What Is a PCV Valve?
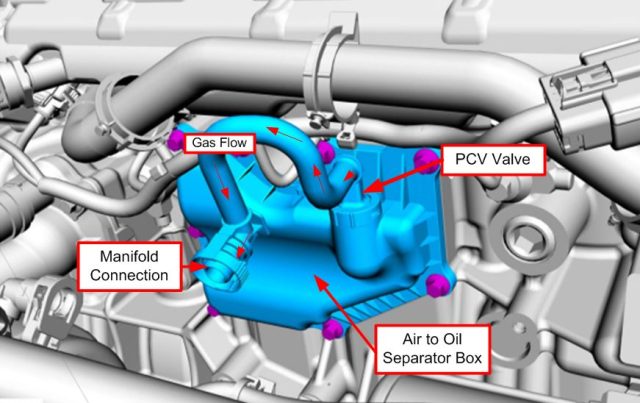
The acronym PCV stands for Positive Crankcase Ventilation. The PCV valve is a one-way valve that forms part of your vehicle’s PCV system — an integral component in the management of gases produced during engine operation.
In simple terms, the PCV valve is responsible for ventilating the crankcase, a part of the engine that contains the motor oil and is located at the bottom of the engine. As the engine burns fuel, gases are produced due to blow-by — a process in which fuel, oil, and exhaust vapors leak past the piston rings. These gases, known as blow-by gases, would otherwise build up inside the crankcase, potentially leading to engine damage and increased emissions.
The PCV valve removes these unwanted gases, directing them back into the intake system where they are re-burned during the combustion process. This process significantly reduces harmful emissions and improves the overall efficiency of the engine.
How Does the PCV Valve Benefit Your Engine?
The PCV valve plays an essential role in keeping your engine’s performance at its best. The primary functions of the PCV valve include:
-
Emission Control: By re-routing blow-by gases back into the combustion chamber, the PCV system helps reduce harmful emissions. This was one of the key reasons why the PCV system was introduced in the early 1960s as part of global efforts to reduce automotive pollution.
-
Oil Life Extension: The PCV valve helps reduce the formation of sludge inside the engine. Without it, blow-by gases could condense in the crankcase, forming deposits that can degrade the quality of engine oil. By venting these gases, the PCV valve helps ensure oil longevity and keeps the engine running cleaner for longer periods.
-
Preventing Engine Build-Up: Blow-by gases are corrosive and can leave behind residues that, if not ventilated, may lead to the build-up of sludge or varnish on engine components. The PCV valve prevents this by venting these gases, helping to maintain engine cleanliness and avoid internal damage.
-
Enhancing Engine Performance: By maintaining proper pressure and reducing the risk of contaminants in the engine, the PCV valve helps ensure smooth operation and efficient combustion. This leads to better fuel efficiency, improved engine power, and extended engine life.

What Happens if the PCV Valve Fails?
The PCV valve, like any engine component, can eventually fail over time due to the buildup of contaminants, sludge, or general wear and tear. When this happens, several signs may indicate that your PCV valve needs attention:
-
Oil Leaks: A clogged or malfunctioning PCV valve can cause excessive pressure buildup in the crankcase, leading to oil leaks around seals and gaskets.
-
Engine Misfires or Rough Idle: If the PCV valve is blocked or not functioning correctly, it may result in improper air-fuel mixture, causing the engine to misfire or idle roughly.
-
Increased Oil Consumption: A defective PCV valve may cause the engine to burn more oil than usual, leading to higher consumption and potential engine damage.
-
Whistling or Hissing Sounds: If you hear strange sounds coming from the engine bay, it could indicate that the PCV valve is clogged or damaged.
-
Emissions Problems: A malfunctioning PCV valve may result in increased emissions, potentially causing your vehicle to fail an emissions test.
How to Ensure Your PCV Valve Is Functioning Properly
Unlike parts such as your car battery or oil filter, there is no set time for when to replace the PCV valve, but it’s crucial to keep an eye out for the symptoms of a faulty valve. Regular maintenance and inspection can help prevent significant engine issues down the line.
Here’s how to ensure your PCV valve is functioning as it should:
-
Inspect for Common Signs of Failure: If you notice any of the symptoms mentioned above — such as oil leaks, rough idle, or increased oil consumption — it may be time to inspect the PCV valve.
-
Regularly Check the Valve: While the PCV valve doesn’t need to be replaced at fixed intervals, checking it during your vehicle’s routine maintenance or oil change can help identify issues early.
-
Replace the PCV Valve When Needed: A clogged or damaged PCV valve can cause a range of engine issues. Fortunately, replacing it is usually a straightforward process that most car owners can handle with minimal tools.
-
Locate the PCV valve: The PCV valve is often located on the valve cover or near the intake manifold. It is typically attached by a hose that directs gases back into the intake system.
-
Remove the Old Valve: Disconnect the hose and twist the valve counterclockwise to remove it. Check the hose, clamps, and grommet for any signs of wear or damage.
-
Install the New Valve: Install the new PCV valve and reattach the hose. Ensure everything is secure before starting the engine.
-
While replacing the PCV valve can often be done as a DIY project, if you’re unsure, it’s always wise to consult with a professional mechanic to ensure the replacement is done correctly.
Summary: Why the PCV Valve Is Essential for Your Car
The PCV valve is a crucial component in your vehicle’s Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) system, responsible for rerouting blow-by gases from the crankcase to the intake system, where they are re-burned in the combustion process. This process reduces harmful emissions, extends oil life, and keeps your engine clean and running efficiently.
While the PCV valve doesn’t need to be replaced on a regular schedule, it’s essential to ensure its proper functionality. Signs of failure — such as oil leaks, rough idle, or increased oil consumption — should prompt immediate attention. Replacing a faulty PCV valve is a relatively simple process and can be done as part of regular engine maintenance.
By understanding and maintaining your PCV valve, you can help ensure that your engine remains in top condition, reduce harmful emissions, and prolong the overall life of your vehicle.

