As modern electronics move toward higher power density, smaller form factors, and more demanding operating environments, thermal performance has become one of the most critical design factors. In applications such as power modules, LED lighting, automotive electronics, industrial power control, and advanced SiC/GaN power devices, conventional FR-4 PCBs may struggle with heat dissipation, long-term reliability, and high temperature operation.
This is where Ceramic PCB technology becomes an ideal solution.
A Ceramic PCB is a high-performance printed circuit board built on a ceramic substrate. Compared with standard PCB materials, ceramic substrates provide outstanding thermal conductivity, strong electrical insulation, and excellent stability at high temperatures. Ceramic PCB solutions are widely used in high power and high reliability applications where efficient thermal management is essential.
What Is a Ceramic PCB?
A Ceramic PCB is a circuit board that uses a ceramic material as the base substrate instead of traditional fiberglass (FR-4). The most common ceramic substrate types include:
-
Alumina (Al₂O₃) Ceramic PCB
-
Aluminum Nitride (AlN) Ceramic PCB
Ceramic PCBs are often produced using advanced processes such as:
-
DBC PCB (Direct Bonded Copper)
-
AMB PCB (Active Metal Brazing)
-
Thick film ceramic PCB and thin film ceramic PCB technologies
These ceramic PCB structures allow strong copper bonding, excellent heat transfer, and stable performance under harsh conditions.
Why Ceramic PCB Is Used in High Power and High Reliability Designs
1. High Thermal Conductivity for Efficient Heat Dissipation
One of the biggest advantages of Ceramic PCB is its excellent thermal conductivity, which helps move heat away from power devices quickly and efficiently.
Ceramic PCB thermal performance supports:
-
Lower junction temperature for power semiconductors
-
Improved heat dissipation in compact power modules
-
Increased lifetime and reliability of high power electronics
-
Better stability for high power LED and laser devices
For high power applications, ceramic PCB provides a major thermal management advantage compared to standard FR-4 PCBs.
2. Excellent Electrical Insulation and High Voltage Capability
Ceramic substrates offer strong electrical insulation, which is essential for high voltage and high power circuits.
Ceramic PCB helps support:
-
High breakdown voltage and safe isolation
-
Reliable performance for high voltage power modules
-
Reduced risk of electrical leakage and short circuits
-
Stable operation in harsh industrial environments
This makes ceramic PCB ideal for high voltage PCB and power electronics PCB designs.
3. High Temperature Stability and Long-Term Reliability
Many power electronics and automotive applications operate in high temperature environments. Ceramic PCB materials maintain stable mechanical and electrical properties under extreme conditions.
Ceramic PCB reliability benefits include:
-
Resistance to thermal cycling stress
-
Stable performance at high temperature operation
-
Reduced warpage and dimensional changes
-
Long service life for demanding applications
For automotive and aerospace systems, ceramic PCB offers superior reliability compared to conventional PCB solutions.
Common Ceramic PCB Types
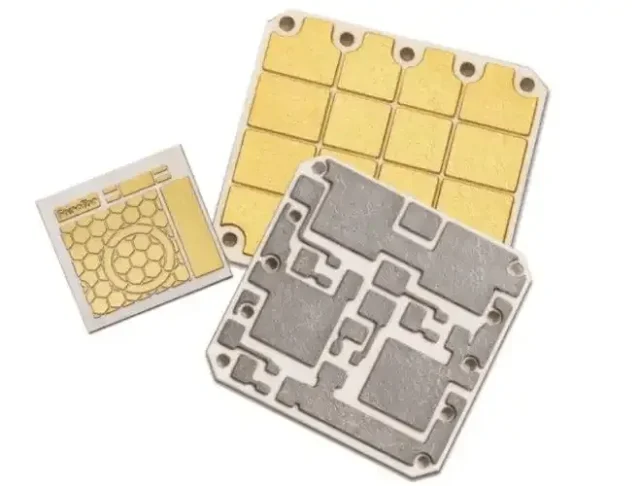

1. Alumina Ceramic PCB (Al₂O₃ PCB)
Alumina ceramic PCB is widely used due to its balanced performance and cost-effectiveness. It provides good insulation, stable mechanical properties, and reliable thermal conductivity for many applications.
Typical uses include LED modules, industrial electronics, and power conversion circuits.
2. Aluminum Nitride Ceramic PCB (AlN PCB)
AlN PCB offers much higher thermal conductivity than alumina, making it ideal for high power density applications where maximum heat dissipation is required.
AlN ceramic PCB is commonly used in advanced power modules, high power lasers, and high reliability aerospace systems.
3. DBC Ceramic PCB
DBC PCB uses direct bonded copper on ceramic substrates, enabling high current carrying capacity and excellent heat dissipation. DBC ceramic PCB is often used in:
-
IGBT modules
-
SiC power modules
-
EV inverters and converters
-
High power motor drives
4. AMB Ceramic PCB
AMB PCB provides strong bonding and high reliability for harsh operating conditions. AMB ceramic PCB is widely used for advanced automotive power modules and industrial power electronics.
Applications of Ceramic PCB
Ceramic PCB is widely used in high power, high voltage, and high reliability industries:
-
Power electronics modules (IGBT, MOSFET, rectifiers)
-
SiC and GaN power devices
-
LED ceramic PCB and high brightness LED modules
-
Automotive electronics (EV power modules, converters, inverters)
-
Aerospace and defense electronics
-
Industrial motor drives and power supplies
-
High temperature sensors and control systems
-
High power RF and microwave modules requiring thermal stability
Ceramic PCB is a key technology for next-generation power electronics and thermal management designs.
Ceramic PCB vs FR-4 PCB vs IMS PCB
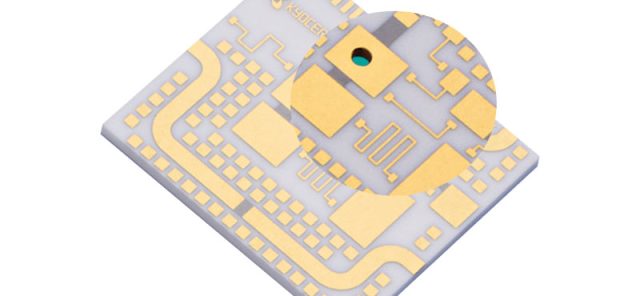
Ceramic PCB vs FR-4
Compared with FR-4, ceramic PCB offers:
-
Much higher thermal conductivity
-
Better high temperature stability
-
Improved electrical insulation
-
Higher reliability in harsh environments
FR-4 is suitable for low to medium power designs, while ceramic PCB is ideal for high power and high reliability applications.
Ceramic PCB vs IMS PCB (Insulated Metal Substrate)
IMS PCB is commonly used for LED applications and provides good heat dissipation through a metal base. However, ceramic PCB often provides:
-
Better electrical insulation
-
Higher temperature stability
-
Improved performance for high voltage and high reliability systems
Ceramic PCB is often selected when advanced thermal management and insulation are both required.
Ceramic PCB Design and Manufacturing Considerations

To ensure high performance and reliability, ceramic PCB manufacturing requires strict process control:
1. Copper Thickness and Current Capacity
Power modules often require thick copper for high current. Ceramic PCB supports heavy copper bonding for improved current carrying capability.
2. Thermal Path and Heat Spreading Design
Designers should optimize pad size, copper distribution, and thermal paths to maximize ceramic PCB heat dissipation.
3. Soldering and Assembly Compatibility
Ceramic PCB assembly may require special considerations due to different thermal expansion characteristics compared with standard PCBs.
4. Quality Control and Reliability Testing
Ceramic PCB applications often demand high reliability testing for thermal cycling, insulation resistance, and long-term stability.
Working with an experienced ceramic PCB manufacturer ensures consistent quality and stable production results.
Conclusion: Ceramic PCB for High Power and High Reliability Electronics
Ceramic PCB is a premium circuit board solution designed for applications requiring high thermal conductivity, strong electrical insulation, and excellent high temperature stability. From LED modules and automotive power electronics to aerospace and advanced SiC/GaN power devices, ceramic PCB enables reliable operation and long service life in demanding environments.
If you are looking for ceramic PCB manufacturing, DBC ceramic PCB fabrication, or high reliability ceramic substrate solutions, KKPCB can provide engineering support, stable production, and professional quality control for your project.

