When designing a PCB, one of the critical decisions you’ll face is whether to use plated or unplated mounting holes. These holes are essential for securing the PCB to an enclosure or package, but the choice between plated and unplated holes depends on your design requirements, grounding needs, and mechanical considerations. Let’s explore the differences, advantages, and best...
HomeAuthor
kkpcba-Cindy - KKPCB - Page 41 of 75
1. Customer Background The customer is a globally leading manufacturer of communication equipment, specializing in the development and production of large-scale routers, switches, servers, and high-speed networking devices. As modern network communications demand increasingly high signal integrity, reliability, and thermal stability, the customer required an 36-layer PCB with low-loss material (S1000-2M) and advanced immersion gold plating to ensure stable signal transmission...
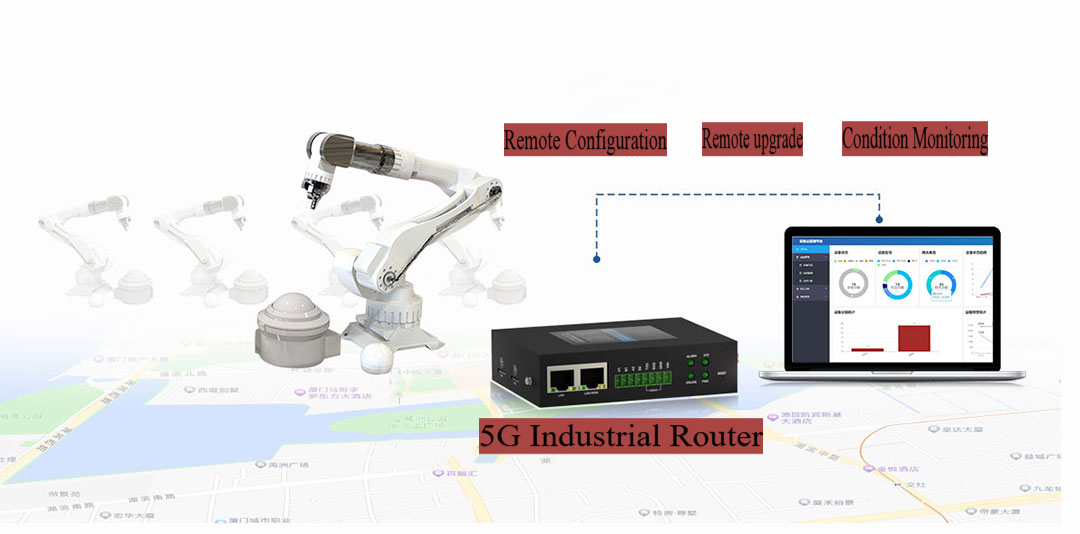
1. Background Overview A European customer in the industrial automation sector required a high-performance and reliable industrial network router for device-to-device communication in their automated systems. The router needed to support high-speed data transfer, strong anti-interference capabilities, remote control functionality, and stable operation in harsh environments. The customer was looking for a supplier with expertise...
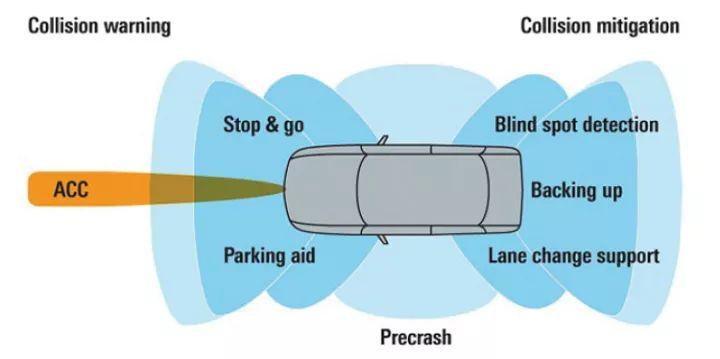
Automotive radar technology is on the rise. Whether it is for current blind spot detection systems or for developing autonomous driving control, high performance, high reliability, compact size, and low cost are indispensable factors and motivations for the continuous development and improvement of core automotive radar technologies. Automotive radar is an essential component of driver...
As complexity and density increase, the long-term reliability of RF/microwave circuit components becomes more challenging to characterize. Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) comprise numerous active and passive components, whose performance can vary over time and with operating environment temperatures. Additionally, PCB substrate materials, such as dielectrics, copper foil conductors, solder mask inks, and final finishes, may change over time, influenced...
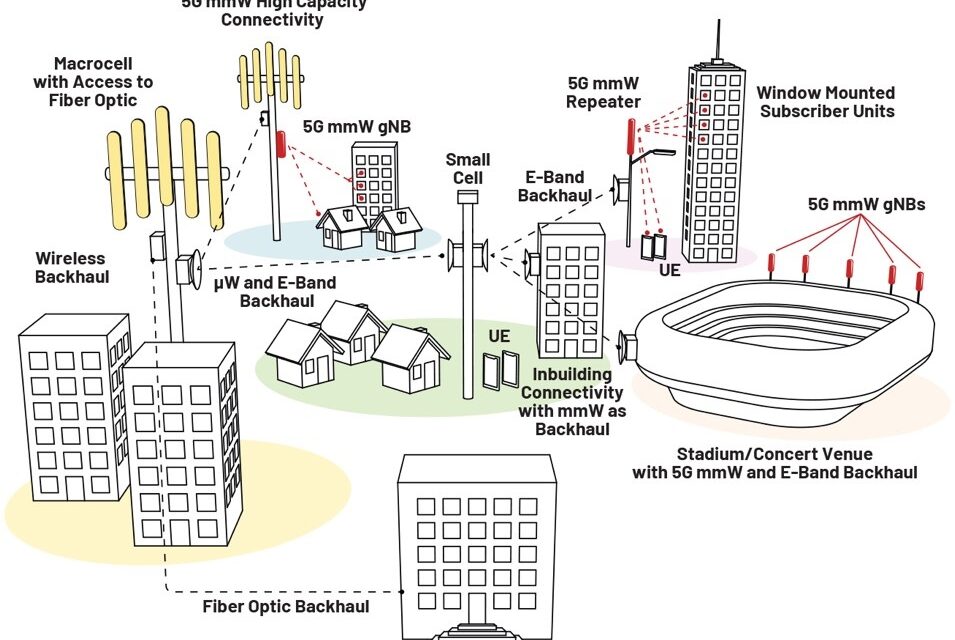
Introduction This article introduces the various backhaul technologies available for 5G networks, focusing on E-band wireless RF links and how they support the continued deployment of 5G networks around the world. We will perform a technical analysis of the system requirements necessary for E-band technology. We will then map the results to the physical radio...
In the Texas Instruments technical article, “How low-power 60GHz mmWave radar sensors enable high-precision sensing in more applications,” we discussed how 60GHz millimeter-wave (mmWave) radar sensors enable high-precision sensing in industrial and consumer electronics applications. In this article, we will explore how low-power 77GHz radar sensors can help achieve reliable and accurate sensing in other challenging applications....
Electrical performance consistency is critical for producing high-volume printed circuit boards (PCBs). As PCB applications move to higher frequencies, such as fifth-generation (5G) cellular wireless networks at millimeter-wave frequencies and 77 GHz automotive radar, any inconsistencies on the PCB become very noticeable, especially when the circuits operate at shorter wavelengths of millimeter-wave frequencies. There will always be...
1. Definition of PCB high frequency board High-frequency boards refer to special circuit boards with higher electromagnetic frequencies. They are used in high-frequency (frequency greater than 300MHz or wavelength less than 1 meter) and microwave (frequency greater than 3GHZ or wavelength less than 0.1 meter) PCBs. They are produced on microwave-based copper-clad boards using some of the...
The electronics industry has undergone many changes over the past few years. Nowadays, millimeter wave radar and millimeter wave communication frequently appear in our sight. In particular, Huawei has made remarkable achievements in 5G, and millimeter wave technology has been put on the table. Why does millimeter wave technology play such a key role in 5G and smart cars?...