What Is an Impedance Controlled PCB?
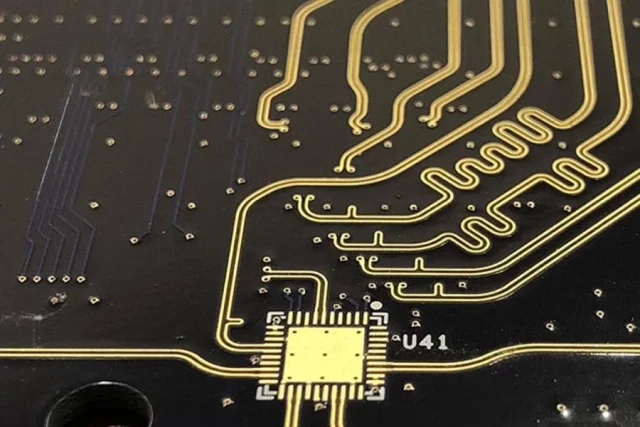
An Impedance Controlled PCB is a printed circuit board engineered to maintain a precise and stable characteristic impedance along signal transmission paths. It is essential for high-speed digital signals and high-frequency RF signals, where impedance mismatches can cause signal reflection, loss, and distortion.
Impedance controlled PCBs are widely used in 5G communication, ADAS systems, sensor modules, and high-speed test equipment.
Why Impedance Control Is Critical
In high-speed and high-frequency designs, uncontrolled impedance can lead to:
-
Signal reflections and ringing
-
Increased insertion loss
-
Crosstalk and EMI issues
-
Degraded eye diagrams
-
Reduced system reliability
A properly designed impedance controlled PCB ensures clean signal transmission and stable system performance.
Types of Impedance Controlled PCB
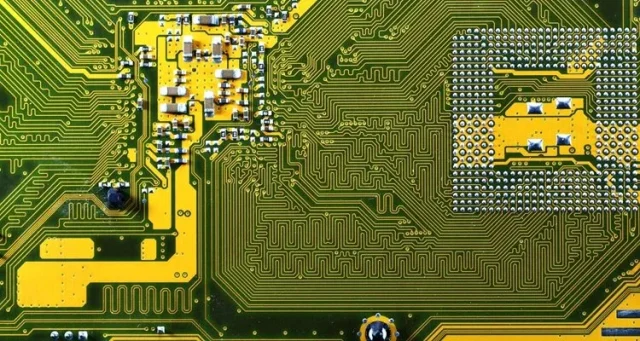
Common impedance structures include:
-
Single-ended impedance (e.g. 50Ω, 75Ω)
-
Differential impedance (e.g. 90Ω, 100Ω)
-
Microstrip and stripline structures
-
Coplanar waveguide with ground (CPWG)
Each structure is selected based on frequency, routing layer, and application needs.
Key Design Factors for Impedance Controlled PCB
Achieving accurate impedance control depends on multiple factors:
-
Dielectric constant (Dk) of PCB material
-
Dielectric thickness
-
Trace width and spacing
-
Copper thickness and surface roughness
-
Stack-up configuration
Precise simulation and close coordination with the PCB manufacturer are critical.
Material Selection for Impedance Controlled PCB
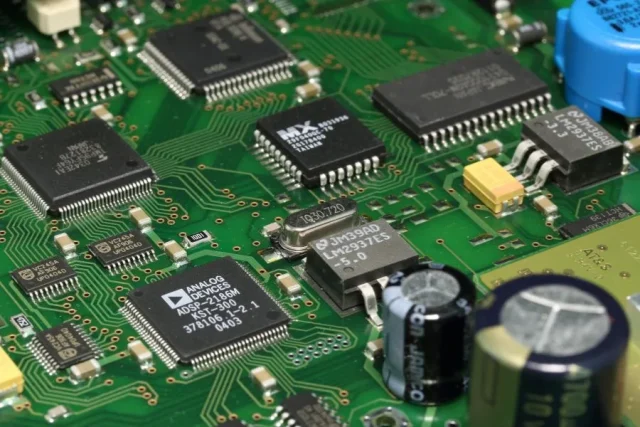
Material stability directly affects impedance accuracy. Common materials include:
-
High-speed laminates (Megtron 6 / Megtron 7)
-
Low-loss RF materials (RO4350B, RF-35)
-
Hybrid PCB materials
-
High-Tg FR-4 for cost-sensitive designs
Low-loss and low-Dk materials are preferred for high-frequency impedance controlled PCBs.
Manufacturing Requirements for Impedance Controlled PCB
Producing a reliable impedance controlled PCB requires advanced manufacturing control:
-
Tight dielectric thickness tolerance
-
High-precision etching and registration
-
Controlled copper roughness
-
Accurate lamination processes
-
100% impedance testing (TDR)
Only experienced PCB manufacturers can consistently meet impedance targets.
Applications of Impedance Controlled PCB

Impedance controlled PCBs are essential in:
-
5G routers and communication equipment
-
High frequency sensor PCB and RF modules
-
ADAS and automotive electronics
-
High-speed computing and networking
-
Semiconductor test and measurement systems
They are critical wherever signal integrity matters.
Conclusion
An Impedance Controlled PCB is the foundation of reliable high-speed and high-frequency electronic systems. Through proper design, material selection, and precise manufacturing control, impedance controlled PCBs deliver superior signal integrity and system performance.
Partnering with a professional impedance controlled PCB manufacturer ensures consistent quality from prototype to mass production

