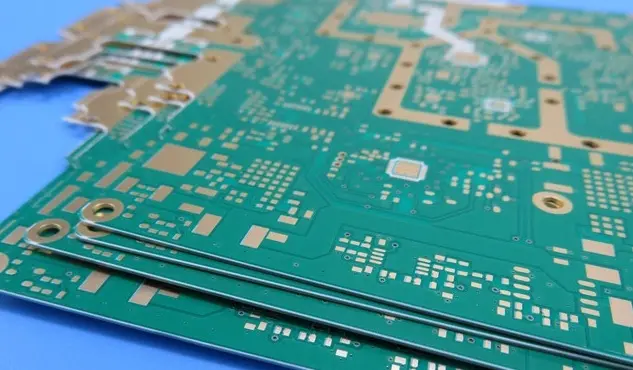
High-density microwave amplifiers, widely used in radar, satellite communication, and 5G mmWave systems, operate under intense thermal stress and high RF power. Maintaining ultra-low insertion loss, precise phase stability, and tight impedance control is critical to ensure amplifier efficiency, signal fidelity, and overall system reliability. RO4835 PCB laminates (Dk = 3.48 ± 0.03, Df =...
HomeTag
RO4835 PCB - KKPCB
High-density microwave power amplifier platforms demand PCB materials capable of maintaining stable dielectric performance, high RF power efficiency, and long-term thermal robustness under continuous high-power loads. RO4835 PCB substrates are engineered precisely for these conditions. By combining a tightly controlled dielectric constant, low dissipation factor, and excellent oxidative stability, RO4835 PCBs offer a reliable foundation...
5G Massive-MIMO radio units rely on a tightly controlled dielectric environment where even slight variations in Dk and Df can break phase alignment across large antenna arrays. The RO4835 PCB platform has become a preferred low-loss material for high-frequency RF layers thanks to its exceptional dielectric stability, low insertion loss, oxidation-resistant resin system, and long-term...
Satellite communication hardware depends on highly stable RF PCB materials capable of maintaining low-loss transmission, tight impedance control, and long-term dielectric stability under extreme environmental shifts. RO4835 PCB laminates—known for oxidation-resistant resin systems, stable Dk over temperature, and low insertion loss up to Ka-band—are frequently selected for mission-critical RF payloads, transceiver modules, phased arrays, and...
The Hidden Killer of Next-Gen RF Front-End Performance in 2025 As 5G mmWave base stations, LEO satellite user terminals, and aerospace active phased-array systems push toward 28–40 GHz and even 60 GHz D-band prototypes, two parameters have become non-negotiable: Third-order intermodulation distortion (IP3) must exceed +50 dBm at the antenna port Passive intermodulation (PIM) must...
1. Why Aerospace RF Boards Are Entering the RO4835 Era in 2025 In aerospace navigation and telemetry links (L/S/C/Ku/Ka bands), temperature swings from –55°C on the ground to +125°C in high-altitude low-pressure environments are routine. Traditional high-frequency materials such as RO4350B or common PTFE either suffer excessive Dk drift or catastrophic oxidation of the “LoPro”...
Heat Dissipation Challenges in High-Power RF Circuits As RF and mmWave systems scale beyond 24 GHz, power density and thermal stress become critical limiting factors for system reliability. Engineers designing automotive radar front-ends, 5G transceivers, and satellite payloads must manage high localized temperatures within densely packed multilayer PCBs. While traditional FR-4 substrates often...
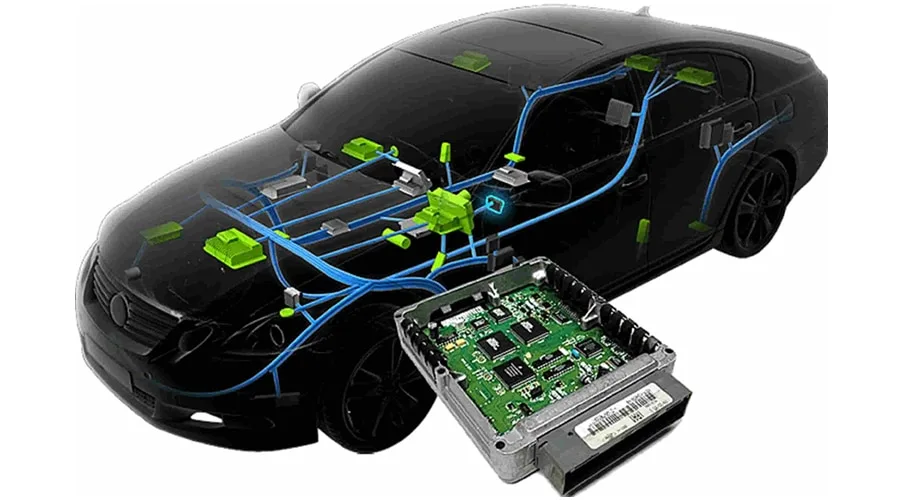
Ensuring Long-Term RF Stability Through KKPCB’s Reliability Validation Process Why Reliability Defines Success in RO4835-Based RF Systems As automotive radar, aerospace communication, and satellite navigation systems expand into 24–77 GHz frequency ranges, PCBs face extreme operational stress. These high-frequency modules must withstand thermal cycling, humidity exposure, and long-term RF power loading, while maintaining...
How Rogers RO4835 Material Enables Stable RF Performance in Harsh Environments The Growing Demand for Thermally Stable, Low-Loss PCBs As 5G networks, automotive radar, and satellite communications evolve toward millimeter-wave frequencies (24–77 GHz), PCB materials face increasing performance pressure.Engineers now require substrates that maintain low insertion loss, tight dielectric control, and thermal stability under...
From High-Frequency Design to Production-Ready Stackups As next-generation RF systems evolve toward 24–77 GHz applications—such as automotive radar, 5G base stations, and satellite communication—engineers require PCB materials that deliver low loss, thermal stability, and consistent manufacturability. Rogers RO4835 PCB has become the preferred substrate for these applications due to its low dissipation factor...