, and when to use them. What Is a Multilayer PCB? A multilayer PCB is an advanced circuit board featuring multiple layers of...
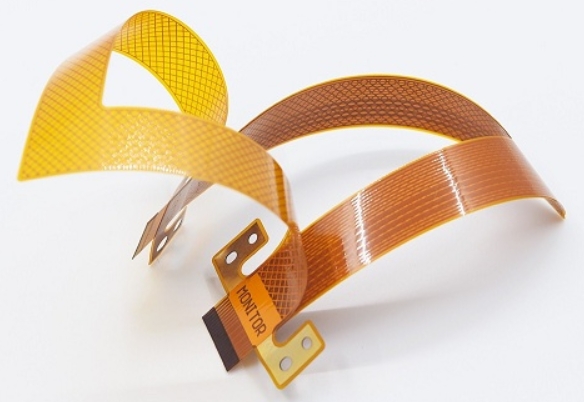
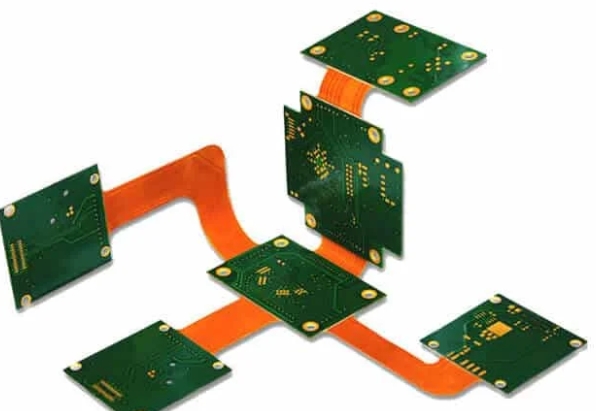
Flexible circuits (also variously referred to around the globe as flex circuits, flexible printed circuit boards, flex print, Flexi-circuits) are members of electronic and interconnection family. They consist of a thin insulating polymer film having conductive circuit patterns affixed thereto and typically supplied with a thin polymer coating to protect the conductor circuits. The technology has...
Flexible PCB technology, also known as FPC (Flexible Printed Circuit), continues to develop and is used in major electronics sectors such as consumer electronics, automotive, electronic medical devices, wearables, telecommunications and aerospace. The introduction of flexible PCBs has revolutionized conventional electrical interconnect technology, which was traditionally used to connect multiple parts of the same circuit or...