When you purchase RF PCB solutions for high-frequency and microwave applications, performance, reliability, and manufacturing precision are critical. RF PCBs are widely used in wireless communication, radar systems, satellite electronics, and RF front-end modules, where even small design or process deviations can significantly impact signal quality.
This article explains what to consider when purchasing RF PCBs, including material selection, impedance control, manufacturing capability, and testing requirements.
What Is an RF PCB?
An RF PCB is a printed circuit board specifically designed to operate at radio frequency and microwave ranges. Compared with standard PCBs, RF PCBs require tighter control over:
- Dielectric constant (Dk) and dissipation factor (Df)
- Trace geometry and impedance matching
- Signal loss and electromagnetic interference
Proper RF PCB design and manufacturing ensure stable signal transmission and minimal power loss.
Key Materials Used in RF PCB Manufacturing
Material selection is one of the most important factors when you purchase RF PCB products.
Common RF PCB materials include:
- Rogers materials for stable impedance and low loss
- PTFE-based laminates for ultra-high-frequency applications
- Hybrid stackups combining RF materials with FR-4 for cost optimization
Choosing the right material depends on operating frequency, thermal requirements, and cost targets.
Importance of Impedance Control for RF PCBs
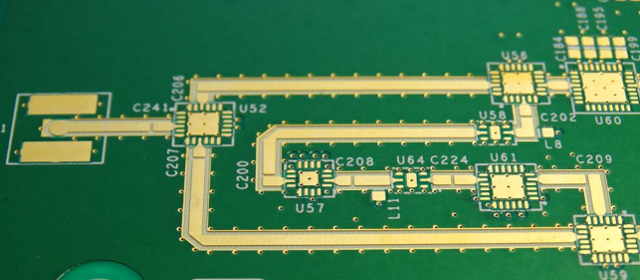
Accurate impedance control is essential in RF PCB manufacturing.
- Impedance mismatch can cause signal reflection and power loss
- Tight tolerance control improves RF performance and consistency
- Controlled impedance structures are critical for antennas, filters, and amplifiers
When purchasing RF PCBs, confirm the manufacturer’s impedance control capability and tolerance standards.
Manufacturing and Quality Control Considerations
A reliable RF PCB supplier should offer:
- Experience in high-frequency PCB manufacturing
- Precise lamination and etching process control
- RF-specific testing such as TDR and network analysis
- Consistent quality from prototyping to mass production
These capabilities ensure that purchased RF PCBs meet performance expectations.
Applications of RF PCBs
RF PCBs are commonly used in:
- Wireless communication systems
- RF front-end modules
- Radar and satellite electronics
- Automotive radar and ADAS
- Industrial and medical RF devices
Each application requires stable RF performance and high manufacturing reliability.
Conclusion
When you purchase RF PCB solutions, selecting the right materials, ensuring accurate impedance control, and working with an experienced manufacturer are essential for achieving reliable high-frequency performance.
By partnering with a trusted RF PCB supplier, engineers can minimize signal loss, improve system stability, and ensure consistent quality throughout the product lifecycle.

