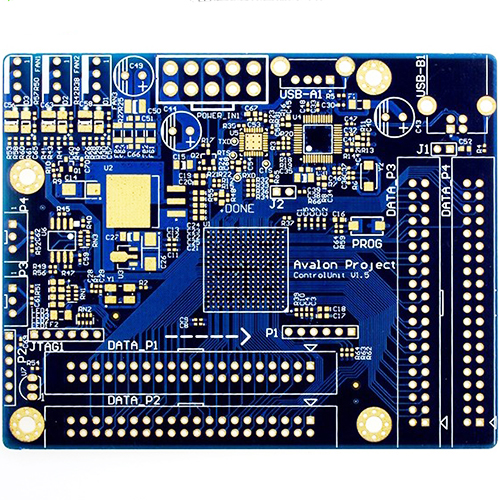
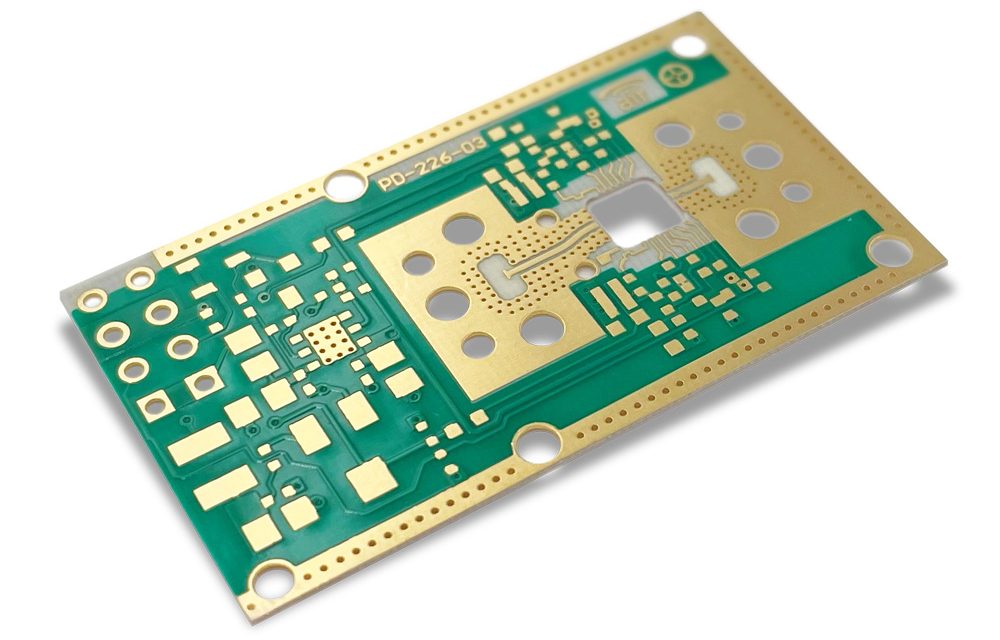
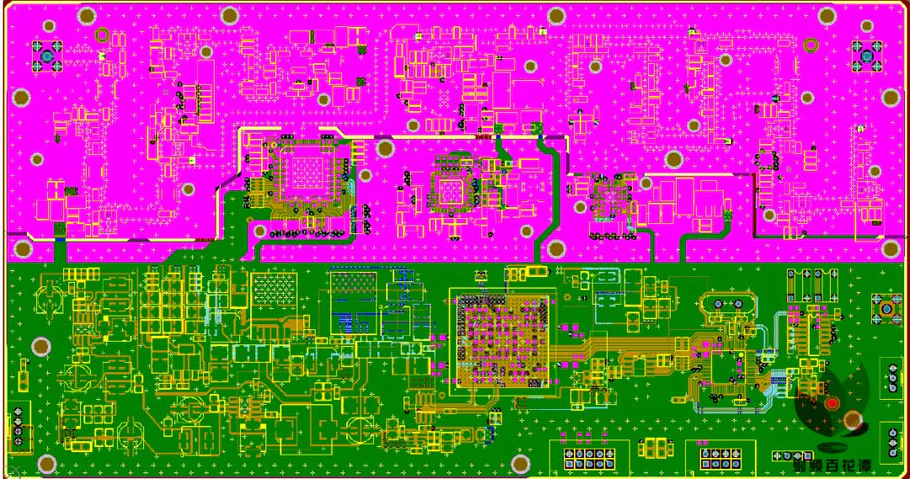
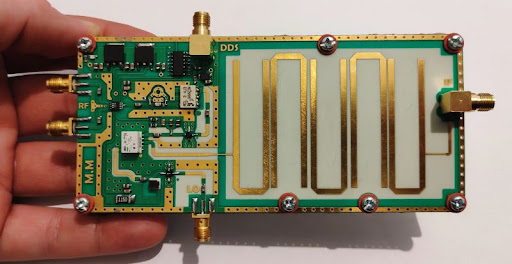
Taconic RF-35 PCB for mmWave: Low-Loss, High-Stability Solutions for Millimeter-Wave Applications
Millimeter-wave (mmWave) technologies are widely used in 5G, radar, and high-capacity wireless systems. At frequencies above 24 GHz, PCB material performance becomes a decisive factor for signal loss, phase stability, and system reliability. Taconic RF-35 PCB for mmWave applications is a proven RF laminate choice, offering low dielectric loss, excellent Dk stability, and reliable manufacturability....