Modern semiconductor testing demands PCBs that combine flexibility, high-density routing, and mechanical reliability. Rigid-Flex Test PCBs provide an ideal solution by integrating rigid and flexible layers into a single board, enabling compact designs, reliable probe alignment, and stable electrical performance in automated test equipment (ATE) applications.
These PCBs support high-speed signal transmission, controlled impedance, and repeated mechanical flexing, making them essential for advanced IC testing and semiconductor validation.
What Is a Rigid-Flex Test PCB?
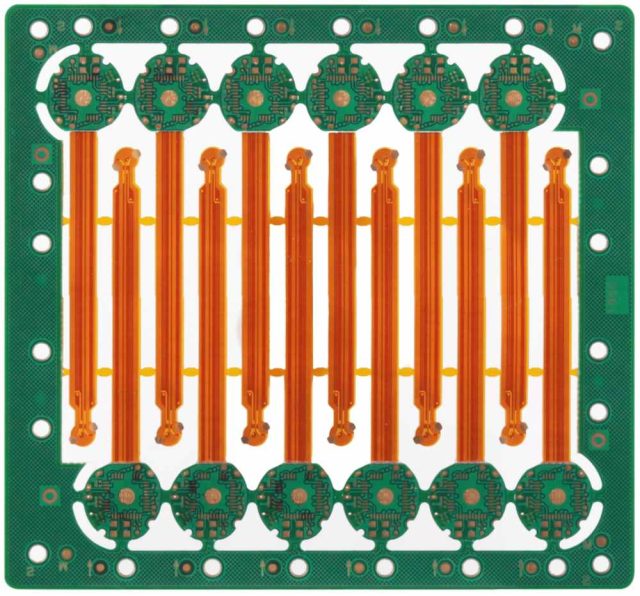
A Rigid-Flex Test PCB combines rigid sections for component mounting and flexible sections to accommodate mechanical movement, board stacking, or unusual form factors. This structure allows engineers to:
-
Optimize space in high-density test fixtures
-
Maintain signal integrity across moving or folded sections
-
Integrate high pin count IC interfaces with robust mechanical support
By providing both flexibility and rigidity, these PCBs improve reliability and reduce mechanical stress in demanding testing environments.
Key Features of Rigid-Flex Test PCBs

-
Hybrid Structure – Rigid layers provide stability for components, while flexible layers enable compact routing and mechanical adaptability.
-
Controlled Impedance – Essential for high-speed digital, RF, and mixed-signal testing to minimize signal reflection and loss.
-
High Pin Count Support – Handles dense interconnects for advanced ICs and ATE probe cards.
-
Mechanical Reliability – Flexible areas absorb stress and reduce fracture risks during repeated test cycles.
-
Compact Design – Enables folding or stacking in constrained test fixture spaces without compromising electrical performance.
Material and Stackup Considerations
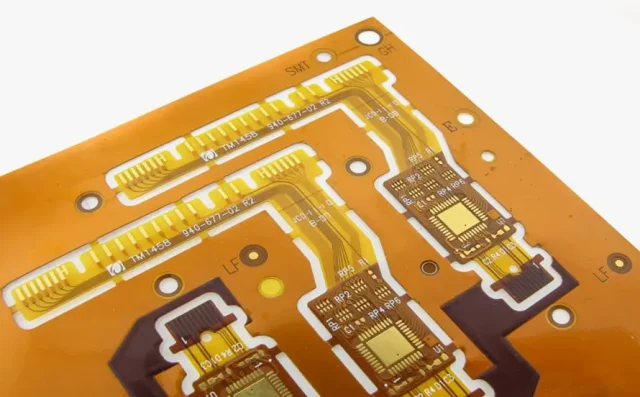
Choosing the right materials is critical for Rigid-Flex Test PCB performance:
-
Flexible Polyimide Layers – Allow repeated bending and mechanical resilience.
-
High-Tg FR-4 Rigid Layers – Provide stable mounting for components and connectors.
-
Hybrid Stackups – Ensure controlled impedance, low loss, and mechanical durability across rigid and flexible sections.
Proper stackup design ensures reliable high-speed signal integrity and long-term mechanical performance.
Applications of Rigid-Flex Test PCBs

Rigid-Flex Test PCBs are widely applied in:
-
High-speed semiconductor IC validation and characterization
-
Wafer-level test boards and probe card integration
-
ATE interface boards requiring compact form factors
-
High-frequency, high-pin-count, and mixed-signal testing
Their ability to combine rigidity and flexibility makes them ideal for modern automated test environments.
Choosing a Rigid-Flex Test PCB Manufacturer

When selecting a Rigid-Flex Test PCB supplier, consider:
-
Experience with high pin count, high-speed, and multilayer rigid-flex designs
-
Capability to provide controlled impedance and low-loss routing
-
Support for rapid prototyping, small batch, and volume production
-
Strict quality control, electrical testing, and mechanical verification
A professional partner ensures reliable, repeatable performance in both prototype and production testing.
Conclusion
Rigid-Flex Test PCBs offer unmatched versatility and reliability for advanced semiconductor and high-speed electronic testing. By combining rigid and flexible sections, these PCBs enable high pin count support, controlled impedance, compact designs, and mechanical durability.
Partnering with an experienced Rigid-Flex Test PCB manufacturer ensures precise electrical performance, high-quality assembly, and long-term reliability for demanding test environments.

