Modern test platforms demand compact form factors, complex interconnections, and stable signal performance. The Rigid-Flex Test PCB addresses these challenges by integrating rigid PCB sections with flexible circuits, creating a single, reliable structure optimized for advanced testing environments.
Rigid-flex test PCBs are increasingly essential in semiconductor testing, ATE systems, and high-density validation platforms.
What Is a Rigid-Flex Test PCB?
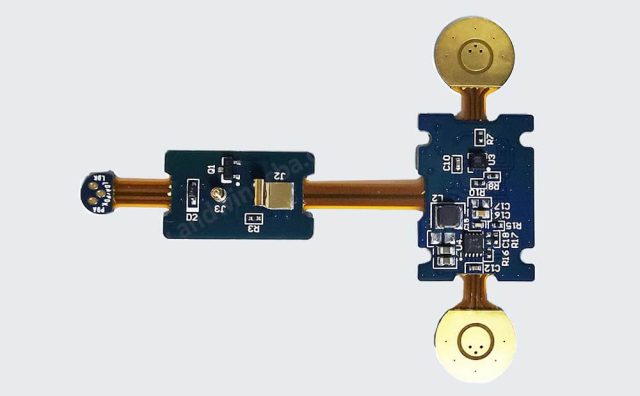
A Rigid-Flex Test PCB is a hybrid circuit board that combines rigid multilayer sections with flexible interconnect layers. This structure eliminates traditional connectors and cables, improving both electrical integrity and mechanical reliability in test applications.
Why Rigid-Flex Test PCBs Are Used in Testing Systems
Test environments place unique demands on PCB structures. Rigid-flex test PCBs enable:
-
Compact system layouts in space-constrained test fixtures
-
Reduced interconnect failures compared to cable-based designs
-
Improved vibration and shock resistance
These benefits are critical for long-term test stability.
Signal Integrity Advantages of Rigid-Flex Test PCBs
High-speed and high-frequency testing requires clean signal transmission. Rigid-flex test PCBs help maintain signal integrity by:
-
Reducing signal discontinuities
-
Shortening interconnect paths
-
Supporting controlled impedance routing across rigid and flex regions
This results in more accurate and repeatable test measurements.
Mechanical Flexibility and Structural Stability
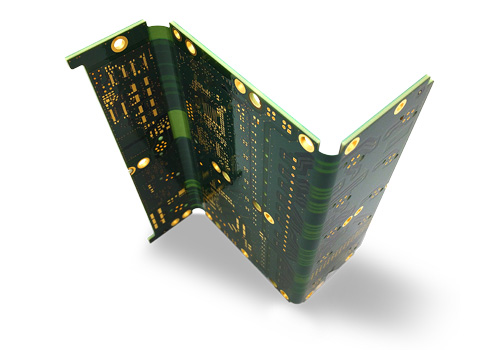
Rigid-flex test PCBs are designed to withstand:
-
Repeated bending during installation and maintenance
-
Thermal cycling in test environments
-
Mechanical stress from sockets and fixtures
Proper flex material selection and bend-radius control ensure durability.
Stackup and Material Considerations
Designing a rigid-flex test PCB requires careful planning of:
-
Layer transitions between rigid and flex areas
-
Dielectric materials for low-loss and stability
-
Reinforcement and stiffener placement
Optimized stackups improve yield and reliability.
Manufacturing Challenges and Process Control
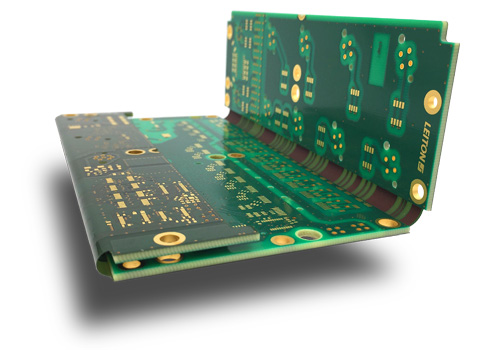
Rigid-flex test PCB manufacturing involves:
-
Precise layer alignment and lamination
-
Tight dimensional tolerance control
-
Electrical and impedance testing across flex transitions
Experienced manufacturing capability is essential for consistent quality.
Typical Applications of Rigid-Flex Test PCBs
Rigid-flex test PCBs are widely used in:
-
ATE systems with complex mechanical constraints
-
Semiconductor test fixtures and interface boards
-
High-density probe and socket assemblies
-
Modular and portable test equipment
These applications benefit from reduced complexity and improved reliability.
Choosing a Rigid-Flex Test PCB Manufacturer
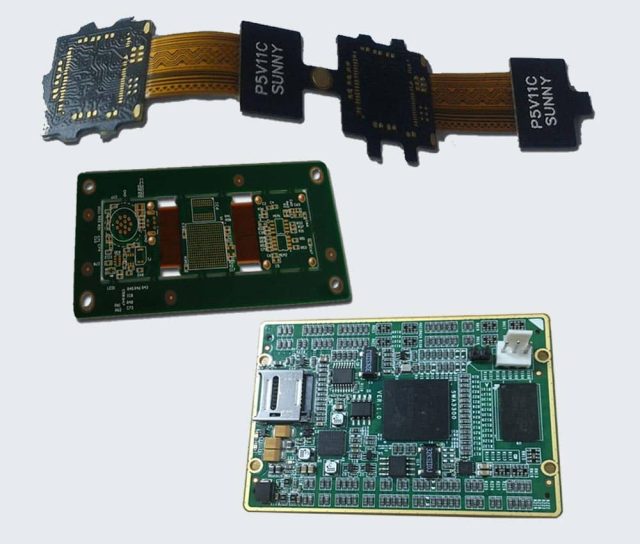
When selecting a rigid-flex test PCB supplier, consider:
-
Proven experience with test and semiconductor PCBs
-
Advanced rigid-flex fabrication capability
-
Controlled impedance and multilayer expertise
-
Support for prototype, small batch, and production
A qualified partner ensures smooth execution and scalability.
Conclusion
The Rigid-Flex Test PCB offers a powerful solution for advanced test systems requiring compact design, mechanical flexibility, and stable electrical performance. By eliminating interconnect weaknesses and supporting high-speed signals, rigid-flex test PCBs enhance reliability and test accuracy.
Partnering with an experienced rigid-flex test PCB manufacturer ensures dependable performance from engineering validation through production deployment.

