What Is an RF Test PCB?
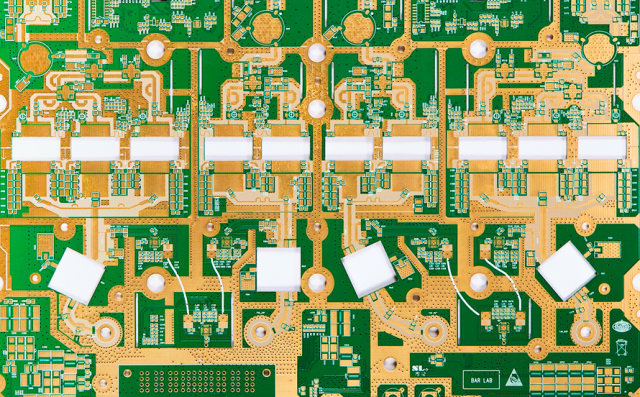
An RF Test PCB is a specialized printed circuit board used to test, validate, and characterize RF and microwave circuits under controlled conditions. RF Test PCBs are widely used to measure critical RF parameters such as insertion loss, return loss, impedance matching, phase stability, and signal integrity.
Unlike standard PCBs, an RF Test PCB is designed with strict impedance control, low-loss materials, and optimized RF layouts to ensure that test results are accurate, repeatable, and representative of real-world performance.
Key Design Requirements for RF Test PCB
Proper RF Test PCB design is essential for reliable RF measurements. Key design requirements include:
-
Controlled impedance transmission lines
RF Test PCBs typically require precise 50Ω or 75Ω impedance control. -
Optimized RF trace routing
Short, straight traces reduce signal attenuation and reflection. -
Via transition optimization
Minimized via stubs and properly placed ground vias improve RF continuity. -
Accurate connector launch design
SMA, SMP, 2.92 mm, or other RF connectors must be precisely matched. -
Effective grounding and shielding
Solid ground planes and via stitching reduce EMI and noise.
These design practices ensure consistent performance across RF Test PCB platforms.
Materials Used in RF Test PCB

Material selection directly impacts RF Test PCB performance. Common RF Test PCB materials include:
-
Rogers laminates (RO4350B, RO4003C, RT/duroid series)
Widely used for RF Test PCBs due to low dielectric loss and stable Dk. -
Taconic PCB materials
Offer excellent RF stability and low loss for microwave testing. -
PTFE-based materials
Ideal for high-frequency and millimeter-wave RF Test PCBs. -
High-performance FR-4 (limited use)
Suitable for lower-frequency RF testing applications.
Low Df and stable Dk are critical for accurate RF Test PCB measurements.
RF Test PCB Manufacturing Considerations

Manufacturing an RF Test PCB requires tighter control than standard PCB production:
-
Tight impedance tolerance control (typically ±5% or better)
-
High-precision etching for fine RF traces
-
Smooth copper surface treatments to reduce conductor loss
-
Accurate layer registration in multilayer RF Test PCBs
-
Strict electrical and impedance testing
An experienced RF Test PCB manufacturer is essential to achieve stable and repeatable test performance.
Advantages of Using RF Test PCB
Using a dedicated RF Test PCB provides several advantages:
-
High measurement accuracy and repeatability
-
Reduced signal reflection and RF loss
-
Improved RF signal integrity
-
Reliable evaluation of RF components and modules
-
Greater confidence in product validation
A well-designed RF Test PCB minimizes external variables during RF testing.
Applications of RF Test PCB
RF Test PCBs are widely used in:
-
RF module and antenna testing
-
5G and wireless communication systems
-
Microwave and millimeter-wave circuit validation
-
Automotive radar and ADAS testing
-
Aerospace and defense RF systems
-
Automated test equipment (ATE)
As operating frequencies increase, RF Test PCBs become increasingly critical.
RF Test PCB vs. Standard PCB

Compared to standard PCBs, RF Test PCBs feature:
-
Tighter impedance control
-
Lower dielectric loss materials
-
Optimized RF layout and grounding
-
Higher manufacturing precision
These differences make RF Test PCBs essential for accurate RF and microwave testing.
Conclusion
An RF Test PCB is a critical tool for achieving accurate, repeatable, and reliable RF measurements. From material selection and impedance control to precision manufacturing, every detail directly impacts test accuracy.
Choosing an experienced RF Test PCB supplier ensures consistent performance, reduced measurement uncertainty, and dependable validation for advanced RF applications.

