A Ceramic PCB is a high-performance circuit substrate engineered for applications that demand excellent thermal conductivity, electrical insulation, and long-term reliability under harsh operating conditions. Unlike organic PCB materials such as FR-4 or PTFE, ceramic PCB substrates are inorganic, enabling stable electrical and mechanical performance at elevated temperatures and high power densities.
Ceramic PCB technology is widely adopted in power electronics, automotive electronics, aerospace systems, LED modules, and high-reliability industrial equipment, where thermal and environmental constraints exceed the limits of conventional PCBs.
Material Characteristics of Ceramic PCBs
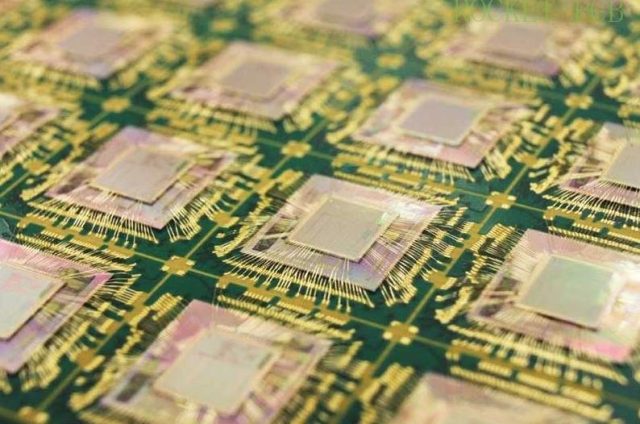
The defining advantage of a ceramic PCB lies in its material properties. Common ceramic PCB substrates include Alumina (Al₂O₃), Aluminum Nitride (AlN), and Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄), each selected based on thermal and mechanical requirements.
Key material characteristics of ceramic PCBs include:
-
High thermal conductivity for efficient heat dissipation
-
Excellent electrical insulation even at high temperatures
-
Low coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) for mechanical stability
-
High dielectric strength and breakdown voltage
These properties allow ceramic PCBs to operate reliably in environments where polymer-based materials would degrade or fail.
Thermal Management Advantages
Thermal performance is the primary driver behind ceramic PCB adoption. Power devices such as IGBTs, MOSFETs, and power modules generate localized heat that must be removed efficiently to maintain reliability.
A ceramic PCB enables:
-
Direct heat spreading from power components to heat sinks
-
Reduced thermal resistance compared to FR-4 PCBs
-
Stable thermal performance over wide temperature ranges
-
Improved power density without excessive board thickness
In high-power applications, ceramic PCBs often eliminate the need for complex thermal interface stacks.
Electrical Performance and Reliability
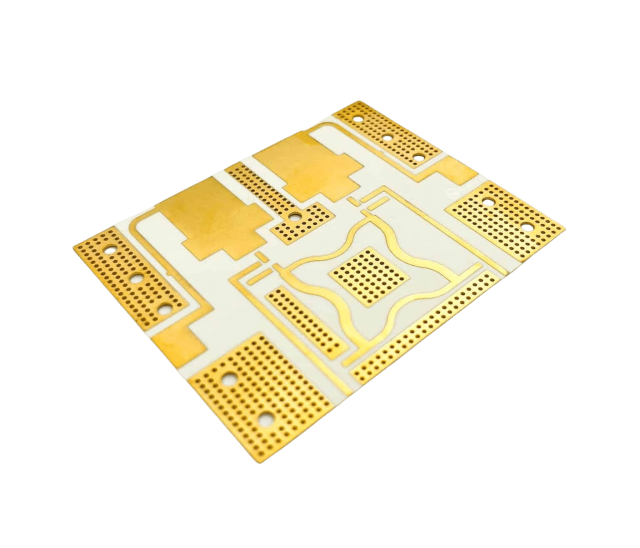
From an electrical standpoint, ceramic PCBs provide stable dielectric behavior over temperature, voltage, and frequency. This stability is critical for power control circuits and high-voltage applications.
Electrical benefits of ceramic PCB technology include:
-
High insulation resistance and dielectric strength
-
Minimal dielectric property drift over time
-
Excellent resistance to partial discharge
-
High reliability in high-voltage and high-current environments
These characteristics make ceramic PCBs well suited for power conversion, motor control, and high-voltage isolation designs.
Manufacturing Technologies for Ceramic PCBs

Ceramic PCBs are produced using specialized fabrication methods rather than standard PCB processes. Common ceramic PCB manufacturing technologies include:
-
Direct Bonded Copper (DBC)
-
Active Metal Brazing (AMB)
-
Thick-film and thin-film metallization
Each process impacts copper adhesion strength, current-carrying capacity, and long-term reliability. Manufacturing control is critical, as ceramic substrates are rigid and brittle compared to organic laminates.
Mechanical and Assembly Considerations
While ceramic PCBs offer superior thermal and electrical performance, they require careful mechanical and assembly handling. Ceramic materials are less tolerant of mechanical shock and improper mounting.
Engineering considerations include:
-
Stress management during assembly and operation
-
Controlled soldering profiles to avoid cracking
-
Proper mounting and support structures
-
Matching CTE between components and substrate
Successful ceramic PCB implementation requires coordination between electrical, thermal, and mechanical design disciplines.
Application Domains of Ceramic PCBs
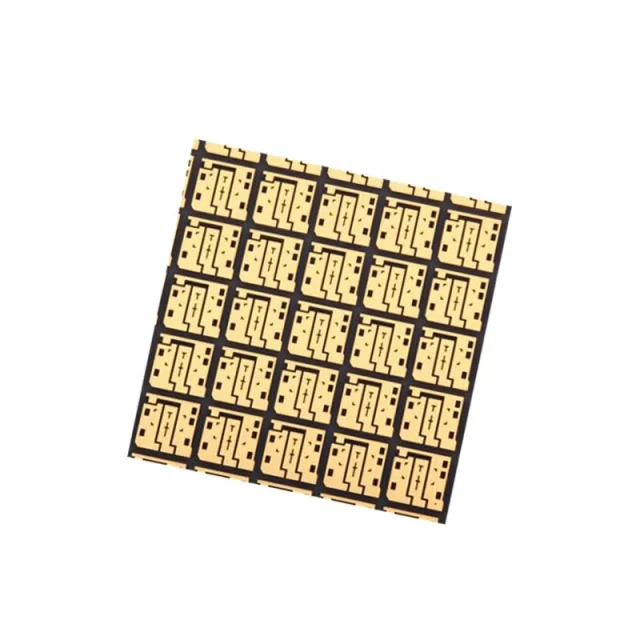
Ceramic PCBs are commonly used in:
-
Power modules and inverters
-
Automotive power electronics
-
Aerospace and defense electronics
-
LED lighting and laser drivers
-
Industrial power control systems
In these applications, ceramic PCB technology enables higher power density, longer service life, and improved system reliability.
Engineering Perspective
A Ceramic PCB is not a general-purpose solution—it is a strategic engineering choice for systems where thermal performance, electrical insulation, and reliability margins are critical. When properly designed and manufactured, ceramic PCBs provide a robust foundation for high-power and high-reliability electronic systems.
By aligning material selection, thermal design, and manufacturing processes, KKPCB supports engineers in delivering ceramic PCB solutions tailored to demanding industrial and power electronics applications.

