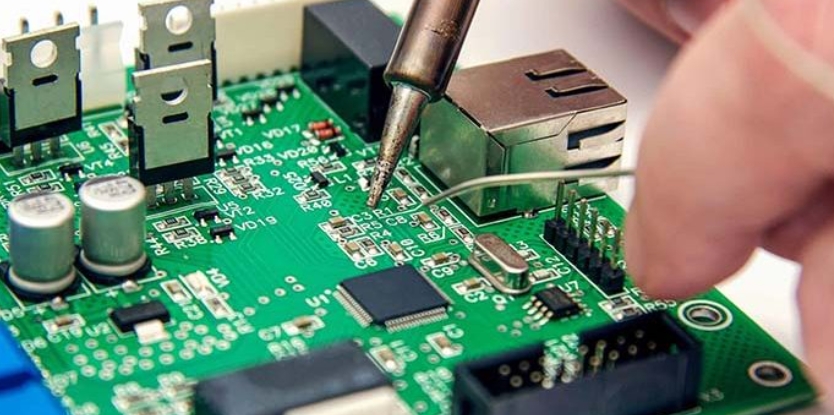
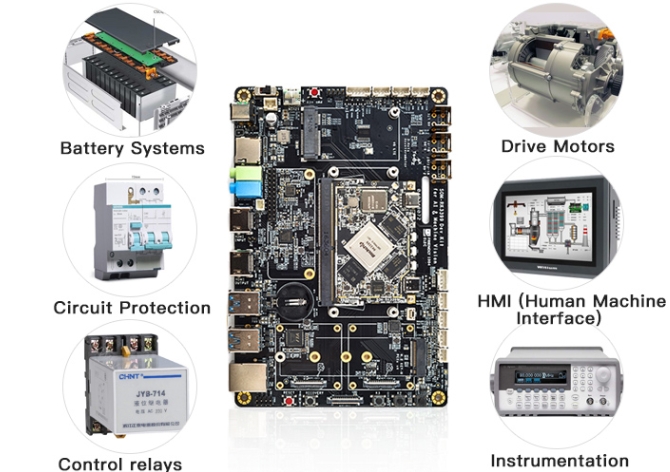
Manufacturers use flux to solder components on PCBs. Depending on the PCB components, flux also varies and is used to fix them on the board. It ensures uninterrupted and strong electrical connections between devices. However, it is crucial to remove excess flux so as not to blur signal traces or damage connections. In this article,...
HomeAuthor
kkpcba-Cindy - KKPCB - Page 53 of 75
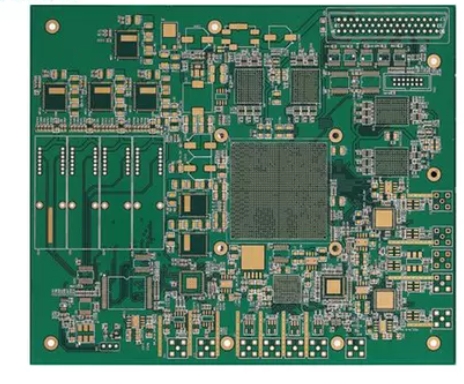
Surface Mount Technology (SMT), SMT Components, and SMT Equipment are all terms for this technology. Almost all commercially produced equipment in the electronics assembly industry today uses Surface Mount Technology (SMT), mainly because of its advantages in the PCB manufacturing process and the fact that a large number of electronic components can fit into a...
In recent years, electronic products have become increasingly complex and integrated into people’s daily lives. However, there are still two popular methods for soldering electronic components together to build circuits: Surface Mount Technology (SMT) for PCB Assembly Through-Hole (PTH) PCB Assembly Both SMT PCB assembly and PTH assembly have unique advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these differences can...
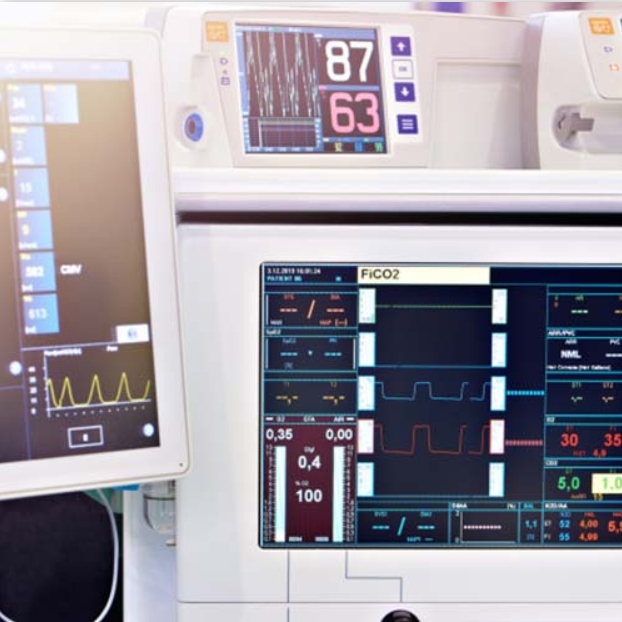
Technology is bringing a major revolution in the medical industry, especially in terms of the functionality and features of medical devices. The desire for innovation has influenced humans to think differently, changing the methods, techniques, and most importantly, the foundations of the medical industry. Modern medicine is the result of the extended role that technology...
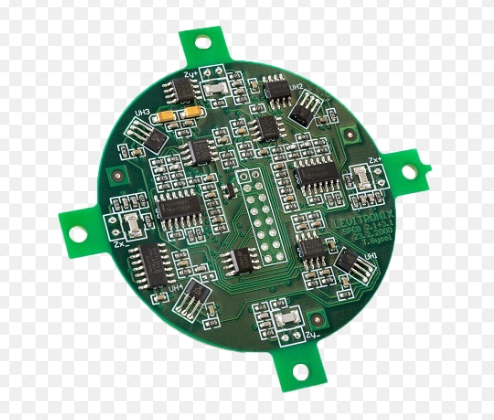
The emergence of humanoid robots, equipped with human-like movement, perception, and intelligence, represents the next frontier of robotics. Central to this development is the advancement of printed circuit boards (PCBs) which enable the intricate control, decision-making, and sensing capabilities of these robots. 1. PCB’s Role in Humanoid Robotics In humanoid robots, PCBs serve as the foundation for...
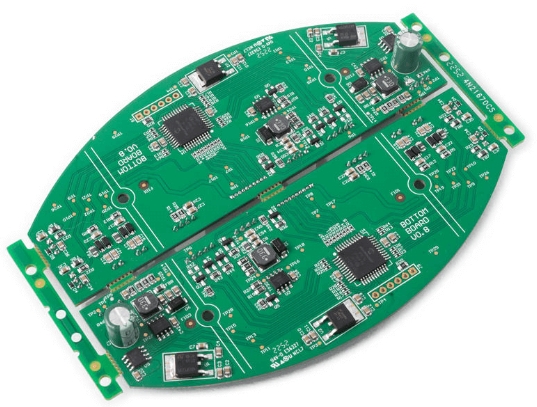
Due to the development of robotics and similar technologies, many different remote control devices are used in numerous fields. The assembly of printed circuit boards is essential for smooth movement and solid electrical connections between controllers and industrial machinery. Electronics must be rugged and able to withstand the harshest environments of industrial use. In addition, industrial control...
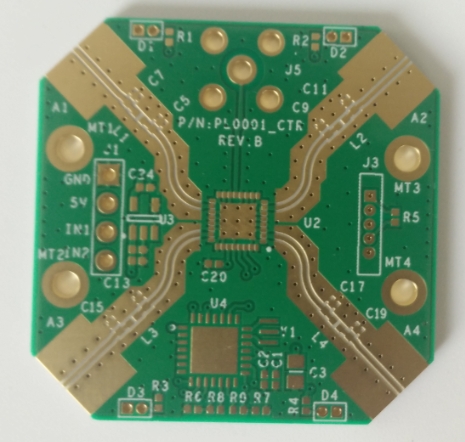
PCB is one of the essential components and devices in electronics due to its wide availability and simplicity. Among the various types and forms of PCB, high-frequency PCB is widely used due to its general purpose. What is High-Frequency PCB? A high-frequency PCB is very similar to any other form of PCB (printed circuit board). It is compatible with...
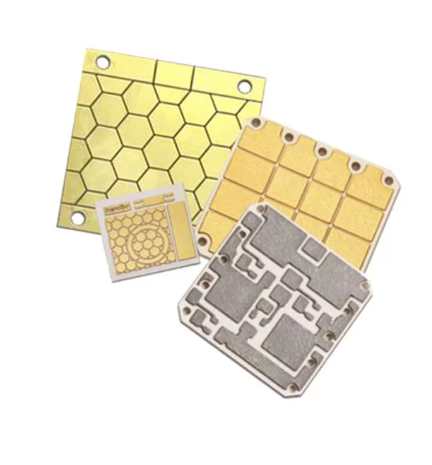
Among the numerous PCB options, two types are widely used. One is Ceramic PCB Substrate and the other is Alumina Substrate PCB. In this article, we will introduce the characteristics and advantages of each substrate in detail. Ceramic printed circuit boards are widely used in technology assembly due to their multiple characteristics and advantages. This type...
If you are new to the PCB industry, you may feel that PCBs look very similar. Can we identify the internal quality of PCBs by appearance? In fact, if there are slight differences in the appearance of PCBs, PCB industry experts can also identify the differences, and a good appearance is essential for the overall...
Customer Background The client specializes in the development and production of a wide range of microwave electronic products. These products are extensively used in satellite communication, television broadcasting, long-range communication, data and image transmission, radar, remote control, remote sensing, electronic reconnaissance, and electronic countermeasures. With deep technical expertise in microwave technology and high-frequency electronic products,...