High Frequency Laminates are specialized PCB materials engineered to support RF, microwave, and high-speed digital circuits operating in multi-GHz and mmWave frequency ranges. As signal frequencies increase, traditional FR-4 laminates introduce excessive dielectric loss, impedance drift, and phase instability, making material selection a primary electrical design decision rather than a secondary cost consideration.
Why High Frequency Laminates Are Critical in Modern Electronics
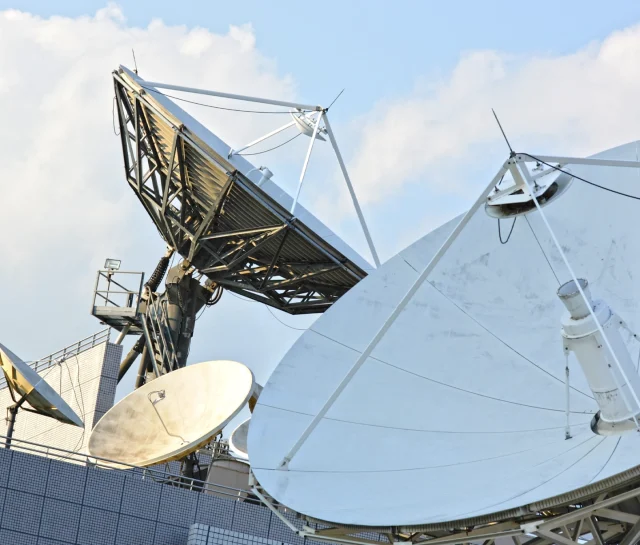

At high frequencies, signal degradation is no longer dominated by copper resistance alone. Instead, dielectric loss, dispersion, and material variability become the dominant limiting factors. High Frequency Laminates are designed to control these effects through stable dielectric properties and low-loss resin systems.
These materials are typically required when:
-
Operating frequencies exceed several GHz
-
Signal loss directly impacts link budget
-
Phase stability affects system accuracy
-
Controlled impedance must remain consistent across temperature and frequency
In such systems, laminate performance directly defines achievable electrical margins.
Key Electrical Properties of High Frequency Laminates
High Frequency Laminates are characterized by carefully controlled material parameters that influence electromagnetic behavior.
From an engineering perspective, these laminates provide:
-
Low dissipation factor (Df) to minimize insertion loss
-
Stable dielectric constant (Dk) over frequency and temperature
-
Reduced dielectric anisotropy for predictable signal propagation
-
Improved impedance consistency in microstrip and stripline structures
These properties simplify simulation correlation and reduce post-layout tuning in RF designs.
Signal Integrity and Phase Behavior

In RF and microwave circuits, phase error accumulation can degrade modulation accuracy, beamforming precision, and timing alignment. High Frequency Laminates reduce these risks by maintaining consistent dielectric behavior across signal paths.
This enables:
-
Better phase matching between parallel channels
-
Lower group delay variation
-
Reduced frequency-dependent signal distortion
-
Improved repeatability between PCB fabrication lots
Such characteristics are critical in 5G, radar, satellite, and high-speed test systems.
Thermal and Mechanical Considerations
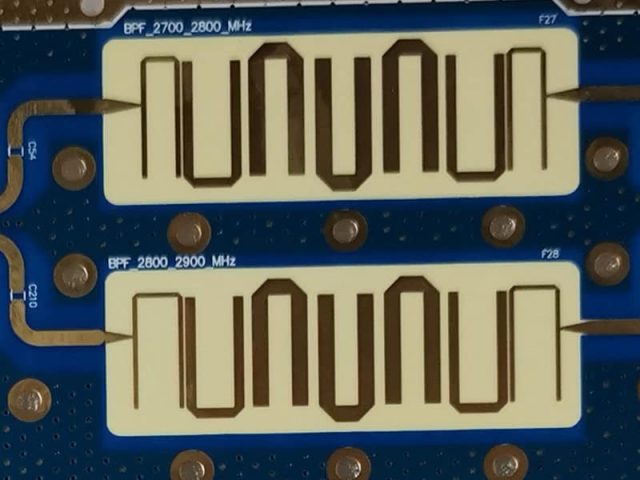
High Frequency Laminates are often based on PTFE, hydrocarbon-ceramic, or modified epoxy systems. While electrically superior, these materials introduce mechanical considerations that must be addressed at the design stage.
Engineering trade-offs include:
-
Managing coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE)
-
Ensuring copper adhesion under thermal cycling
-
Controlling board flatness in multilayer stackups
-
Balancing rigidity with RF performance
Proper stackup design and material pairing are essential to achieve both electrical and mechanical reliability.
Manufacturing and Process Control
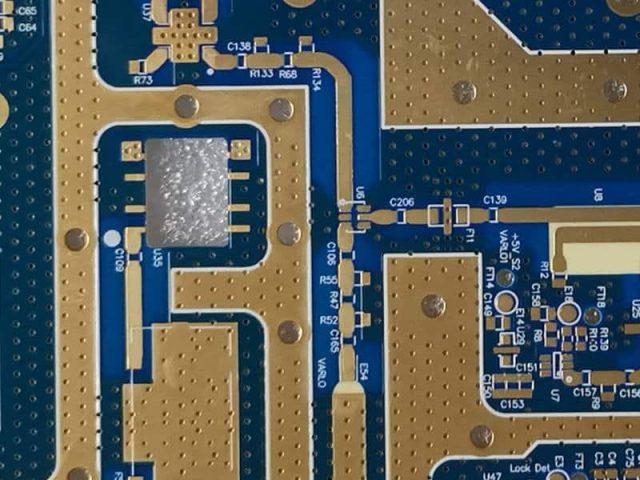
Fabrication of High Frequency Laminates requires process discipline beyond standard PCB manufacturing. Variations in drilling, lamination pressure, and surface treatment can directly affect impedance and loss performance.
Critical manufacturing controls include:
-
Precise thickness control for impedance accuracy
-
Specialized surface treatments for PTFE-based materials
-
Tight lamination profiles to prevent material deformation
-
Electrical testing focused on impedance and insertion loss
A capable PCB supplier aligns manufacturing processes with RF performance targets.
Typical Applications of High Frequency Laminates
High Frequency Laminates are widely used in:
-
RF front-end modules and transceivers
-
5G and mmWave base stations
-
Satellite communication systems
-
Radar and aerospace electronics
-
High-speed test and measurement equipment
In these applications, laminate performance directly translates into system-level signal integrity and reliability.
Engineering Perspective
High Frequency Laminates should be viewed as electromagnetic control materials, not interchangeable substrates. Their selection influences impedance accuracy, loss budget, and phase behavior across the entire system. When combined with controlled impedance stackups and disciplined manufacturing, High Frequency Laminates enable predictable performance in the most demanding RF and high-speed electronic designs.
KKPCB supports High Frequency Laminate projects through material selection guidance, impedance-focused stackup engineering, and RF-oriented manufacturing control, helping customers achieve consistent high-frequency performance.

