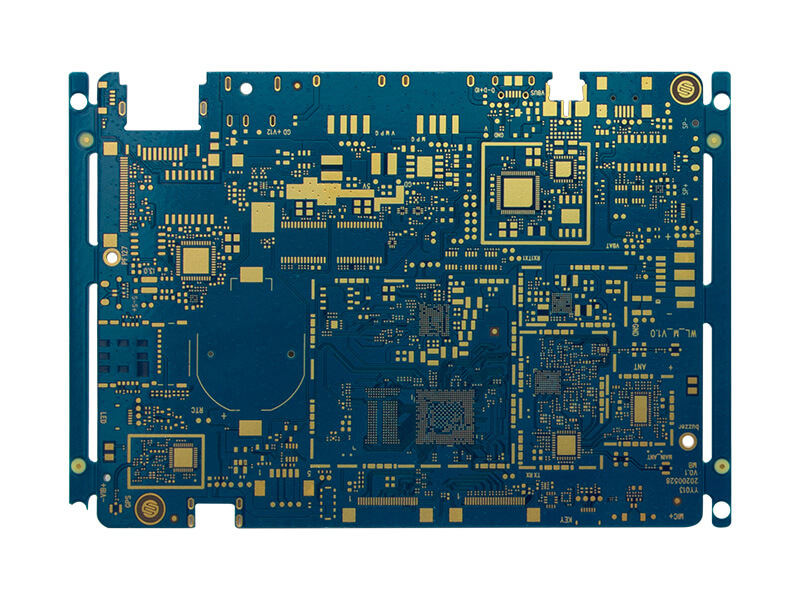
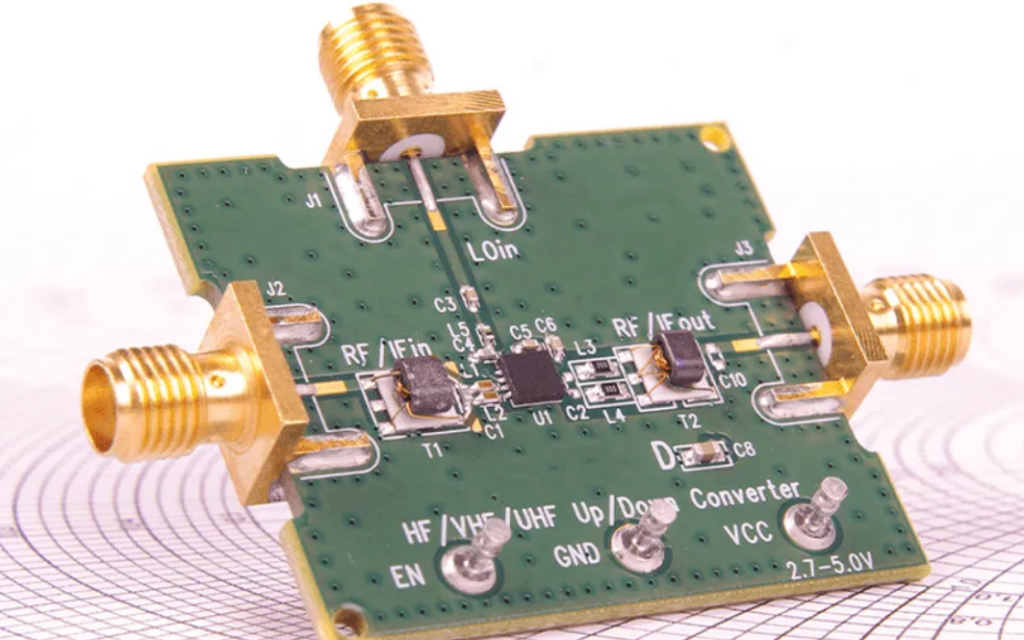
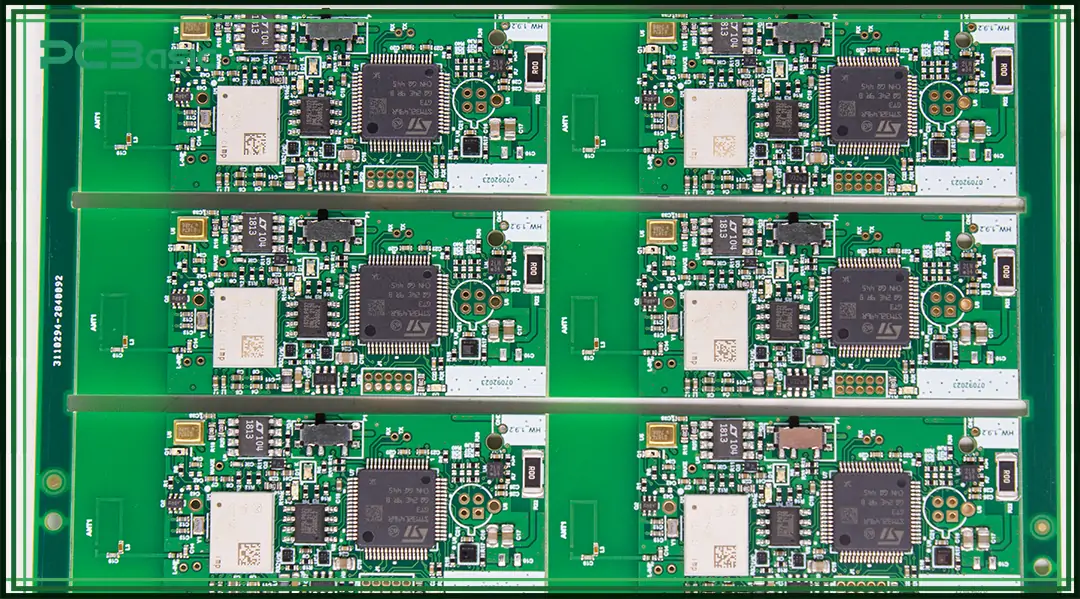
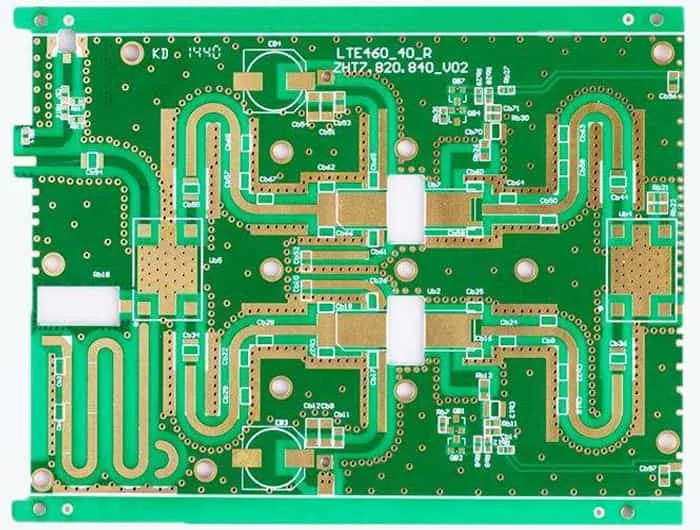
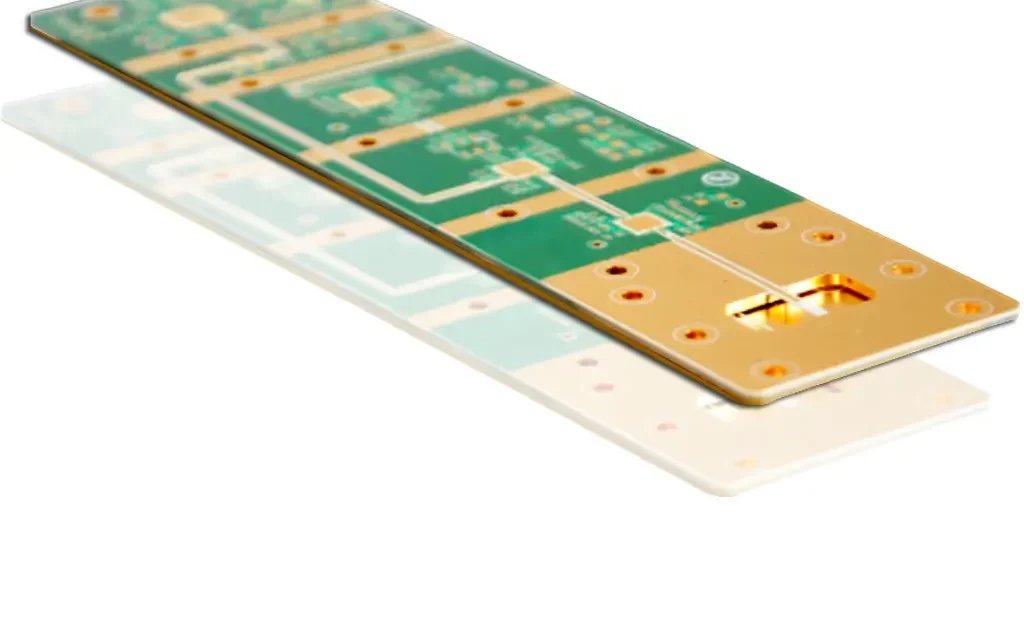
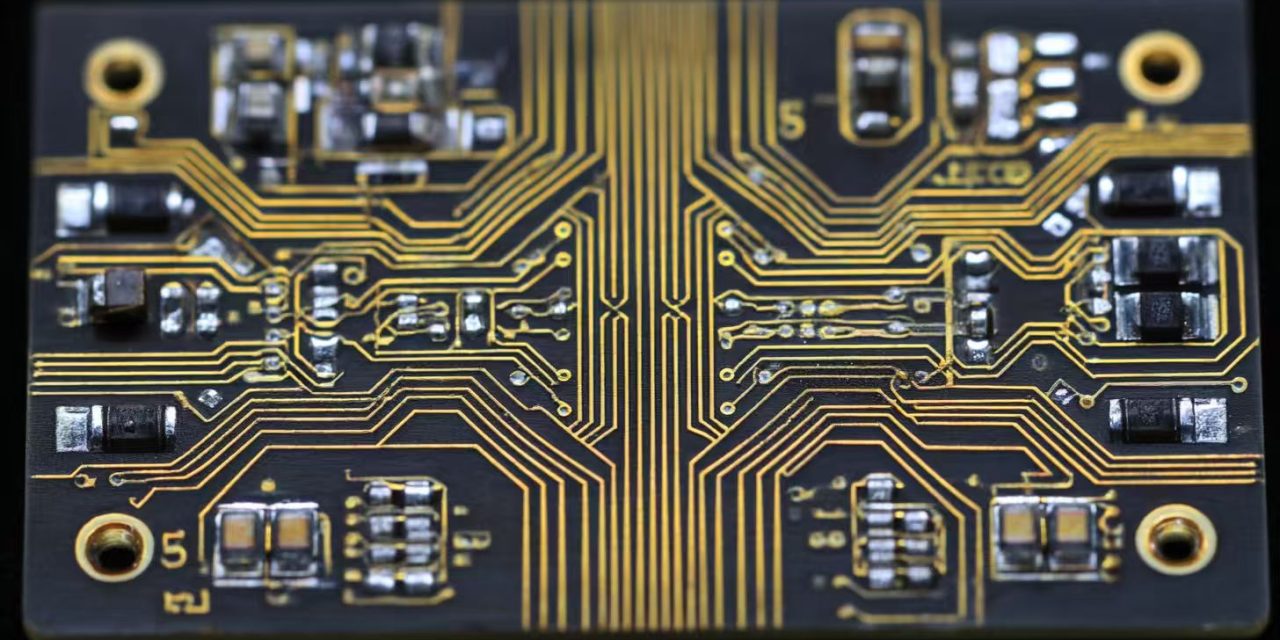
As 5G technology continues to expand across telecommunications, IoT, and industrial applications, the demand for reliable 5G module PCB assembly has grown rapidly. 5G modules integrate high-speed digital circuits, RF front-end components, and antennas into compact form factors, making PCB assembly quality critical to overall system performance. This article explores the key requirements, challenges, and...
HomeCategory
PCB Manufacturing Services | High-Quality PCB & PCBA - KKPCB
Millimeter-wave (mmWave) technologies are rapidly expanding in applications such as 5G, automotive radar, satellite communication, and advanced sensing systems. At these extremely high frequencies, PCB material selection becomes critical. Taconic RF-35 PCB for mmWave applications is widely recognized for its low loss, stable dielectric properties, and excellent manufacturing reliability. This article explores why Taconic RF-35...
With the rapid deployment of 5G networks, antenna performance has become a critical factor in achieving high data rates, low latency, and stable wireless communication. Selecting the right PCB material is essential, and RO4003 PCB for 5G antenna applications has become a popular choice due to its excellent high-frequency performance, stable dielectric properties, and cost-effective...
Electronics Industry NewsCustomer CaseEngineering TechnologiesPCB DesignPCB ManufacturingPCB Materials
PCB Factory Direct: Cost-Effective and Reliable PCB Manufacturing from the Source
In today’s global electronics supply chain, many companies are choosing PCB factory direct sourcing to reduce costs, improve communication, and ensure consistent manufacturing quality. Working directly with a PCB factory eliminates unnecessary intermediaries and gives customers greater control over pricing, lead time, and production transparency. This article explains what PCB factory direct means, why it...
As RF, microwave, and high-speed communication technologies continue to advance, partnering with a qualified high frequency PCB OEM has become essential for companies seeking stable performance, consistent quality, and scalable production. High frequency PCBs require far more than standard fabrication—they demand specialized materials, precise impedance control, and strict manufacturing discipline. This article explains what a...
Submitting a clear and complete PCB price request is the first step toward accurate pricing, short lead times, and smooth production. Whether you are sourcing prototype PCBs, small batch orders, or mass production, providing the right information helps PCB manufacturers evaluate cost, manufacturability, and delivery schedules efficiently. This article outlines the essential details required for...
In high-speed communications, radar systems, 5G infrastructure, and other cutting-edge electronics, the role of a high frequency PCB manufacturer is more important than ever. High frequency PCBs operate at gigahertz (GHz) and millimeter-wave frequencies, requiring precision design, specialized materials, and advanced fabrication techniques that differ significantly from standard PCB production. Selecting the right manufacturer influences...
In high-speed wireless systems, radar, 5G networks, and other advanced electronic products, selecting the right high frequency PCB supplier is critical to ensure signal integrity, minimize losses, and achieve reliable performance. Unlike standard PCB manufacturing, high frequency PCB production demands tight material control, precise impedance management, and advanced fabrication technology. This article provides a comprehensive...
When you order microwave PCB solutions for advanced electronic systems, precision, material performance, and manufacturing expertise are critical. Microwave PCBs operate at extremely high frequencies, where signal loss, impedance mismatch, and dielectric instability can severely impact overall system performance. This article explains the key factors to consider when ordering microwave PCBs, helping engineers and purchasing...
When you purchase RF PCB solutions for high-frequency and microwave applications, performance, reliability, and manufacturing precision are critical. RF PCBs are widely used in wireless communication, radar systems, satellite electronics, and RF front-end modules, where even small design or process deviations can significantly impact signal quality. This article explains what to consider when purchasing RF...