A Rigid-Flex Test PCB combines rigid PCB sections with flexible circuits to create compact, reliable, and high-performance test boards for automated test equipment (ATE) and semiconductor testing systems. As test environments become more complex and space-constrained, rigid-flex test PCBs provide an effective solution by reducing connectors, improving signal integrity, and enhancing mechanical reliability.
Rigid-flex test PCBs are widely used where traditional rigid PCBs cannot meet layout flexibility, durability, or integration requirements.
What Is a Rigid-Flex Test PCB?
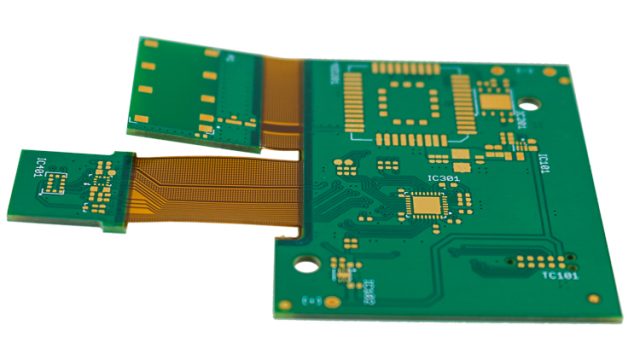
A Rigid-Flex Test PCB is a hybrid circuit board that integrates rigid PCB layers with flexible polyimide-based circuits. In test applications, rigid sections typically support connectors, sockets, and components, while flexible sections enable folding, bending, or compact 3D assembly within test fixtures or ATE systems.
This structure allows rigid-flex test PCBs to maintain electrical performance while adapting to complex mechanical constraints.
Why Use Rigid-Flex PCBs in Test Applications
Space-Saving and Compact Design
Rigid-flex test PCBs enable tighter integration and reduced board size, which is critical in high-density ATE and test environments.
Improved Signal Integrity
Eliminating board-to-board connectors reduces signal discontinuities, reflection, and insertion loss, improving high-speed test accuracy.
Higher Mechanical Reliability
Flexible interconnections are more resistant to vibration and repeated movement compared to traditional connectors and cables.
Simplified Assembly
Rigid-flex designs reduce the number of separate boards and connectors, simplifying assembly and improving overall system reliability.
Key Technical Requirements for Rigid-Flex Test PCBs
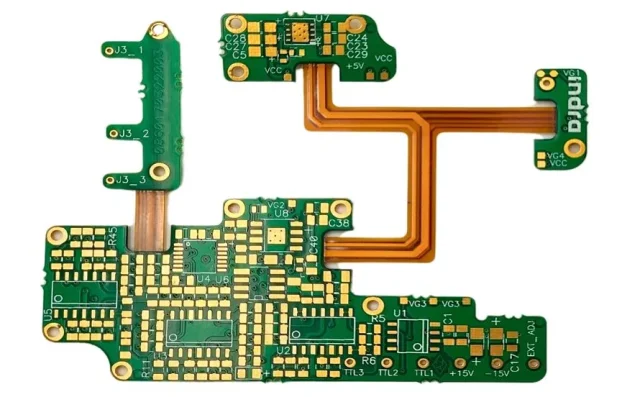
Controlled Impedance
Rigid-flex test PCBs must maintain consistent impedance across rigid and flex sections to support high-speed and RF test signals.
High Speed Signal Integrity
Optimized stack-ups, reference planes, and via transitions are essential to minimize loss and crosstalk.
Mechanical Durability
Flex sections must withstand repeated bending and mechanical stress without cracking or delamination.
Precise Layer Registration
Accurate alignment between rigid and flex layers is critical for reliable routing and connectivity.
Materials Used in Rigid-Flex Test PCB Manufacturing
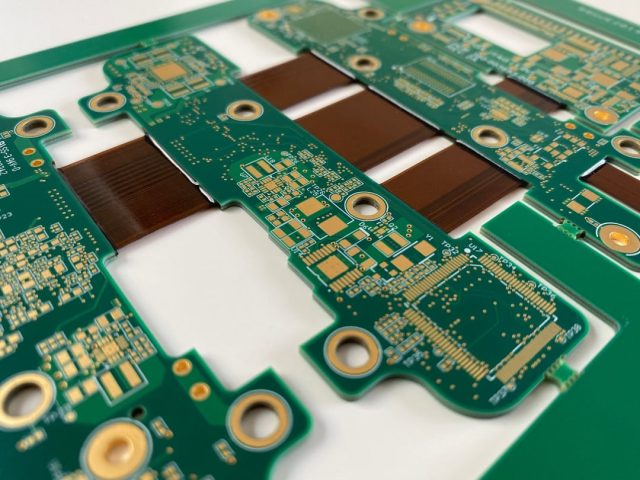
Rigid-flex test PCBs use specialized materials to ensure electrical and mechanical stability:
-
High-Tg FR-4 for rigid sections
-
Polyimide materials for flexible circuits
-
Low-loss laminates for high-speed test signals
-
Adhesiveless flex materials for improved reliability
-
Hybrid stack-ups combining RF and digital layers
Material selection is tailored to test frequency, bending requirements, and operating conditions.
Manufacturing Capabilities for Rigid-Flex Test PCBs
Professional rigid-flex test PCB manufacturing includes:
-
Multilayer rigid-flex lamination
-
Controlled impedance fabrication and testing
-
HDI, blind via, and buried via technology
-
Precision drilling and laser via processing
-
Tight tolerance thickness and registration control
These capabilities ensure consistent performance and long-term reliability.
Rigid-Flex Test PCB Assembly
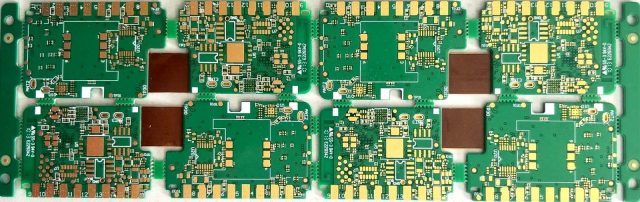
Assembly of rigid-flex test PCBs requires specialized processes:
-
Controlled handling of flexible sections
-
Fine-pitch and high pin count component assembly
-
Precision connector and socket installation
-
AOI and X-ray inspection
-
Functional and electrical testing
Proper assembly ensures mechanical integrity and preserves signal performance.
Applications of Rigid-Flex Test PCBs
Rigid-flex test PCBs are commonly used in:
-
ATE load boards and interface boards
-
Semiconductor wafer sort and final test systems
-
High speed logic and memory testing
-
RF and mixed-signal test fixtures
-
Automotive and industrial reliability testing
In these applications, rigid-flex designs improve test stability and reduce system complexity.
Prototype and Small Batch Rigid-Flex Test PCBs
Rigid-flex test PCBs are often produced in prototype or small batch quantities to validate mechanical fit, signal integrity, and system integration. Once approved, designs can be scaled to higher volumes with consistent materials and manufacturing processes.
Working with an experienced rigid-flex test PCB supplier helps reduce design risk and accelerates development cycles.
Conclusion
A Rigid-Flex Test PCB offers a powerful solution for modern ATE and semiconductor testing environments that demand compact design, high reliability, and excellent signal integrity. By combining advanced materials, controlled impedance design, and precision manufacturing, rigid-flex test PCBs deliver stable and repeatable test performance.
Choosing a capable rigid-flex test PCB manufacturer is essential for supporting complex test requirements and long-term system reliability.

