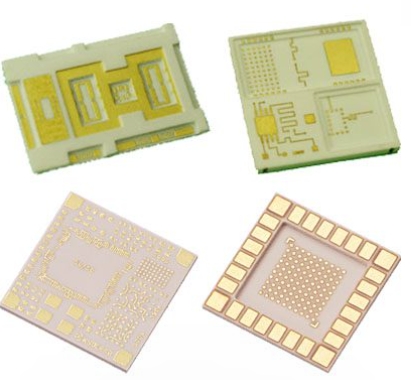
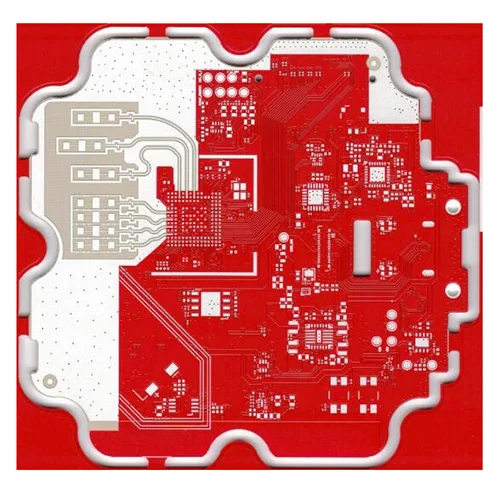
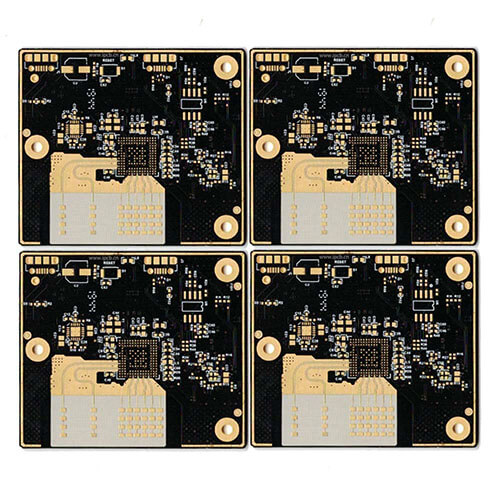
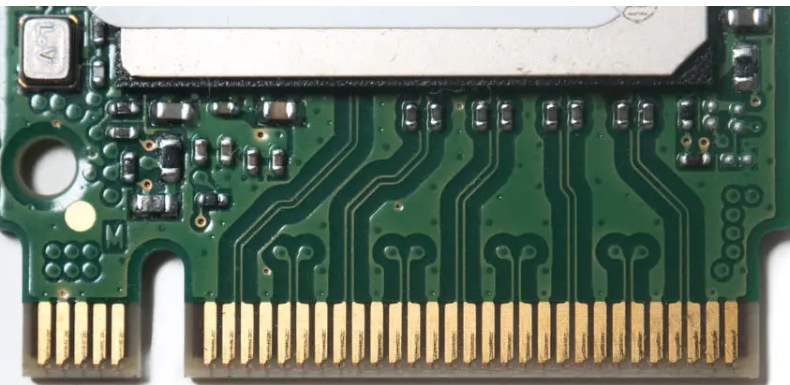
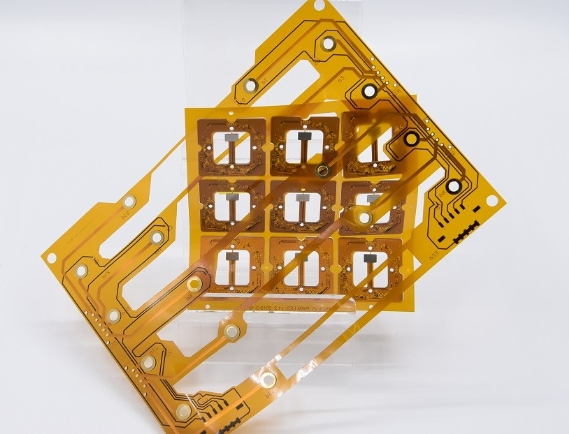
A ceramic substrate is an insulating material that provides a stable and rigid platform for mounting electronic components and creating electrical circuits. Ceramic substrates are often used as an alternative to epoxy-based materials like FR-4 (Flame Retardant 4). FR-4 is a popular substrate material for PCBs, but ceramic substrates offer certain advantages in specific applications. Key Characteristics...
HomeAuthor
kkpcba-Cindy - KKPCB - Page 40 of 75
Explore KKPCB’s 77GHz Millimeter Wave Radar PCB made with Rogers RO4835 + FR4 hybrid material. Engineered for automotive radar, ADAS, and 5G applications, this high-frequency PCB offers ultra-low loss, stable dielectric performance, and superior reliability. Ideal for 77GHz radar antennas, collision avoidance systems, and vehicle sensor modules requiring precision signal integrity and long-term stability.
In the fast-evolving world of high-frequency electronics, selecting the right PCB material is essential for achieving the performance required in modern applications such as automotive radar, wireless communication systems, and advanced microwave technology. The Rogers RO4835 + IT180 hybrid PCB, combining high-performance materials from Rogers, has emerged as a robust solution that delivers superior performance in these demanding fields....
PCB edge plating is a specialized process that involves applying a metal coating to the exposed copper connections at the edge of a printed circuit board (PCB). This technique, also known as side plating, battlement, or metallized edge plating, enhances electrical connectivity, structural rigidity, and electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding. This article provides an in-depth look at the...
When designing for PCB prototyping, the cost of individual parts does not always play a big role. If you’re designing one-offs or hobby projects, you’ll probably only look at parts prices when your assembly house sends you an invoice. But if you’re eventually going to produce at scale, the cost of the prototype is small compared...
PCB tolerances for manufacturing refer to the allowable variations from specified dimensions, encompassing: material thickness, copper thickness, drilling, plating, and solder masks. These PCB tolerances ensure that PCB circuit boards are produced precisely and can function as intended. Manufacturers adhere to specific in-house tolerance guidelines, based on international standards like IPC-A-600 Class 2, to maintain quality throughout the...
Combining the flexibility of flex circuits with the robustness of rigid boards, while leveraging High-Density Interconnect (HDI) technology, represents a significant breakthrough in modern electronics. Traditional methods like board-to-board stacking connectors or standard flex circuits often present challenges, such as cumbersome assembly and potential damage during connection. Rigid-flex PCBs offer a seamless solution, eliminating these bottlenecks and...
PCB routing involves laying out traces to minimize interference, ensure signal integrity, and meet design requirements such as impedance control and thermal management. Traces carry electrical signals between components such as integrated circuits, resistors, and capacitors. PCB traces are usually made of copper. They are created by applying a layer of photosensitive material onto a copper-clad board, exposing...
It wasn’t long ago that rigid circuit boards were the only possible electronic system method available. Whether it was entertainment or industrious, the shape of most devices was an extension of an intractable rigid board. More recently, the tide has turned: as technology has developed and matured, the enclosure is shaping the electronics inside them. Despite additional...
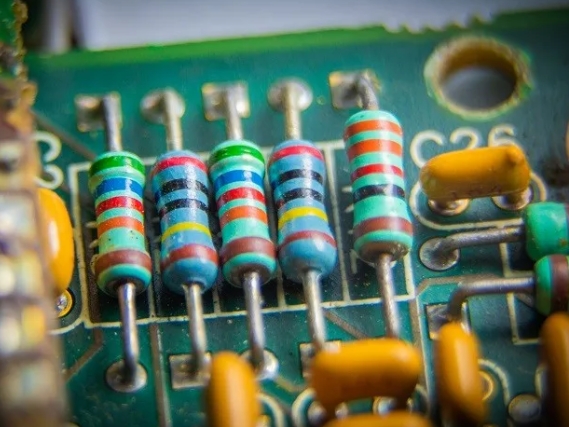
PCB resistors are designed to be mounted and soldered to printed circuit boards; they control current flow and divide voltages, among other things. PCB resistors come in many shapes and sizes, but they’re all designed to fit easily into board layouts. They have two terminals that can be soldered to the conductive traces on the PCB so they...