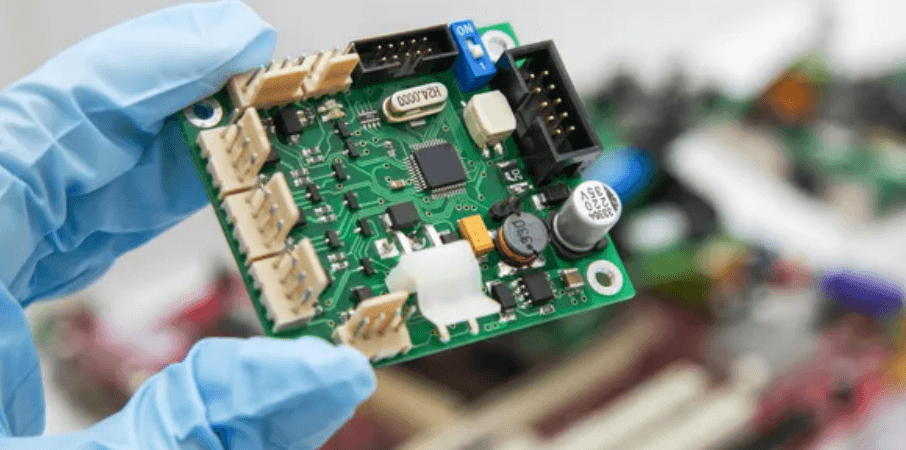
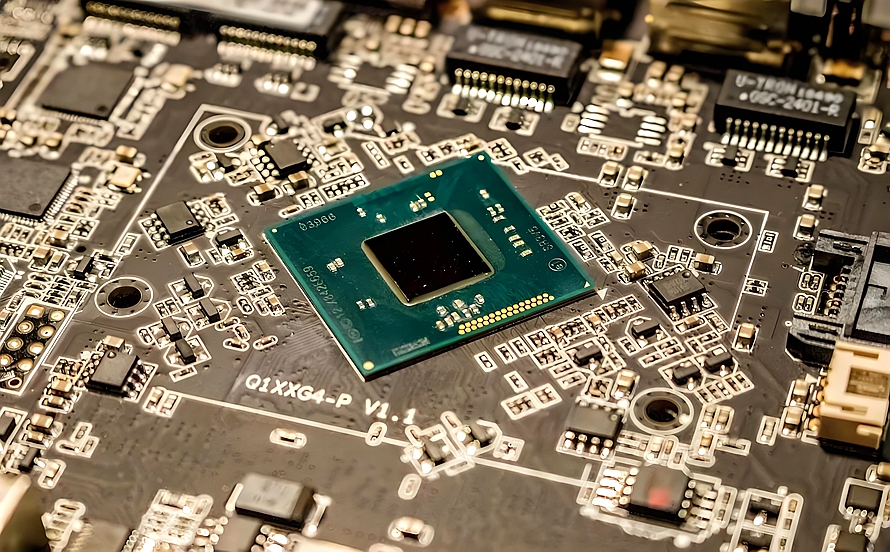
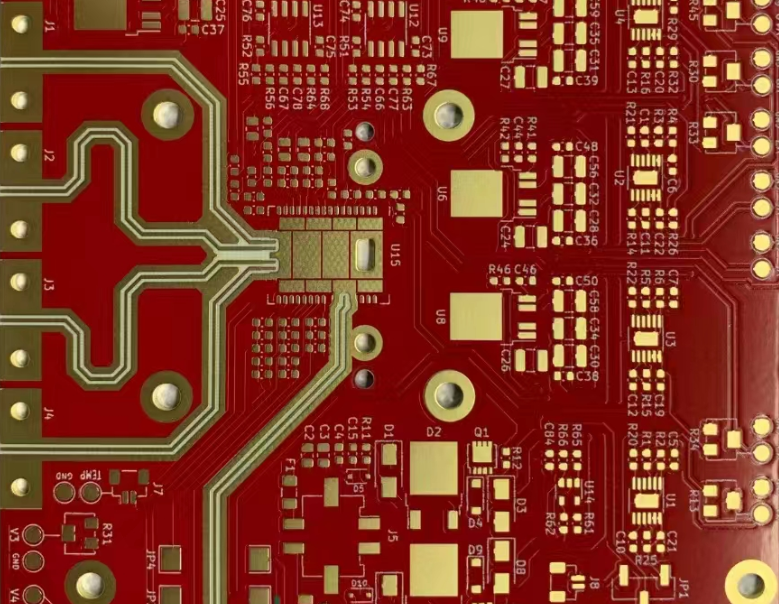
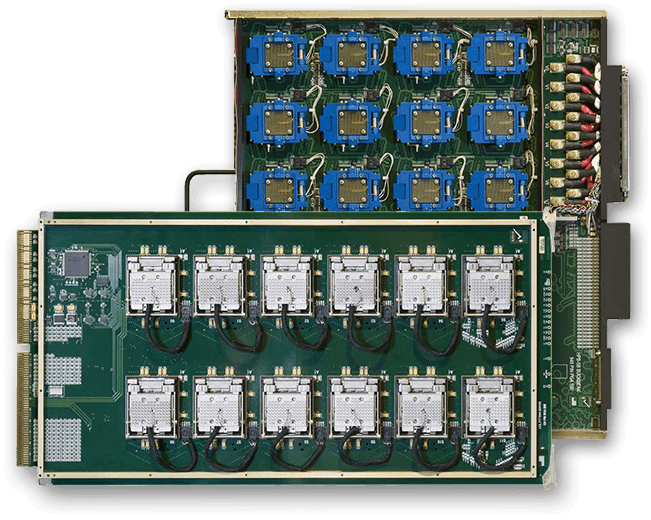
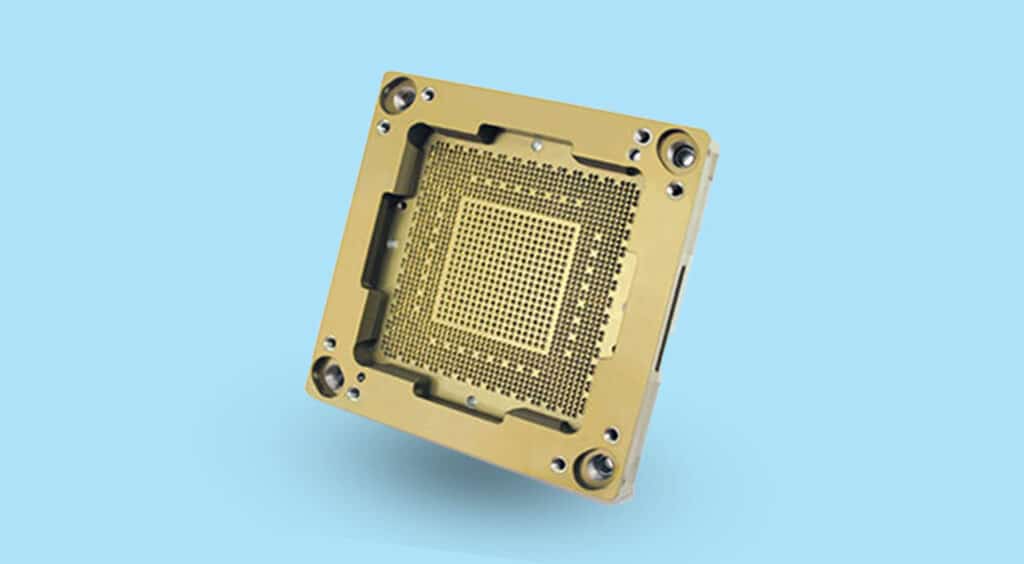
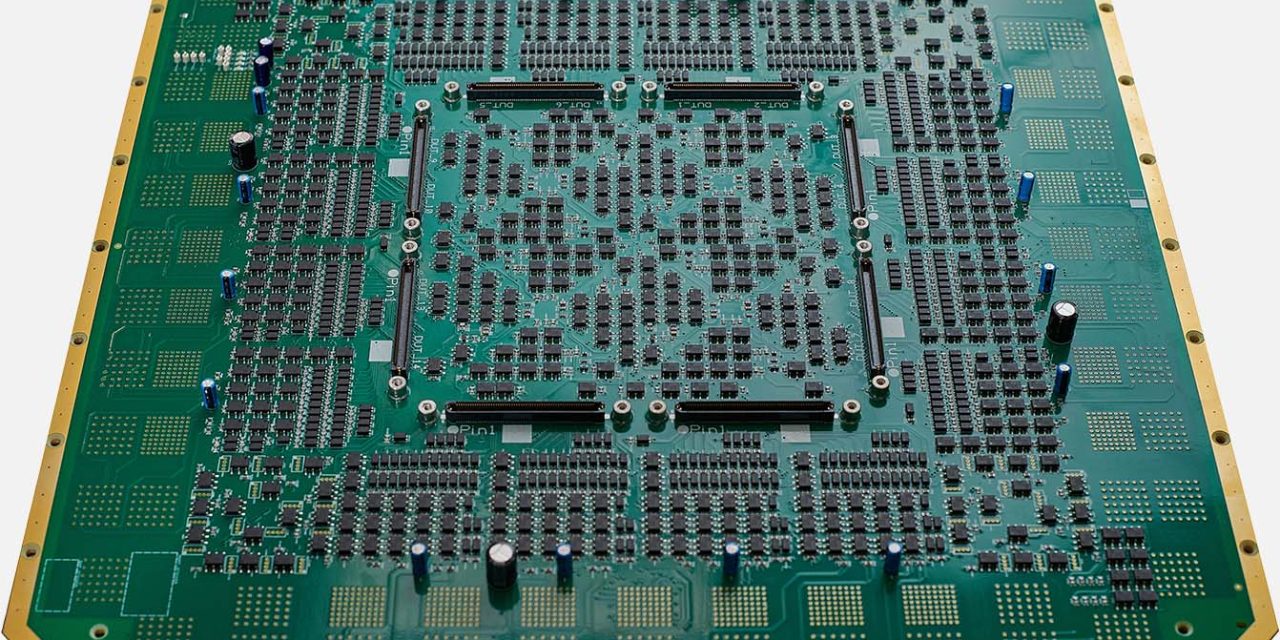
What Is an IoT IC Test PCB? An IoT IC Test PCB is a specialized printed circuit board used to test Internet of Things (IoT) integrated circuits during development, validation, and mass production. It provides a stable electrical interface between the IoT IC under test (DUT) and automated test equipment (ATE), ensuring accurate functional, RF,...
HomeCategory
PCB Design Services | Professional PCB Layout & Design - KKPCB
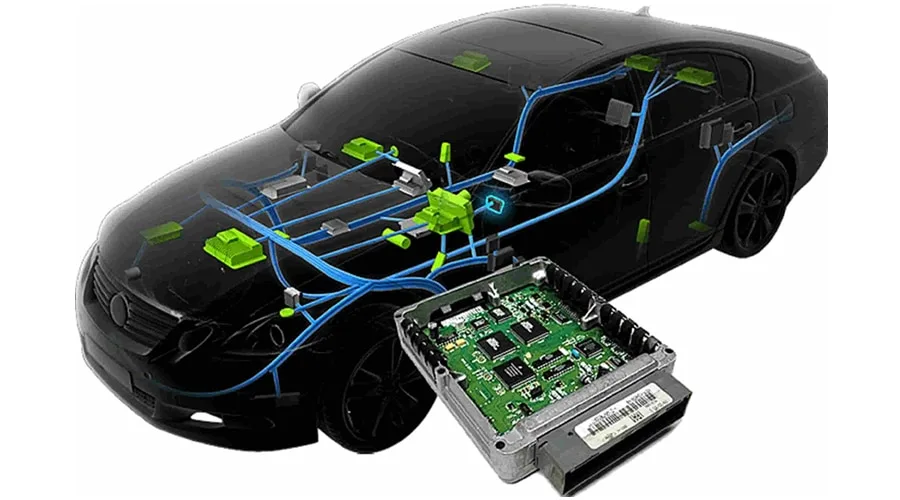
What Is an Automotive IC Test PCB? An Automotive IC Test PCB is a specialized printed circuit board used to test automotive-grade integrated circuits during development, validation, and mass production. It connects the automotive IC under test (DUT) to automated test equipment (ATE), enabling precise electrical, functional, and reliability testing. These PCBs are widely used...
What Is a 5G IC Test PCB? A 5G IC Test PCB is a specialized printed circuit board used to test 5G-related integrated circuits, including RF transceivers, baseband chips, power amplifiers, and mmWave ICs. It serves as the critical interface between the device under test (DUT) and automated test equipment (ATE), ensuring accurate electrical and...
What Is a High Speed IC Test PCB? A High Speed IC Test PCB is a specialized printed circuit board used to test integrated circuits operating at high data rates and high frequencies. It functions as the electrical interface between the device under test (DUT) and automated test equipment (ATE), ensuring accurate transmission and measurement...
What Is a Mixed Signal IC Test PCB? A Mixed Signal IC Test PCB is a specialized printed circuit board designed for testing mixed-signal integrated circuits that combine analog and digital functions on a single chip. It serves as the interface between the device under test (DUT) and automated test equipment (ATE), enabling accurate measurement...
What Is a Burn-in Board PCB? A Burn-in Board PCB is a specialized printed circuit board used in semiconductor reliability testing to identify early device failures. It connects packaged integrated circuits to burn-in test systems, allowing devices to operate under elevated temperature, voltage, and electrical stress conditions over extended periods. Burn-in board PCBs play a...
What Is a Package Test PCB? A Package Test PCB is a specialized printed circuit board designed for package-level semiconductor testing, where integrated circuits are tested after packaging but before final shipment. It serves as the electrical and mechanical interface between the packaged IC (DUT) and automated test equipment (ATE). Package test PCBs are commonly...
What Is a High Pin Count IC Test Board? A High Pin Count IC Test Board is a specialized printed circuit board designed to support integrated circuits with a large number of I/O pins during semiconductor testing. It serves as the electrical interface between the device under test (DUT) and automated test equipment (ATE), enabling...
What Is a Test Socket PCB for IC? A Test Socket PCB for IC is a specialized printed circuit board designed to mount and support IC test sockets used in semiconductor testing. It acts as the electrical and mechanical interface between the integrated circuit (IC) and automated test equipment (ATE), enabling accurate functional, parametric, and...
What Is a Semiconductor Load Board? A Semiconductor Load Board is a critical interface PCB used in IC testing systems, connecting the automated test equipment (ATE) to the device under test (DUT). It provides electrical routing, signal conditioning, power delivery, and mechanical support during functional, parametric, and performance testing of semiconductor devices. Load boards are...