Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are a fundamental component in electrical engineering. They are used to create electronic circuits by arranging components such as transistors and resistors on a copper-based wiring pattern on the surface of an insulator (typically plastic) and then soldering them. PCBs are integral to nearly all electronic devices, providing the necessary pathways for...
HomeAuthor
kkpcba-Cindy - KKPCB - Page 38 of 75
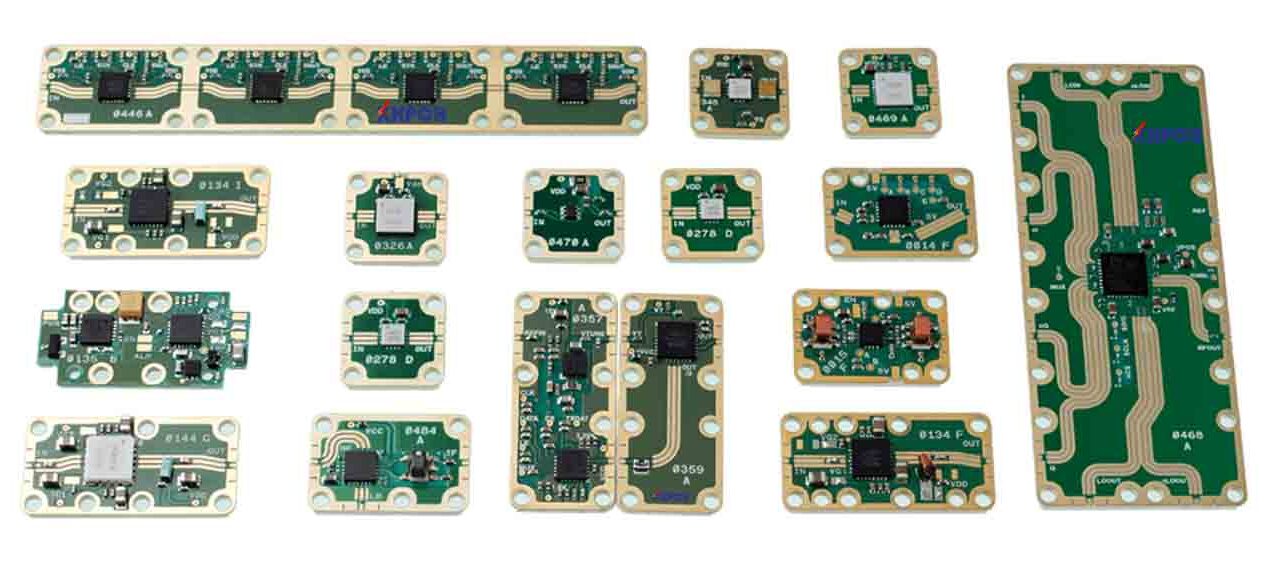
Key Points of Millimeter-Wave Applications—Phase Accuracy Affected by Multiple Variables From anti-collision radar systems used in autonomous vehicles to the fifth-generation (5G) high data rate New Radio (NR) networks, the application of millimeter-wave (mmWave) circuits is growing rapidly. Many applications are pushing the operating frequency bands to higher frequencies (such as >24GHz). However, for circuits with shorter...
PCB Processing The precise dimensions required for millimeter-wave circuits demand well-controlled PCB processing techniques to produce circuits with consistently excellent performance. Variations in copper plating thickness and final surface treatment on the conductor surface can impact the performance of millimeter-wave circuits. To ensure the successful fabrication of high-performance millimeter-wave circuits, both of these processes must be carefully controlled. For...
As high-density interconnect (HDI) designs with larger layer counts become more prevalent, the use of microvias is increasing. In builds with 3+N+3 or larger configurations, sequential lamination now often relies on skipped vias, staggered microvias, and stacked microvias. However, one of the key challenges is that microvias are more susceptible to failure than plated through-holes. The small...
Customer Background: Our customer is a leading communication equipment company specializing in the development and manufacturing of high-frequency devices for 5G communication systems. Due to the high-frequency signal transmission requirements of their products, their PCB design demands extremely high signal integrity and strong anti-interference capabilities. Product Complexity: The primary challenge of this project was ensuring that the high-frequency...
When designing a printed circuit board (PCB), engineers often focus on ensuring the correct impedance structures and electrical performance of the board. However, the physical characteristics, such as PCB thickness, are equally important and can significantly impact the cost, manufacturability, and performance of the final product. While standard PCB thicknesses are widely used, they are more of a...
Designing double-sided PCBs requires careful planning to ensure efficient assembly, high yields, and reliable solder joints. Solder paste application and stencil design play a critical role in achieving these goals. This article explores key considerations for solder paste and stencil design, focusing on double-sided PCBs, component orientation, and advanced techniques for fine-pitch devices. Key Considerations for Double-Sided...
As the demand for more compact, reliable, and flexible electronic devices grows, rigid-flex PCBs are becoming increasingly popular. These boards combine the best of both rigid and flexible circuits, offering unique advantages such as enhanced durability, reduced package size, and fewer connectors. However, the cost of designing and manufacturing rigid-flex PCBs can be significantly higher than traditional...
Troubleshooting printed circuit boards (PCBs) can be a daunting task, but with a systematic approach, it becomes manageable and efficient. This guide provides a step-by-step process to identify faulty components on PCBs, along with methods tailored to specific component types and advanced techniques for batch inspection. Step-by-Step Guide to Finding Faulty Components on PCBs Step 1: Power...
High-density interconnect (HDI) PCBs have become a standard in modern electronics, enabling designers to create smaller, more functional devices. However, designing HDI PCBs requires careful attention to detail due to their complexity and the advanced technologies involved. This article outlines key HDI PCB design guidelines, highlights the advantages and disadvantages of HDI layouts, and provides insights into overcoming common...