Automated Test Equipment (ATE) relies on meticulously assembled PCBs to deliver precise electrical performance during semiconductor testing. ATE PCB Assembly involves integrating test-specific components, connectors, and sockets onto a purpose-built test board to ensure reliable and repeatable operation.
Properly executed ATE PCB assembly is critical for maintaining signal fidelity, power stability, and long-term test accuracy.
What Is ATE PCB Assembly?
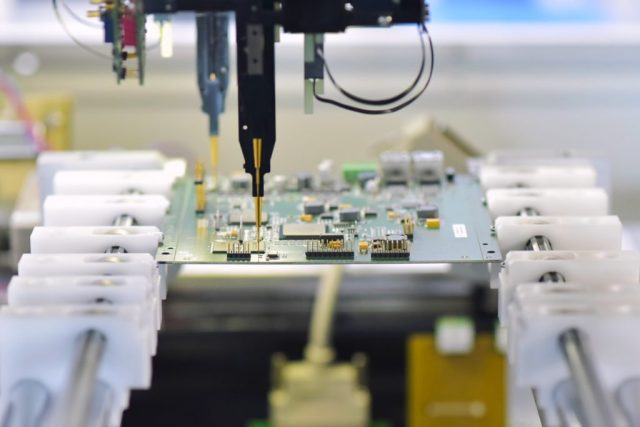
ATE PCB Assembly refers to the process of mounting components, connectors, and test interfaces onto an ATE-specific PCB. This process often involves:
-
High-pin-count connectors and sockets
-
Controlled impedance signal routing
-
Integration with probe cards, load boards, and test modules
It bridges the gap between PCB fabrication and fully functional automated test systems.
Why Precision Matters in ATE PCB Assembly
Precision assembly ensures:
-
Stable electrical contact for high-speed signals
-
Accurate voltage and current delivery
-
Long-term reliability across thousands of test cycles
Any assembly inconsistency can compromise test accuracy and yield.
Controlled Impedance and Signal Integrity
During ATE PCB assembly:
-
Critical high-frequency traces must maintain designed impedance
-
Careful component placement prevents crosstalk
-
Proper grounding and shielding maintain signal quality
Signal integrity is essential for repeatable semiconductor testing.
Power Delivery and Thermal Management

ATE PCB assemblies often carry multiple voltage domains. Assembly considerations include:
-
Proper routing of power planes
-
Decoupling capacitors placed close to active devices
-
Thermal vias and heat dissipation paths
Stable power ensures consistent test results and protects components.
Component Placement and Mechanical Stability
Effective assembly requires:
-
Accurate positioning of sockets, connectors, and test points
-
Reinforced mounting areas for high insertion-force connectors
-
Flatness and planarity control for probe card interfaces
Mechanical precision maintains long-term contact reliability.
Quality Control and Testing During Assembly
High-quality ATE PCB assembly includes:
-
Automated optical inspection (AOI)
-
Electrical and functional testing
-
Impedance verification for critical signal paths
Rigorous QC ensures that assembled boards perform reliably in test environments.
Typical Applications of ATE PCB Assembly

ATE PCB assemblies are widely used in:
-
Semiconductor wafer testing
-
IC parametric and functional testing
-
High-speed memory and logic device testing
-
Automated reliability and production screening
Each application benefits from fully integrated and precisely assembled PCBs.
Choosing a Reliable ATE PCB Assembly Partner
When selecting an ATE PCB assembly manufacturer, consider:
-
Experience with high-pin-count and high-speed designs
-
Capability in controlled impedance and HDI PCB assembly
-
Electrical testing and verification support
-
Engineering collaboration for prototyping and volume production
A skilled assembly partner ensures that test PCBs deliver accurate, repeatable results.
Conclusion
ATE PCB Assembly is a critical step in the creation of high-precision automated test equipment. By integrating controlled impedance routing, stable power distribution, and mechanically robust components, assembled ATE PCBs provide reliable and repeatable semiconductor testing performance.
Working with an experienced ATE PCB assembly manufacturer ensures high-quality boards that support modern semiconductor production and validation.

