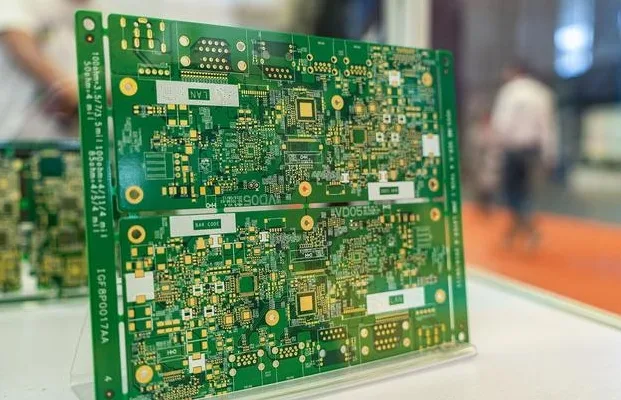
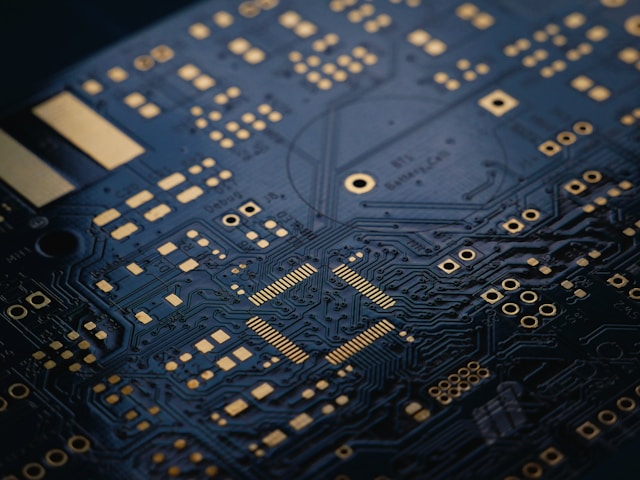
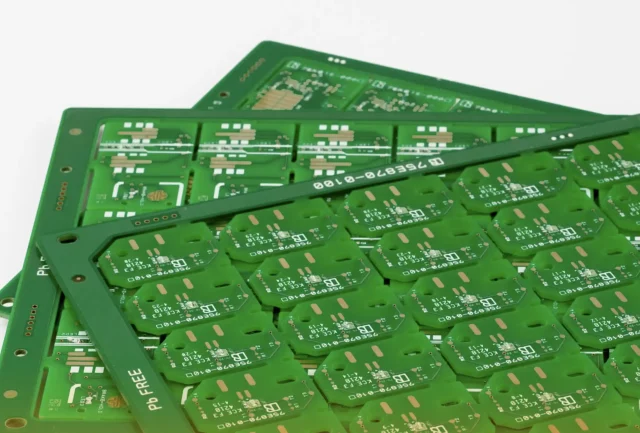
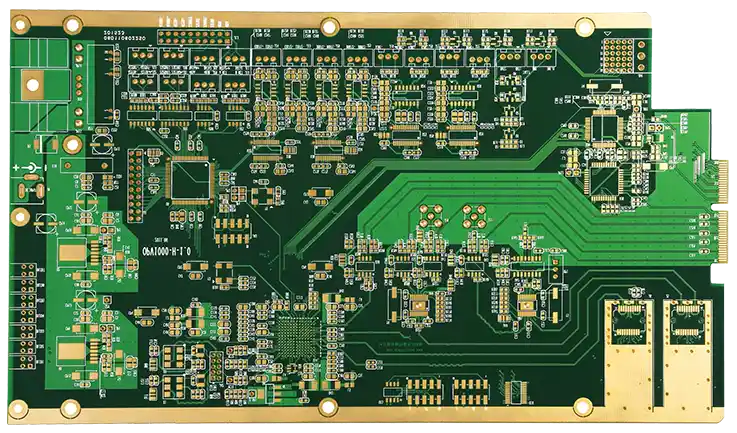
Automated Test Equipment (ATE) PCBs are critical components in high-precision testing systems for semiconductors, modules, and electronic assemblies. Unlike standard PCBs, ATE PCBs must support high-density routing, controlled impedance, fine-pitch interconnects, and reliable signal integrity, ensuring accurate and repeatable test results. Why ATE PCBs Require Specialized Materials ATE systems often operate under high-speed digital or...
HomeAuthor
kkpcb04 - KKPCB - Page 8 of 65
Hybrid PCB materials combine two or more substrate types—such as high-speed laminates, low-loss materials, BT epoxy, and ceramics—to create boards optimized for electrical performance, thermal management, and mechanical stability. Unlike single-material PCBs, hybrid designs allow engineers to tailor material properties to different areas of the circuit, achieving performance levels unattainable with conventional laminates. Why Hybrid...
High TG materials are specialized PCB laminates and prepregs engineered to operate reliably under elevated temperatures, repeated thermal cycling, and high-density multilayer stackups. TG, or glass transition temperature, defines the point at which the resin matrix softens, directly affecting mechanical stability, dimensional integrity, and electrical performance. In advanced electronic systems, selecting high TG materials is...
Low Loss Materials are a foundational requirement in modern PCB design where signal integrity, insertion loss, and timing accuracy directly determine system performance. As data rates increase and operating frequencies extend into multi-GHz and mmWave ranges, dielectric loss transitions from a secondary concern to a primary limiting factor in electronic system design. Why Low Loss...
High Frequency Laminates are specialized PCB materials engineered to support RF, microwave, and high-speed digital circuits operating in multi-GHz and mmWave frequency ranges. As signal frequencies increase, traditional FR-4 laminates introduce excessive dielectric loss, impedance drift, and phase instability, making material selection a primary electrical design decision rather than a secondary cost consideration. Why High...
A BT Epoxy PCB is a material system specifically developed to meet the demands of semiconductor packaging, IC substrates, and high-density interconnect structures. Unlike general-purpose FR-4, BT epoxy resin is engineered for environments where thermal stability, dimensional control, and long-term reliability are non-negotiable design constraints. Material Characteristics of BT Epoxy PCB BT epoxy, derived from...
Aluminum Nitride PCB (AlN PCB) is a ceramic substrate technology specifically engineered for electronic systems where power density, thermal stress, and operating temperature exceed the limits of conventional PCB materials. In high-power and high-temperature environments, Aluminum Nitride PCBs serve not only as circuit carriers but as primary thermal management and reliability enablers. Why Aluminum Nitride...
A Ceramic PCB is a substrate technology selected when thermal limits, electrical insulation, and mechanical stability become primary system constraints. In high-power and high-voltage electronic systems, ceramic substrates are not simply alternatives to organic laminates—they function as integrated thermal and structural elements within the overall design architecture. Ceramic PCB as a Thermal Path Element In...
In high-frequency electronic systems, a PTFE PCB is not selected to improve margins—it is selected because the loss budget leaves no alternative. When signal fidelity, phase coherence, and predictable impedance directly affect system functionality, PTFE-based laminates become a system-level engineering decision rather than a material upgrade. Why PTFE PCB Is Chosen at the Architecture Level...
Taconic PCB materials are widely recognized in high-frequency and microwave PCB applications for their low dielectric loss, stable dielectric constant (Dk), and high thermal reliability. As RF and high-speed digital systems continue to demand higher bandwidths and tighter signal integrity, Taconic laminates provide a proven solution for minimizing insertion loss and maintaining performance consistency. Material...