In the accelerating era of Industry 4.0 and intelligent manufacturing, the Industrial Automation PCB has become the fundamental hardware platform enabling stable operation of automated production lines, robotic motion systems, IIoT equipment, and mission-critical industrial controllers. A high-quality Industrial Automation PCB determines whether robotic actuators synchronize accurately, whether PLC modules communicate without latency, and whether sensors deliver real-time, error-free feedback.
Unlike consumer electronics, the Industrial Automation PCB must withstand extreme temperatures, vibration, electromagnetic noise, high transient loads, and continuous 24/7 industrial operation. This requires advanced materials, reinforced stackups, robust power networks, and precision-engineered signal integrity strategies.
1. Core Engineering Functions of the Industrial Automation PCB
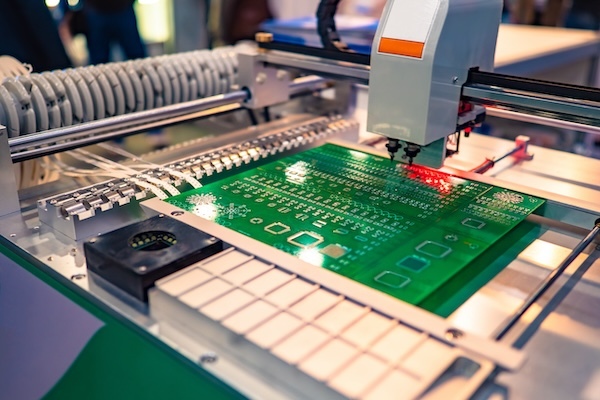

The Industrial Automation PCB serves as the operational backbone for:
-
Programmable logic controllers (PLC PCB)
-
Industrial PCs and edge-computing platforms
-
Motor controllers and servo drive modules
-
IIoT monitoring devices and gateway units
-
Machine vision and AI inspection systems
-
Predictive-maintenance and sensor acquisition boards
Every intelligent factory component depends on the precision, stability, and durability of the Industrial Automation PCB.
2. High-Reliability Engineering Requirements for Industrial Automation PCB
Industrial-Grade Durability and Long-Life Operation
A true Industrial Automation PCB requires:
-
High-Tg PCB materials capable of wide-temperature endurance
-
2–3 oz copper layers for sustained high-current distribution
-
Reinforced mechanical structure for vibration resistance
-
Corrosion-resistant finishes (ENIG, ENEPIG, OSP)
-
Conformal coating against dust, oil, moisture, and chemicals
Factories run continuously; therefore, the Industrial Automation PCB must maintain reliability under years of mechanical and thermal stress.
Precision Power Distribution and Transient Protection
Power integrity is central to any Industrial Automation PCB, especially those driving motors, actuators, solenoid valves, and real-time processors. Engineering requirements include:
-
Wide copper planes to minimize IR drop
-
Multi-stage decoupling networks for transient suppression
-
Galvanic isolation between high-current and logic domains
-
Thermal via arrays for heat extraction
-
Surge, ESD, EFT, and lightning-transient protection circuits
Stable power delivery ensures predictable system behavior and safety compliance.
Real-Time Control Processing and Deterministic Timing
Robotics, conveyors, packaging equipment, and machine tools rely on Industrial Automation PCB platforms that support:
-
Real-time MCU/MPU architectures
-
FPGA-based deterministic timing logic
-
High-frequency PWM motor-control switching
-
Low-latency encoder/feedback signal processing
-
Redundancy-ready hardware watchdog systems
The integrity of control signals on the Industrial Automation PCB directly influences industrial precision.
3. High-Speed Industrial Communication on the PCB

Modern factories demand seamless, deterministic communication. The Industrial Automation PCB integrates:
-
EtherCAT high-speed differential pairs
-
PROFINET and Industrial Ethernet
-
CAN / CAN-FD networks for robotic systems
-
RS-485/Modbus for legacy equipment
-
Wireless IIoT modules for distributed monitoring
Achieving error-free communication requires impedance-controlled routing, SI/PI engineering, ground isolation, and EMI-optimized layout.
4. Sensor Integration and High-Resolution Signal Acquisition
An advanced Industrial Automation PCB must support a wide variety of sensors:
-
Encoder and resolver feedback
-
Temperature, pressure, and flow sensors
-
Machine vision modules and optical detectors
-
Vibration and predictive-maintenance sensors
-
Force, torque, and robotic joint sensors
This requires:
-
Low-noise analog routing
-
Shielded differential sensor inputs
-
Hardware filtering networks
-
High-resolution ADC front-end circuits
Sensor accuracy determines the overall precision of the manufacturing system.
5. EMI/EMC Engineering for Harsh Industrial Environments
The industrial environment is electrically noisy—motors, welders, high-current drivers, and switching power supplies introduce aggressive interference. Therefore, an Industrial Automation PCB must incorporate:
-
Ground-plane segmentation with stitching vias
-
Shielded high-speed traces
-
LC/RC filtering at every sensor and power input
-
Optimized stackup for EMI/EMC compliance
-
Separation of digital, analog, and power domains
Strong EMI/EMC design ensures consistent performance and full regulatory compliance.
6. Multilayer Stackup Optimization for Industrial Automation PCB
A typical Industrial Automation PCB ranges from 4 to 12 layers, with stackup engineered to balance:
-
High-current power planes
-
Isolated analog sensing layers
-
High-speed communication channels
-
Controlled-impedance differential pairs
-
Thermal and mechanical reinforcement layers
The stackup architecture is a decisive factor in the durability and reliability of any Industrial Automation PCB deployed in automated systems.
7. KKPCB Case Study — 12-Layer Industrial Automation PCB

KKPCB recently manufactured a 12-layer Industrial Automation PCB for an advanced automation company requiring:
-
EtherCAT communication layers
-
High-current copper distribution for servo motors
-
FPGA-based real-time logic
-
Multi-frequency isolated ground domains
-
Precision high-speed differential routing
-
Extended burn-in and thermal cycling tests
The result:
Higher uptime, improved cycle precision, and 28% reduction in field maintenance events.
Engineering Summary
The Industrial Automation PCB is the structural and electrical foundation of modern intelligent manufacturing. Its performance determines:
-
Real-time control accuracy
-
Sensor data integrity
-
Industrial communication stability
-
Predictive maintenance reliability
-
Factory automation efficiency
-
Long-term operational uptime
As global manufacturing evolves toward connected, autonomous production ecosystems, the engineering quality of the Industrial Automation PCB will define factory competitiveness and overall system intelligence.
KKPCB delivers fully engineered, high-reliability Industrial Automation PCB solutions with advanced fabrication, comprehensive PCBA, and long-term industrial lifecycle support.

