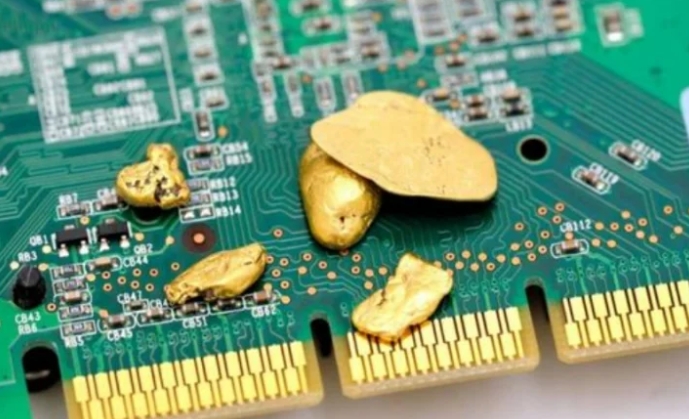
Surface finishes in PCBs are vital for ensuring solderability, electrical conductivity, and corrosion resistance. They help components bond securely to the board, ensure smooth signal flow, and protect the PCB from environmental damage. Without a proper surface finish, a PCB may not function correctly or could wear out faster. Immersion Gold (ENIG) and Gold Plating are two popular gold...
HomeAuthor
kkpcba-Cindy - KKPCB - Page 9 of 75
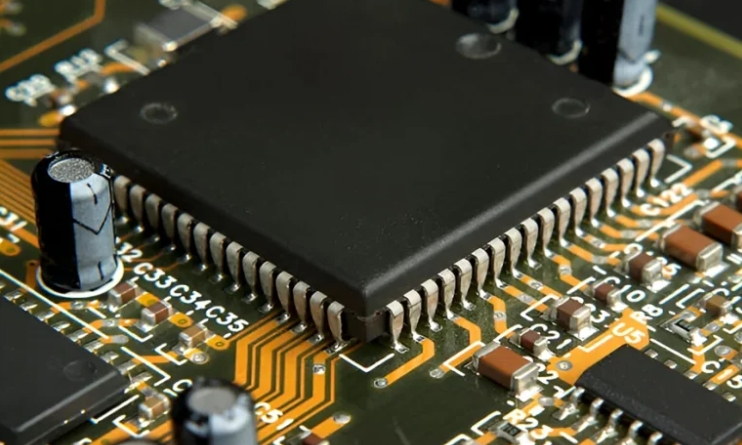
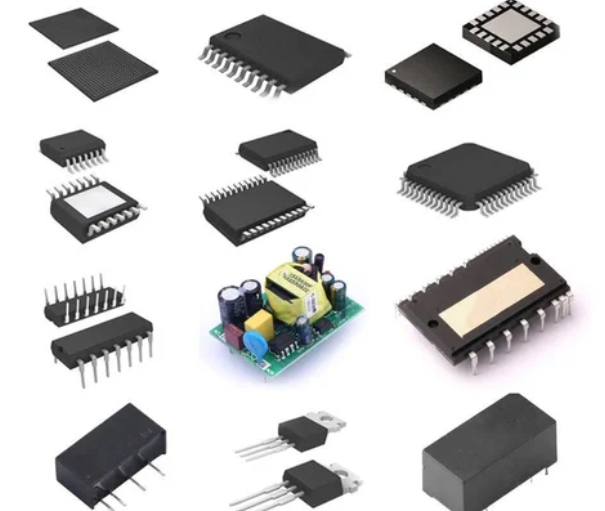
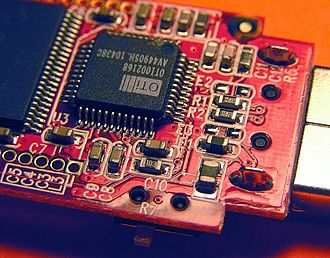
Integrated Circuits (ICs) are small, compact electronic components that combine multiple elements—such as transistors, capacitors, and resistors—onto a single microchip. These ICs are essential for processing data and controlling signals in countless devices, powering everything from smartphones to industrial machinery. IC PCBs (Printed Circuit Boards) enable the integration of ICs into electronic devices, making them smaller, faster,...
In electronics, PCBs (Printed Circuit Boards) and ICs (Integrated Circuits) are two foundational components. While both are indispensable, they serve very different purposes. Understanding their roles is essential for anyone interested in electronics design or manufacturing. PCB: Acts as the backbone of electronic devices, connecting and supporting all components. IC: A compact chip designed for specific tasks, such as...
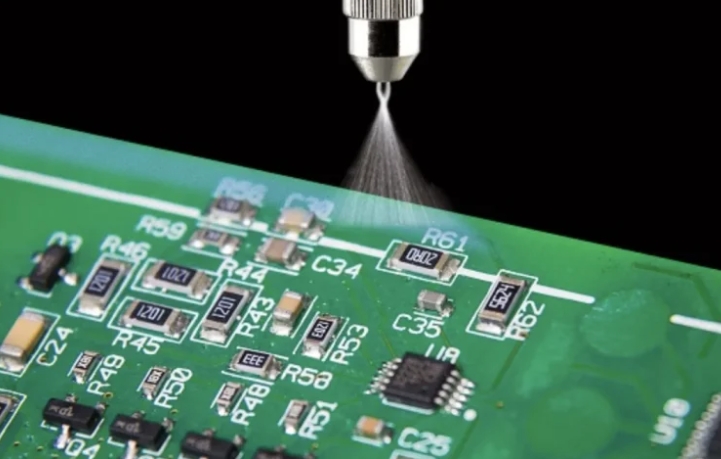
Conformal coatings play a critical role in ensuring the longevity and reliability of printed circuit boards (PCBs). Whether designing electronics for consumer devices, automotive systems, or military applications, selecting the right conformal coating is essential. In this guide, we’ll cover everything about conformal coatings, from types and benefits to best practices for application. What is Conformal Coating?...
What is the standard of a good PCB board? Reasonable layout, sufficient power redundancy of power line, high-frequency impedance and simple low-frequency wiring. What kind of PCB design layout can reach the best heat dissipation There are three main sources of heat in PCB: heat from electronic components; heat from PCB itself; Heat from other parts. Among the three heat sources, the...
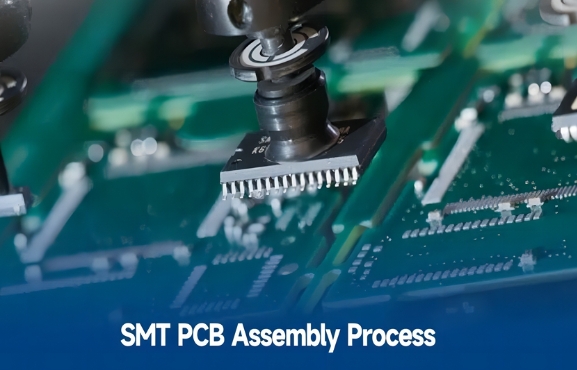
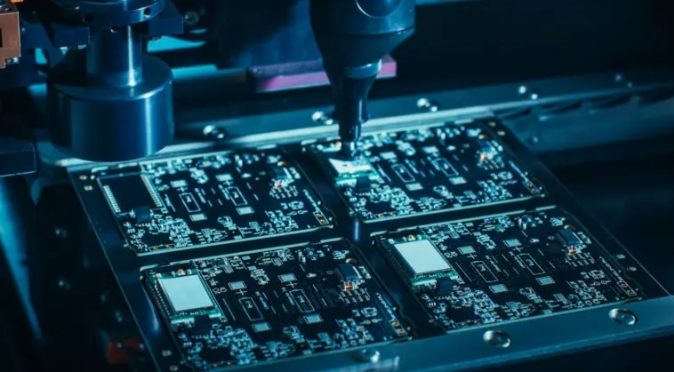
Introduction to SMT Assembly As electronics become more compact and complex, Surface Mount Technology (SMT) has emerged as the standard method for assembling PCBs. Since its rise to prominence in the 1980s, SMT has revolutionized manufacturing and is now integral to modern electronics, from smartphones to automotive systems. What is SMT Assembly? SMT is a process of constructing...
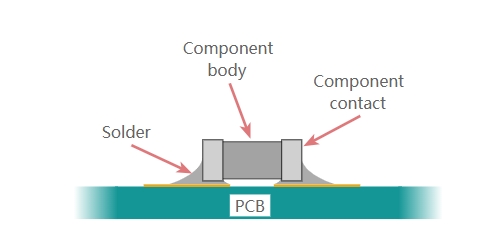
When assembling a printed circuit board (PCB), components are mounted onto the board through one of two primary methods: Surface Mount Technology (SMT) or Through-Hole Technology (THT). Each method has distinct advantages and is suited to different applications depending on the project requirements. This guide explores the SMT and THT assembly processes, their differences, and how to choose the right...
Have you ever wondered how our gadgets have become so powerful yet so compact? The secret lies in a manufacturing marvel: Surface Mount Technology (SMT) for PCB assembly. In this guide, we’ll break down the essentials of SMT PCB assembly, why it’s the go-to method for modern electronics, and how it’s shaping the tech we rely on...
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) is a method of mounting electronic components directly onto the surface of a printed circuit board (PCB). The components used in SMT, called Surface Mount Devices (SMDs), have largely replaced the older through-hole technology in modern electronics manufacturing due to their compact size and compatibility with automated assembly processes. While SMT offers significant benefits, it...
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) has revolutionized the electronics industry by enabling compact, efficient, and cost-effective PCB assembly. Today, nearly all commercially manufactured electronic devices utilize SMT for its ability to pack more functionality into smaller spaces and improve manufacturing processes through automation. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of SMT, its evolution, benefits, challenges, and applications....