Modern electronics often require boards capable of handling high currents safely and efficiently. High Current PCBs are specially designed to manage large amounts of electrical current while maintaining thermal stability, signal integrity, and mechanical reliability. These PCBs are widely used in power electronics, automotive systems, industrial machinery, and energy storage applications.
What is a High Current PCB?
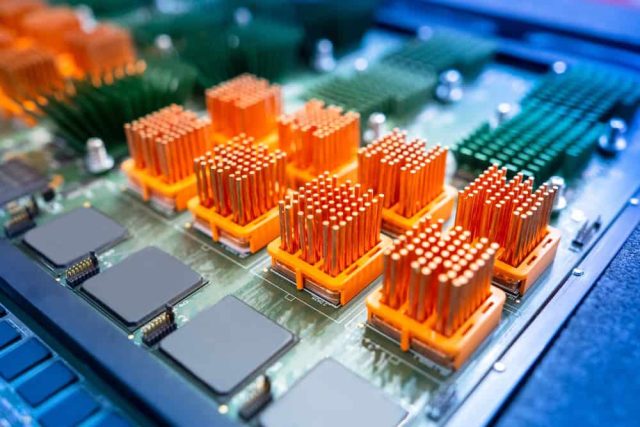
A High Current PCB is designed to carry high levels of electrical current without overheating or causing performance degradation. Unlike standard PCBs, these boards require:
-
Thicker copper layers for reduced resistance.
-
Optimized trace width and thickness to minimize voltage drops.
-
Efficient thermal management to dissipate heat generated by high currents.
Key Design Considerations for High Current PCBs

-
Copper Thickness
Standard PCBs use 1 oz copper per square foot, but High Current PCBs often require 2 oz, 3 oz, or more to handle high amperage safely. -
Trace Width and Spacing
Wider traces reduce resistance and heat buildup. PCB designers calculate the optimal trace width using IPC-2221 or IPC-2152 standards based on current load and temperature rise. -
Thermal Management
Heat dissipation is critical. Techniques include thermal vias, heat sinks, heavy copper planes, and embedded cooling solutions. -
Material Selection
High current boards often use FR4 with high Tg, metal-core PCBs, or specialized laminates for improved thermal stability and mechanical strength. -
Current Carrying Capacity
Designers must calculate the expected maximum current and ensure PCB traces, vias, and planes can handle it without excessive heating. -
Layer Stack-Up
Multi-layer designs with dedicated power and ground planes improve current distribution and reduce voltage drops.
Applications of High Current PCBs
-
Automotive Electronics: Electric vehicles, battery management systems, and motor controllers.
-
Industrial Power Equipment: Inverters, power converters, and motor drives.
-
Renewable Energy Systems: Solar inverters, wind turbine controllers, and battery storage systems.
-
Consumer Electronics: High-power LED lighting and audio amplifiers.
-
Military and Aerospace: High-power control systems requiring reliable current handling.
Manufacturing Challenges
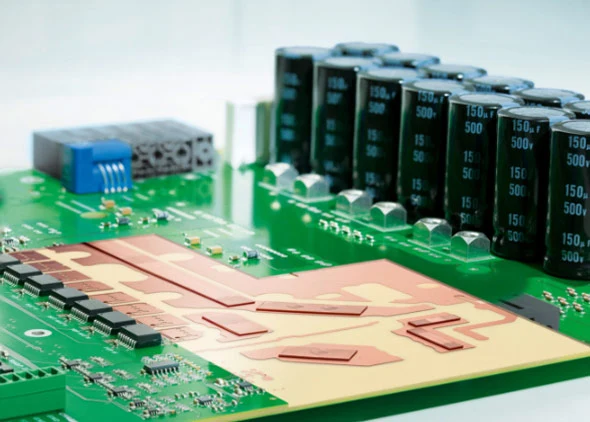
High Current PCBs require precision manufacturing techniques:
-
Heavy Copper Plating: Ensures sufficient conductivity and mechanical stability.
-
Accurate Thermal Vias: For efficient heat transfer.
-
Quality Control: AOI, X-ray inspection, and current testing ensure reliability under high load conditions.
Conclusion
High Current PCBs are essential for modern electronics that demand power, reliability, and thermal stability. Proper design considerations—copper thickness, trace width, thermal management, and materials—are critical to ensuring performance under high current loads. Choosing an experienced PCB manufacturer is crucial for achieving safe, reliable, and high-performance high current boards.

