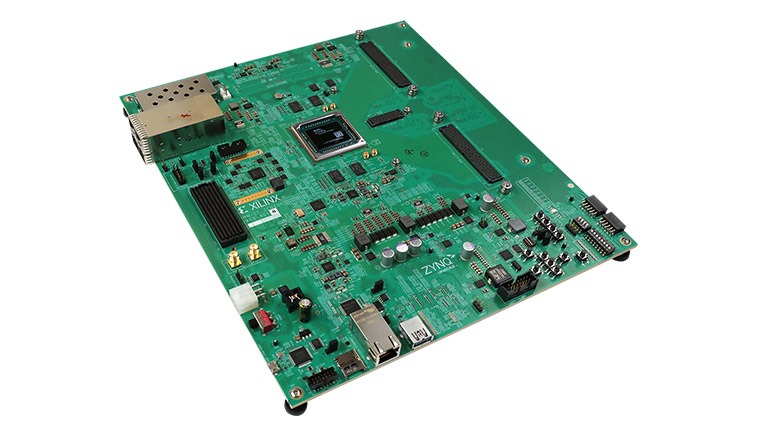
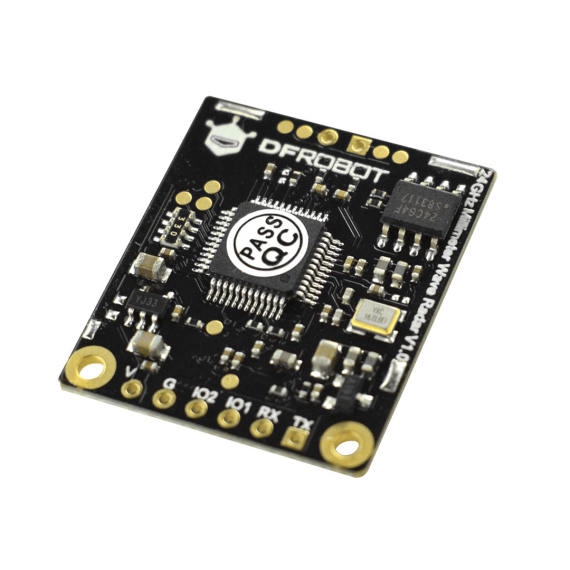
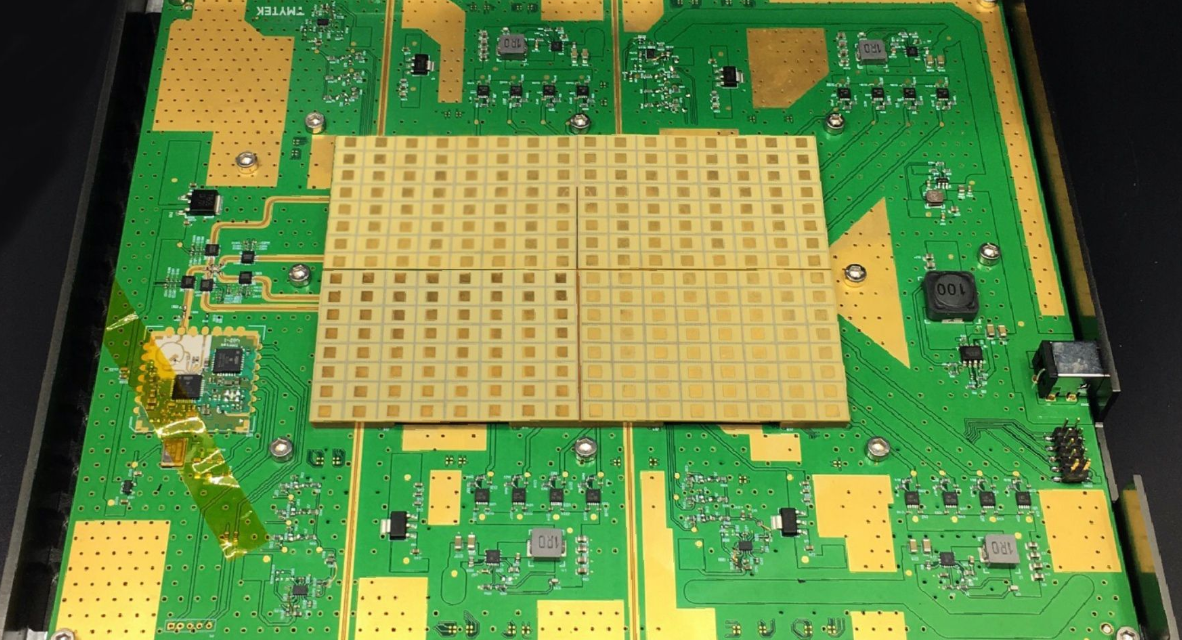
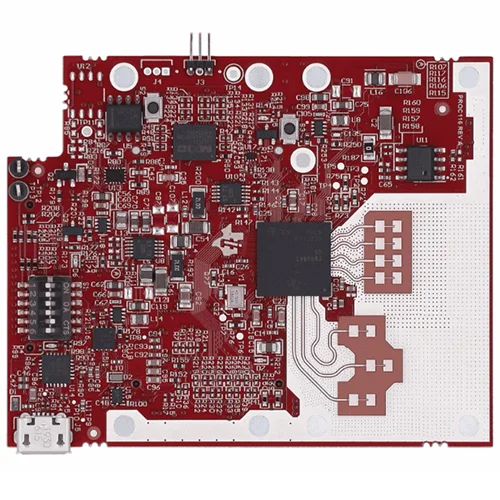
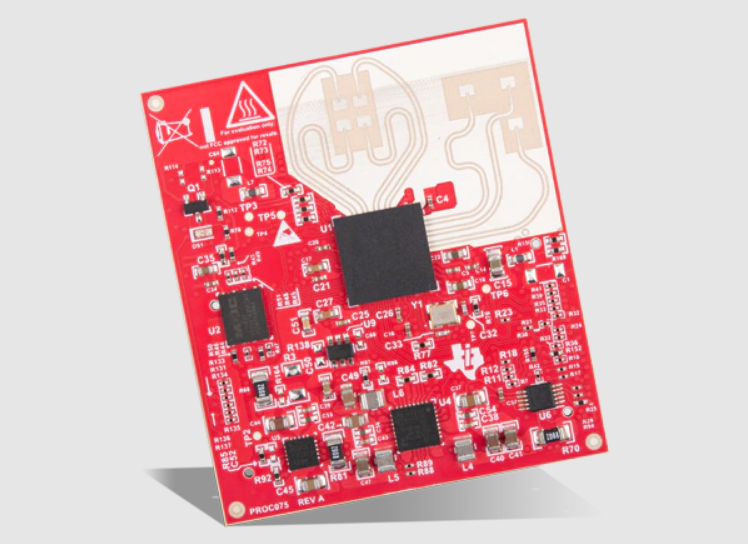
What Is a 5G mmWave PCB? A 5G mmWave PCB is a high frequency printed circuit board engineered to operate at millimeter wave frequencies (typically 24 GHz to 100 GHz and above). These PCBs are used in advanced 5G communication systems where ultra-high bandwidth, low latency, and high data throughput are required. At mmWave frequencies,...
HomeTag
mmWave Module PCB - KKPCB
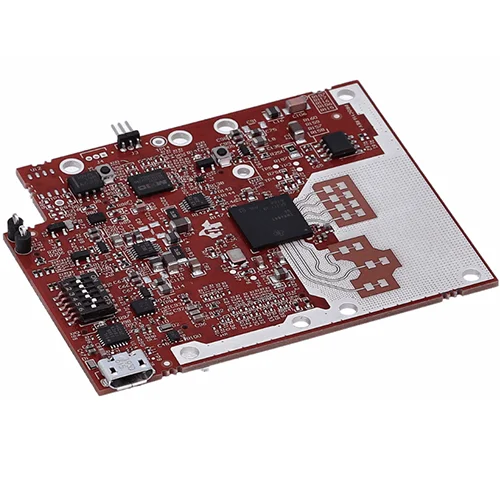
What Is an mmWave Module PCB? An mmWave Module PCB is a high frequency printed circuit board specifically designed for millimeter-wave applications (30–300 GHz), including: 5G communication modules Automotive radar systems High frequency IoT devices Satellite communication modules mmWave Module PCB ensures low signal loss, precise impedance control, and stable RF performance for high frequency...
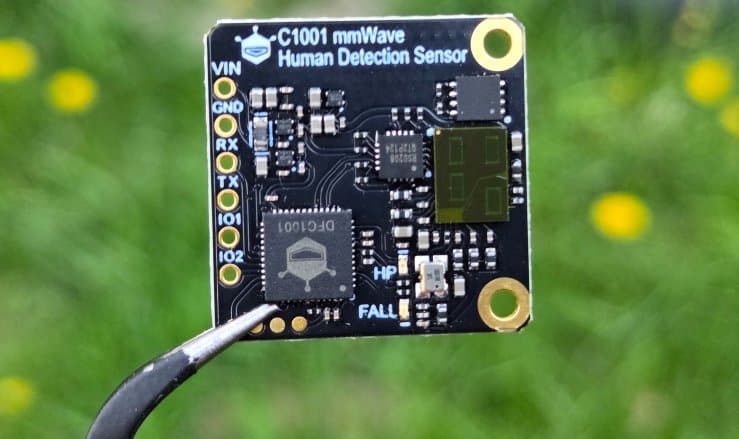
What Is a mmWave Module PCB? A mmWave Module PCB is a specialized printed circuit board designed to operate at millimeter-wave frequencies (typically 24 GHz to 110 GHz). These PCBs are used in compact RF modules where signal loss, impedance variation, and electromagnetic interference must be tightly controlled. mmWave module PCBs are core components in...
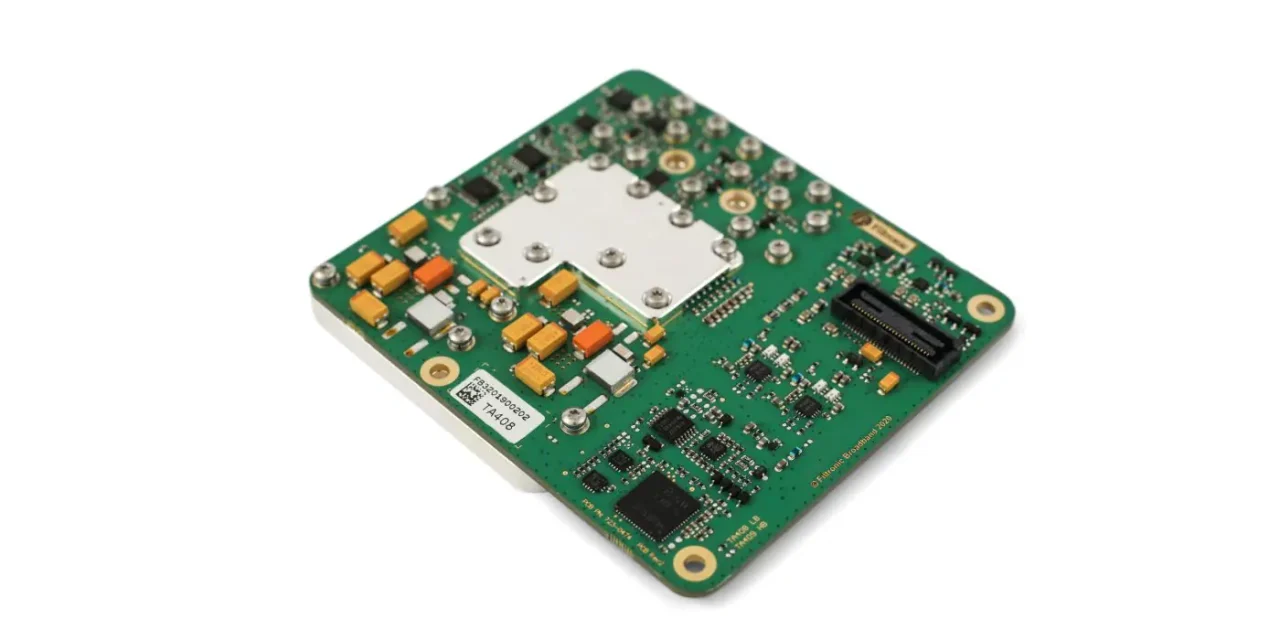
What Is a mmWave Module PCB? A mmWave Module PCB is a specialized printed circuit board used in millimeter-wave (mmWave) modules, typically operating at frequencies above 24 GHz, such as 26 GHz, 28 GHz, 39 GHz, and 77 GHz. These PCBs integrate RF transceivers, antennas, filters, and high-speed interfaces into compact modules. Due to the...
Next-generation RF transceivers—whether for 5G mmWave, SATCOM terminals, phased-array antennas, or short-range high-bandwidth links—place brutal demands on PCB materials. To maintain ultra-low insertion loss, wideband consistency, stable phase response, and clean radiation efficiency, mmWave module PCB materials must deliver precision alignment, ultra-low dielectric loss, tight Dk control, and minimal copper roughness across every layer. In...
mmWave Module PCB Engineering for High-Frequency, Low-Loss and Thermally Stable RF Front-End Systems
The shift toward 5G FR2, advanced radar, high-resolution sensing and satellite communication has placed intense performance pressure on mmWave Module PCB design. At frequencies from 24 GHz to 86 GHz, the PCB is no longer a passive carrier—it becomes an active RF component whose materials, stackup, via transitions and routing geometries directly dictate performance. A...
High-frequency mmWave module PCB architectures define the performance boundary of 28–60 GHz wireless platforms, where beamforming accuracy, ultra-low-loss routing, and tight impedance control determine every detail of system efficiency. In dense phased-array units, even microscopic changes in Dk/Df, copper roughness, dielectric uniformity, or via transition geometry produce measurable degradation in beam steering vectors, noise floors,...
Electronics Industry NewsEngineering TechnologiesPCB Assembly (PCBA)PCB DesignPCB ManufacturingPCB Materials
Reinforce Shock Reliability and High-Frequency Integrity Through Ruggedized mmWave Module PCB Designs for Harsh-Environment Communication Terminals
Harsh-environment communication terminals—used in battlefield radios, mining telemetry units, emergency response networks, and remote industrial gateways—depend on mmWave Module PCB architectures that can preserve signal integrity, impedance accuracy, and structural reliability under extreme stress. High-frequency circuits operating from 24 GHz to 71 GHz experience sensitivity far greater than conventional RF PCB designs, making material stability,...