As semiconductor devices and high-performance modules continue to scale in complexity, the number of required electrical connections has increased dramatically. The High Pin Count PCB is designed to manage hundreds or even thousands of pins while maintaining signal integrity, mechanical reliability, and manufacturability.
A well-designed High Pin Count PCB is critical for advanced computing, communication, and semiconductor test systems.
What Is a High Pin Count PCB?
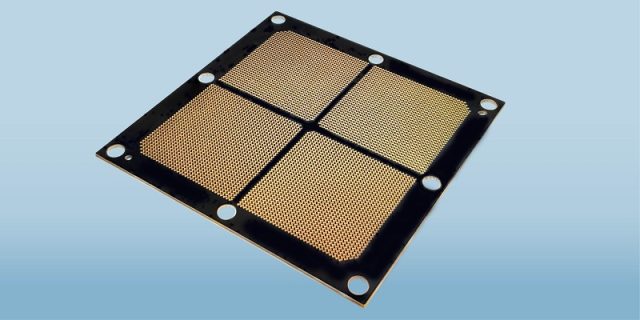
A High Pin Count PCB is a printed circuit board engineered to support devices or connectors with a very large number of electrical pins. These boards are commonly used in:
-
Semiconductor test platforms
-
High-speed computing and networking systems
-
Advanced IC packaging and validation environments
High pin count designs demand exceptional routing density and precision.
Why High Pin Count PCB Design Is Challenging
Increasing pin count introduces multiple design challenges, including:
-
Routing congestion and escape limitations
-
Signal integrity degradation
-
Power distribution complexity
Without careful design, a high pin count PCB can suffer from noise, crosstalk, and manufacturing yield issues.
Advanced Routing and Breakout Strategies
Effective routing is the foundation of a High Pin Count PCB. Key strategies include:
-
Fine-line trace and space technology
-
Microvia and via-in-pad structures
-
Layer-by-layer breakout planning
These techniques maximize routing efficiency while maintaining reliability.
Signal Integrity at High Pin Density
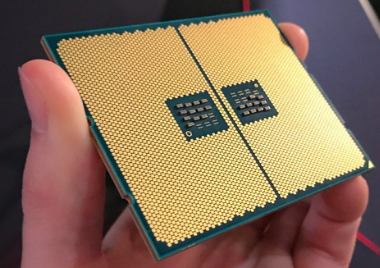
High-speed signals in dense environments are prone to interference. High pin count PCBs address this by:
-
Controlled impedance routing
-
Length matching for timing-critical signals
-
Dedicated reference planes for clean return paths
Maintaining signal integrity is essential for reliable system operation.
Power Integrity and Ground Management
Supplying stable power to a large number of pins requires careful planning. A High Pin Count PCB includes:
-
Multiple power and ground planes
-
Low-inductance decoupling networks
-
Strategic isolation between power domains
Good power integrity minimizes noise and voltage fluctuation.
Mechanical Considerations and Reliability
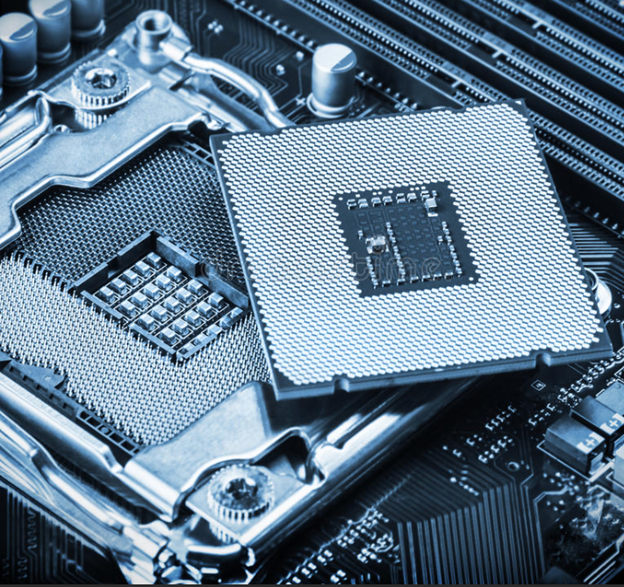
High pin count connectors and packages place significant mechanical stress on PCBs. Reliable designs feature:
-
Reinforced mounting regions
-
Balanced stackups to reduce warpage
-
Tight flatness and coplanarity control
Mechanical stability ensures long-term performance.
Material and Stackup Selection
Material choice impacts both electrical and mechanical behavior. High pin count PCBs often use:
-
High-Tg FR-4 for structural durability
-
Low-loss laminates for high-speed signals
-
Hybrid stackups for mixed-signal applications
Proper stackup design supports density and performance.
Manufacturing Precision and Yield Control

High pin count PCBs demand strict manufacturing control, including:
-
Tight trace width and spacing tolerances
-
Accurate drilling and via plating
-
Consistent layer registration
Precision manufacturing is critical to achieving high yield.
Typical Applications of High Pin Count PCBs
High Pin Count PCBs are commonly used in:
-
ATE and semiconductor test systems
-
High-performance computing platforms
-
Networking and data center equipment
-
Advanced IC validation and prototyping
Each application requires density and reliability.
Choosing a High Pin Count PCB Manufacturing Partner
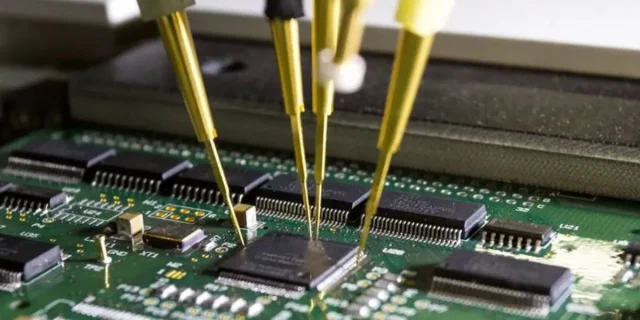
When selecting a High Pin Count PCB manufacturer, consider:
-
Experience with dense and complex PCB designs
-
HDI and fine-line manufacturing capability
-
Controlled impedance and electrical testing support
-
Engineering collaboration throughout development
The right partner ensures manufacturable, reliable designs.
Conclusion
The High Pin Count PCB enables modern electronics by supporting dense interconnections without compromising signal integrity or reliability. Through advanced routing strategies, careful power and signal design, and precise manufacturing, high pin count PCBs meet the demands of today’s most complex systems.
Partnering with an experienced High Pin Count PCB supplier is essential for success in advanced electronics and semiconductor testing.

