Microwave circuits operate at extremely high frequencies where even minor PCB variations can significantly affect performance. When engineers and purchasing teams order microwave PCBs, precision manufacturing, low-loss materials, and strict impedance control are essential to ensure stable and reliable microwave signal transmission.
This article outlines key considerations when ordering microwave PCBs and how professional manufacturers support high-frequency applications.
What Is a Microwave PCB?
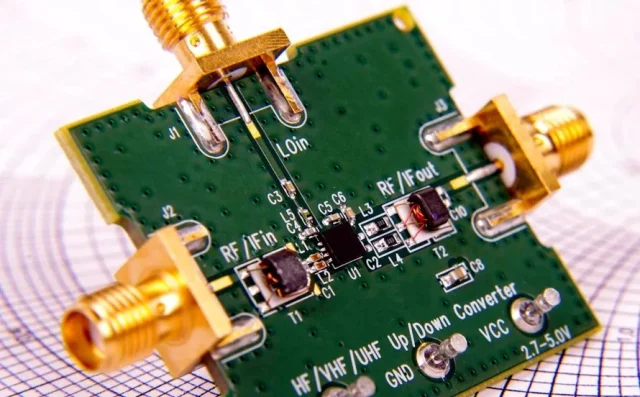
A microwave PCB is specifically designed to support signal transmission in the microwave frequency range, typically above 1 GHz and extending into mmWave bands. Compared with standard PCBs, microwave PCBs require:
-
Ultra-low dielectric loss (low Df)
-
Highly stable dielectric constant (Dk)
-
Tight impedance control
-
Precise fabrication tolerances
These requirements make microwave PCB manufacturing highly specialized.
Material Selection When You Order Microwave PCB
Material choice is critical when you order microwave PCBs. Common microwave PCB materials include:
-
PTFE-based substrates for ultra-low loss applications
-
Rogers laminates (RO3003, RO3006, RO4350)
-
Taconic RF materials such as RF-35 and TLY series
-
Hybrid stackups combining microwave materials with FR-4
These materials provide excellent performance at microwave and millimeter-wave frequencies.
Controlled Impedance for Microwave Circuits

Accurate impedance control is mandatory when you order microwave PCBs.
Professional manufacturers ensure:
-
Stack-up modeling and impedance calculation
-
Tight control of trace width and dielectric thickness
-
Controlled impedance fabrication (±5% or tighter)
-
TDR impedance testing and documentation
This minimizes signal reflection and insertion loss in microwave circuits.
Manufacturing Precision and Process Control
Microwave PCB performance depends heavily on manufacturing quality. Reliable suppliers focus on:
-
High-precision lamination and etching
-
Copper roughness control to reduce conductor loss
-
Clean drilling and via plating processes
-
Strict AOI and electrical testing
These processes ensure consistent quality from prototype to volume production.
Typical Applications for Microwave PCBs

Microwave PCBs are widely used in:
-
Microwave RF front-end modules
-
5G and wireless communication systems
-
mmWave transceivers and antenna arrays
-
Automotive radar systems
-
Satellite and aerospace communication equipment
These applications demand high stability and low loss at microwave frequencies.
How to Choose the Right Supplier When You Order Microwave PCB
When selecting a supplier to order microwave PCBs, consider:
-
Proven experience in microwave PCB manufacturing
-
Support for PTFE, Rogers, and hybrid materials
-
Impedance control and RF testing capability
-
Engineering support and fast DFM feedback
-
Prototype and volume production flexibility
The right manufacturer reduces development risk and ensures long-term reliability.
Conclusion
Ordering microwave PCBs requires careful consideration of materials, impedance control, and manufacturing precision. By working with an experienced manufacturer and selecting the right materials, engineers and buyers can order microwave PCBs that deliver reliable performance in demanding high-frequency and microwave applications.
Choosing the right partner ensures consistent quality, faster development, and scalable production for advanced microwave systems.

