With the rapid growth of 5G communications, automotive radar, satellite systems, and high-speed data transmission, modern electronic designs are increasingly operating at higher frequencies. At these frequencies, traditional PCB materials may lead to signal loss, impedance instability, and reduced overall system performance.
That’s why high frequency laminates are widely used in RF and microwave circuit boards. They provide stable dielectric properties, low signal loss, and improved reliability for demanding high-frequency applications.
In this article, we’ll explain what high frequency laminates are, their main advantages, typical applications, and how to choose the right material for your PCB project.
What Are High Frequency Laminates?

High frequency laminates are specialized PCB substrate materials designed for circuits operating in RF (radio frequency) and microwave ranges. Compared with standard FR4, these laminates offer:
-
Lower dielectric loss (Df)
-
More stable dielectric constant (Dk)
-
Better thermal and mechanical stability
-
Improved signal integrity for high-speed and high-frequency designs
They are commonly used for RF PCBs, antenna boards, microwave modules, and other precision circuits where electrical performance must remain stable across temperature and frequency variations.
Why High Frequency Laminates Matter in RF PCB Design
As frequency increases, PCB performance becomes more sensitive to material properties. Even small changes in dielectric constant or loss can significantly impact:
-
Insertion loss
-
Phase delay
-
Impedance matching
-
Crosstalk and noise
-
Overall RF efficiency
High frequency laminates help designers maintain stable performance, especially in critical applications such as 5G base stations and radar systems.
Key Benefits of High Frequency Laminates
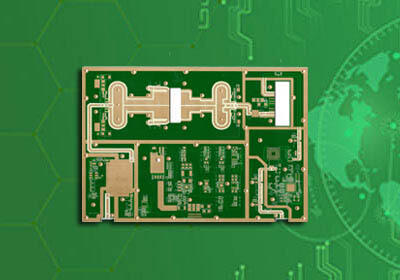
1. Low Dielectric Loss (Low Df)
One of the biggest advantages is low dissipation factor (Df), which means less energy is lost as heat during signal transmission.
Benefits include:
-
Lower insertion loss
-
Better signal strength over longer distances
-
Higher efficiency for antennas and RF modules
This is essential for high-frequency circuits where performance can degrade quickly due to material loss.
2. Stable Dielectric Constant (Dk)
High frequency laminates provide a more consistent dielectric constant (Dk) across different frequencies and temperatures.
Why it matters:
-
More accurate impedance control
-
Stable phase and timing performance
-
Improved repeatability in mass production
For RF transmission lines and controlled impedance structures, Dk stability is critical.
3. Improved Signal Integrity
High frequency laminates help reduce common issues in RF PCB design such as:
-
Signal distortion
-
Reflection and mismatch
-
Crosstalk
-
Unstable impedance
As a result, they are widely used for high-speed and RF designs where signal integrity directly affects product performance.
4. Better Thermal Stability and Reliability
Many high frequency laminates are designed to withstand harsh operating conditions. They offer strong performance in environments involving:
-
Temperature cycling
-
High-power RF operation
-
Outdoor installations
-
Automotive-grade requirements
This improves long-term reliability and reduces failure risks in high-demand applications.
Common Types of High Frequency Laminates
High frequency laminate materials vary depending on performance requirements and cost considerations. Common categories include:
PTFE-Based Laminates
PTFE materials are well-known for excellent RF performance, including very low loss. They are commonly used in:
-
Microwave circuits
-
High-end antennas
-
Satellite communication boards
Hydrocarbon/Ceramic Laminates
These materials provide a good balance between RF performance and process compatibility. They are often used in:
-
5G and telecom equipment
-
Automotive radar modules
-
RF front-end circuits
High-Speed Digital Laminates
Some high frequency laminates are optimized for high-speed digital applications such as:
-
Data centers
-
Network equipment
-
High-speed interconnects
They support low loss and controlled impedance for high-speed signals.
Typical Applications of High Frequency Laminates
High frequency laminates are widely used across multiple industries:
5G Communication Equipment
In 5G systems, high frequency laminates are used in:
-
Base station RF modules
-
Antenna arrays
-
Power amplifiers and filters
They help achieve low loss and stable performance in high-frequency bands.
Antenna and RF Modules
High frequency laminates are ideal for:
-
Wi-Fi antennas
-
GPS antennas
-
IoT communication modules
-
RF front-end boards
Stable dielectric properties improve antenna efficiency and consistency.
Automotive Radar Systems
Automotive radar requires highly reliable RF performance under harsh conditions. High frequency laminates are widely used in:
-
24GHz and 77GHz radar modules
-
ADAS sensor systems
-
Vehicle communication systems
Satellite and Aerospace Electronics
High frequency laminates are also common in:
-
Satellite communication equipment
-
Aerospace radar systems
-
High-reliability microwave modules
They provide stable performance in extreme environments.
High Frequency Laminates vs FR4: What’s the Difference?
FR4 is widely used for general electronics, but it may not meet performance requirements at high frequencies.
| Feature | Standard FR4 | High Frequency Laminates |
|---|---|---|
| Dielectric Loss (Df) | Higher | Lower |
| Dk Stability | Less stable | More stable |
| RF Performance | Limited | Excellent |
| Impedance Control | Harder | More reliable |
| Typical Use | General PCBs | RF/Microwave/5G |
In summary:
If your design operates at high frequencies and requires stable signal performance, high frequency laminates are a better choice than standard FR4.
PCB Manufacturing Considerations for High Frequency Laminates
Producing RF PCBs with high frequency laminates requires specialized control in manufacturing processes, including:
-
Material handling and storage
-
Controlled impedance design and testing
-
Precise etching for fine RF traces
-
Accurate lamination process control
-
Warpage management for thin boards
-
Surface finish selection (ENIG, immersion silver, etc.)
A manufacturer with RF experience can help improve yield and ensure consistent performance.
How to Choose the Right High Frequency Laminate
When selecting high frequency laminates, it’s recommended to evaluate:
-
Operating frequency range
-
Dk and Df requirements
-
Thermal stability and Tg
-
Board thickness and stack-up design
-
Cost and availability
-
Manufacturing compatibility
For high-power or ultra-high-frequency applications, selecting the right laminate is critical to achieving stable RF performance.
Conclusion
High frequency laminates are essential materials for modern RF and microwave PCB designs. With advantages such as low loss, stable Dk, strong signal integrity, and improved reliability, they enable high-performance applications in 5G, antennas, radar, satellite, and high-speed communication systems.
If you are developing an RF PCB or microwave circuit board and need stable performance, high frequency laminates are the ideal material choice.

