In semiconductor manufacturing, test accuracy directly affects yield, reliability, and time-to-market. Whether during engineering validation or high-volume production, the semiconductor test PCB serves as the critical electrical interface between automated test equipment (ATE) and the device under test (DUT).
A professionally engineered semiconductor test PCB ensures stable measurements, consistent signal behavior, and long-term test reliability across the entire product lifecycle.
What Is a Semiconductor Test PCB?
A semiconductor test PCB is a specialized printed circuit board designed for IC testing rather than end-product operation. It routes power, control, and high-speed signals between the tester and the DUT while maintaining precise electrical characteristics.
Unlike standard PCBs, semiconductor test PCBs must operate flawlessly under:
-
Continuous test cycles
-
High-speed switching
-
Repeated mechanical interaction
-
Strict measurement tolerances
Any deviation can lead to yield loss or incorrect test decisions.
Why Semiconductor Test PCBs Matter in IC Testing
Even with advanced ATE systems, poor test board design can cause:
-
Signal distortion and reflection
-
Unstable contact resistance
-
Noise coupling and ground bounce
-
False failures or test escapes
A high-quality semiconductor test PCB eliminates these risks by delivering consistent electrical and mechanical performance.
Key Electrical Requirements
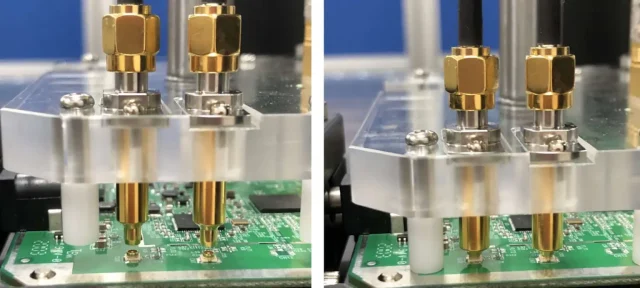
Controlled Impedance and Signal Integrity
Modern ICs operate at high speeds and tight margins. Semiconductor test PCBs require:
-
Controlled impedance routing
-
Optimized stackups with solid reference planes
-
Short, symmetrical signal paths
These features ensure repeatable measurements across all test channels.
Power Integrity and Noise Control
Stable power delivery is essential for accurate testing. Effective designs include:
-
Low-impedance power planes
-
Proper decoupling strategies
-
Well-structured ground systems
Clean power prevents measurement drift and intermittent failures.
Mechanical Reliability in Semiconductor Test PCBs
Semiconductor test PCBs experience frequent mechanical stress from:
-
Socket insertion and removal
-
Probing cycles
-
Thermal expansion
Critical mechanical considerations include PCB flatness, reinforced test areas, and material stability to ensure long-term consistency.
Materials Used in Semiconductor Test PCBs
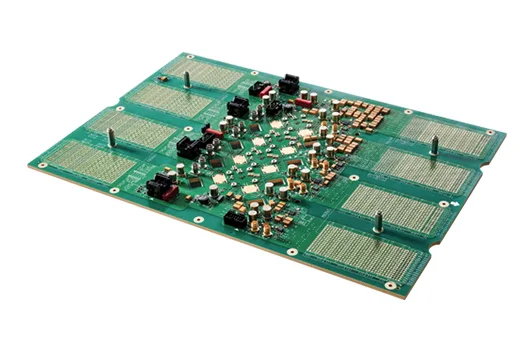
Material selection depends on test requirements and environment:
-
High-Tg FR-4 for durability and cost efficiency
-
Low-loss laminates for high-speed or RF testing
-
Hybrid stackups for mixed-signal test platforms
Stable dielectric properties are essential for repeatable test results.
Manufacturing Consistency Is Critical
Unlike one-time prototype boards, semiconductor test PCBs must deliver identical performance across multiple builds. This requires:
-
Tight control of laminate thickness and Dk
-
Uniform copper distribution
-
Precise drilling and plating
-
Accurate layer registration
Manufacturing repeatability directly impacts test accuracy.
Applications of Semiconductor Test PCBs
Semiconductor test PCBs are widely used in:
-
Wafer-level testing
-
IC package testing
-
Final production testing
-
Automotive and industrial semiconductor validation
Each application places strict demands on reliability and precision.
Choosing the Right Semiconductor Test PCB Partner

An experienced semiconductor test PCB manufacturer should offer:
-
Proven expertise in ATE and test PCB design
-
Controlled impedance capability
-
Advanced quality inspection processes
-
Fast support for test board revisions
The right partner helps reduce debug cycles and improve overall test yield.
Conclusion
A semiconductor test PCB is the foundation of reliable IC testing. By ensuring stable signal integrity, robust mechanical performance, and consistent manufacturing quality, well-designed test PCBs enable accurate measurements, higher yields, and efficient semiconductor production.
Selecting a professional semiconductor test PCB supplier is a strategic decision that directly influences test performance and product success.

