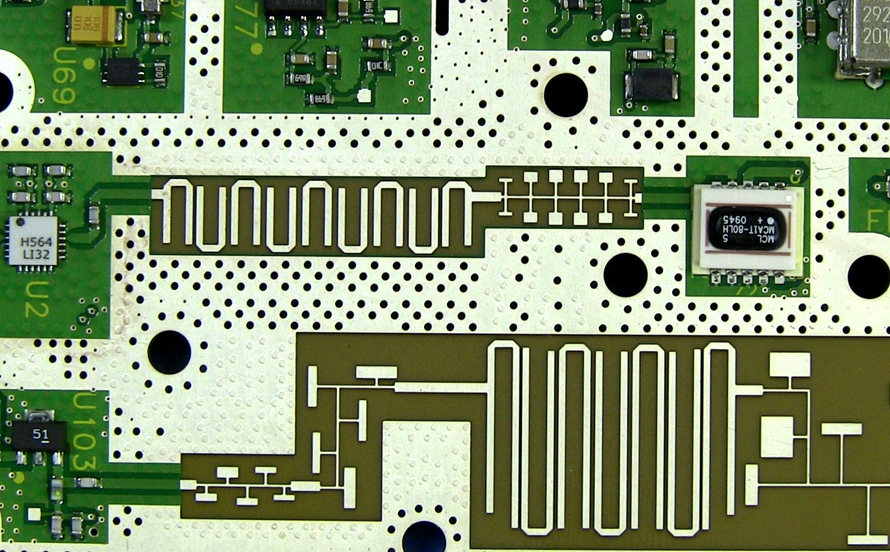
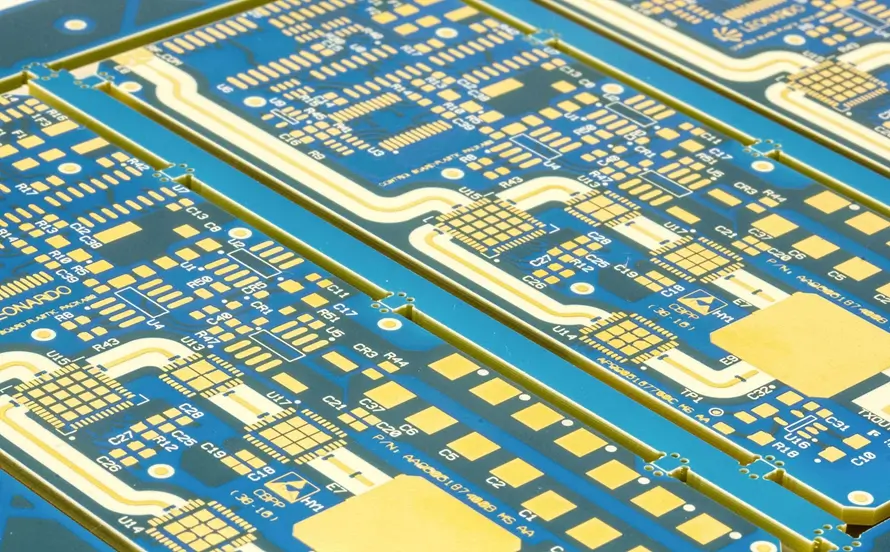
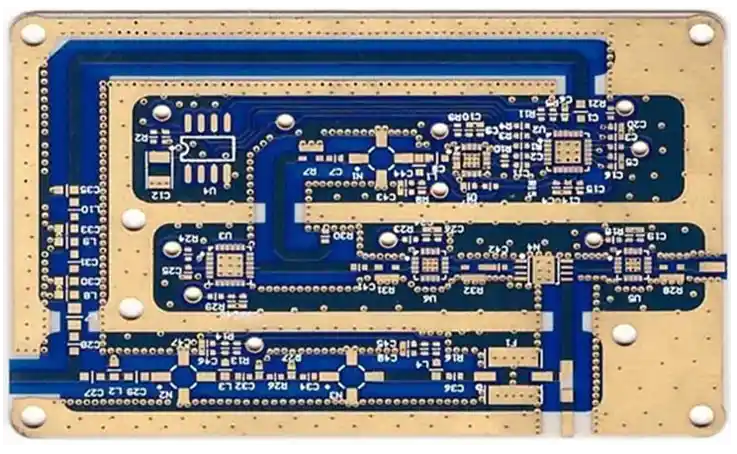
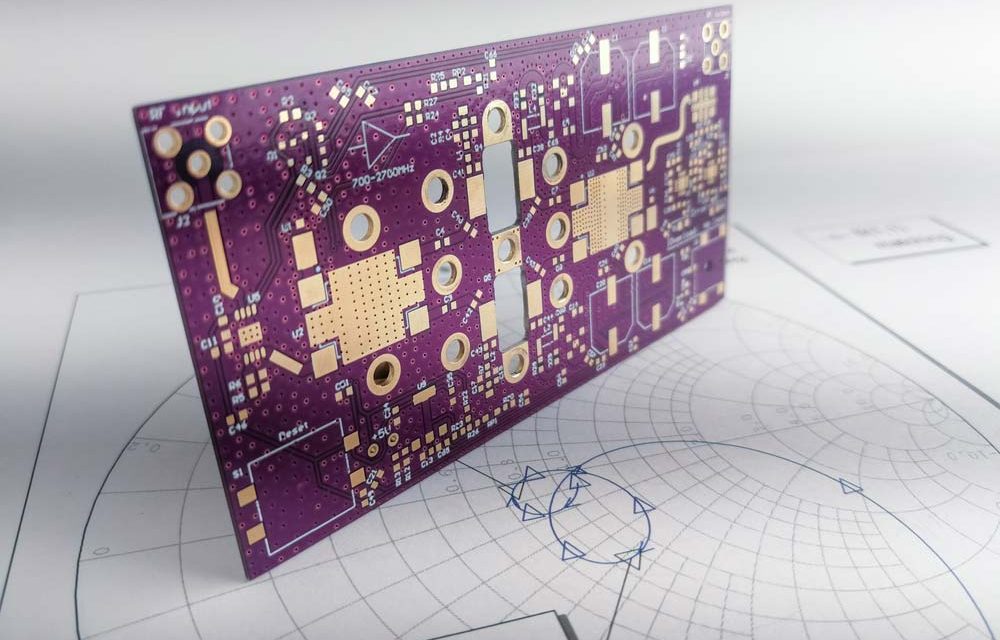
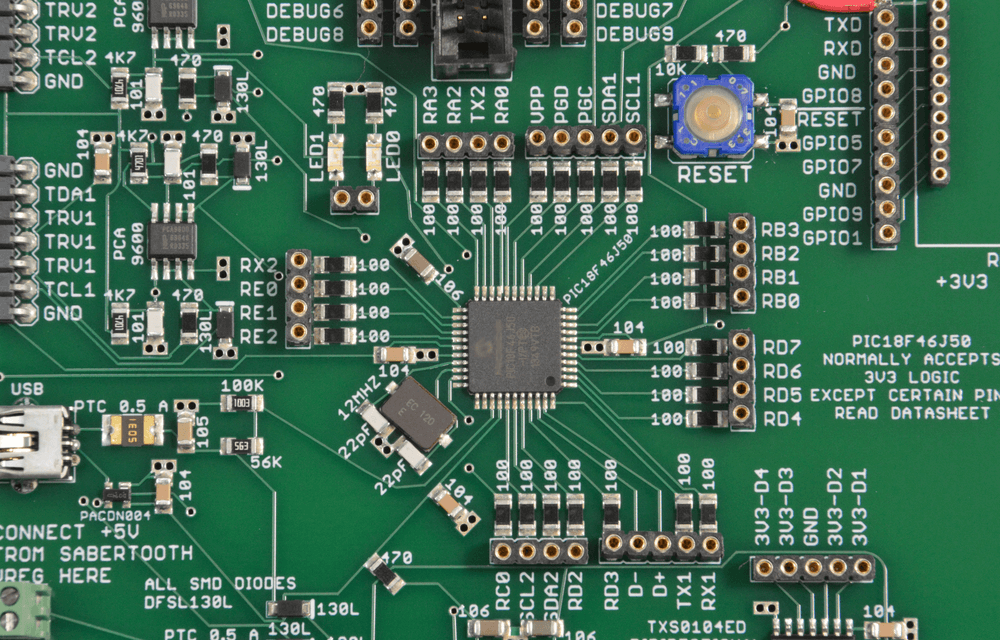
What Are High Frequency Laminates? High Frequency Laminates are specialized PCB base materials engineered for high-speed and high-frequency electronic applications. Unlike standard FR-4 materials, high frequency laminates offer: Low dielectric constant (Low Dk) Low dissipation factor (Low Df) Stable electrical performance at GHz frequencies Excellent signal integrity Reliable controlled impedance performance High frequency laminates are...
HomeCategory
PCB Design Services | Professional PCB Layout & Design - KKPCB
What Is a BT Epoxy PCB? A BT Epoxy PCB is a high-performance printed circuit board manufactured using Bismaleimide Triazine (BT) resin-based epoxy material. BT Epoxy PCB is widely used in IC substrate applications, semiconductor packaging, memory modules, and high-density electronic devices, where thermal stability, dimensional accuracy, and electrical performance are critical. Compared with standard...
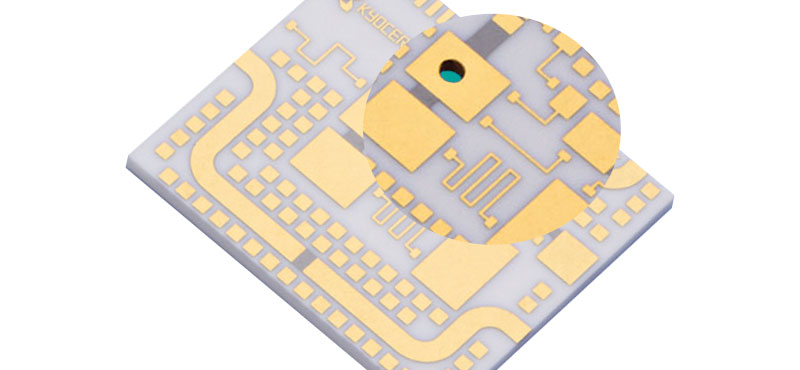
What Is a Ceramic PCB? A Ceramic PCB is a high-performance printed circuit board manufactured using ceramic substrate materials such as Alumina (Al₂O₃), Aluminum Nitride (AlN), or Beryllium Oxide (BeO). Unlike traditional FR-4 PCBs, Ceramic PCBs provide: Excellent thermal conductivity High mechanical strength Superior electrical insulation Stable performance in extreme environments Ceramic PCB technology is...
What Is an RO4003C PCB? An RO4003C PCB is a high-frequency printed circuit board manufactured using Rogers RO4003C laminate, a hydrocarbon ceramic-filled material specifically engineered for low loss RF and microwave applications. RO4003C PCBs are widely used in: RF and microwave circuits 5G base station modules Automotive radar systems Satellite communication equipment High-speed digital and...
What Is a PTFE PCB? A PTFE PCB is a printed circuit board made from polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) laminates, known for extremely low dielectric loss, stable dielectric constant, and excellent high-frequency performance. PTFE PCBs are widely used in 5G, mmWave modules, RF/microwave systems, aerospace electronics, and high-speed computing, where signal integrity and low insertion loss are...
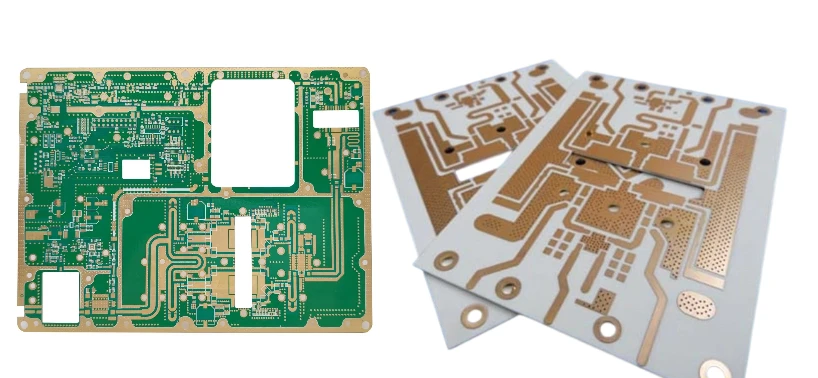
What Is a Rogers PCB? A Rogers PCB is a printed circuit board that uses Rogers high-frequency laminates, such as RO4003C, RO4350B, and Duroid series, designed for low dielectric loss, precise impedance control, and high-frequency signal transmission. Rogers PCBs are essential in 5G communications, RF/microwave modules, high-speed computing, and aerospace electronics. Why Rogers PCB Technology...
What Is a High Frequency Signal PCB? A High Frequency Signal PCB is a printed circuit board designed to carry high-speed and high-frequency signals with minimal loss, reflection, or distortion. These PCBs are crucial in RF, microwave, 5G, high-speed computing, and semiconductor test applications, where signal integrity and low insertion loss are essential for system...
What Is an RF Trace PCB? An RF Trace PCB is a printed circuit board designed to route high-frequency RF signals with minimal signal loss, reflection, and distortion. These PCBs are optimized for controlled impedance, low insertion loss, and high signal integrity, making them essential for applications such as 5G modules, mmWave systems, wireless communication,...
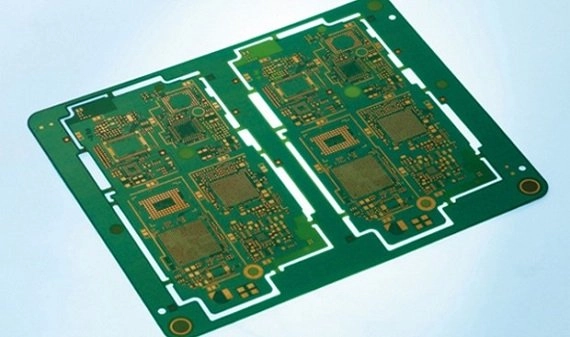
What Is a Differential Pair PCB? A Differential Pair PCB is a printed circuit board designed to route differential signal pairs, which are two complementary signals transmitted simultaneously to improve noise immunity, reduce crosstalk, and maintain signal integrity. Differential pair technology is critical in high-speed digital interfaces, such as USB, HDMI, PCIe, Ethernet, DDR memory,...
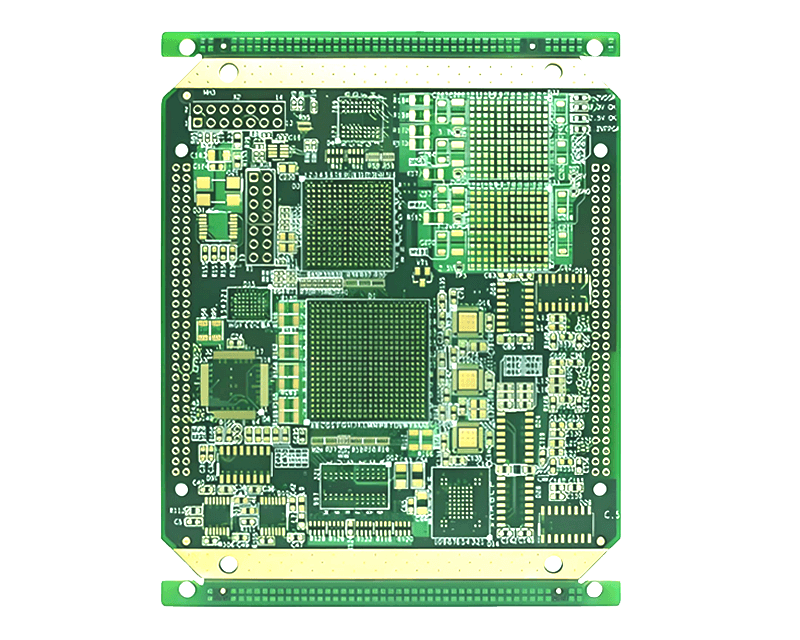
What Is a Fine Line PCB? A Fine Line PCB is a printed circuit board that uses extremely narrow traces and spaces to support high-density, complex electronic designs. Fine line technology is essential for applications where board real estate is limited but high-speed performance and signal integrity are required, such as smartphones, 5G modules, high-speed...