As electronic devices become more compact and powerful, effective Thermal Management PCB solutions are critical to ensure performance, reliability, and product lifespan. High-power components such as CPUs, power MOSFETs, IGBTs, LEDs, and RF amplifiers generate significant heat during operation. Without proper PCB thermal management, excessive temperature rise can lead to signal instability, reduced efficiency, and premature failure.
This article explores key thermal management PCB technologies, design strategies, materials, and applications in modern electronics.
What Is a Thermal Management PCB?
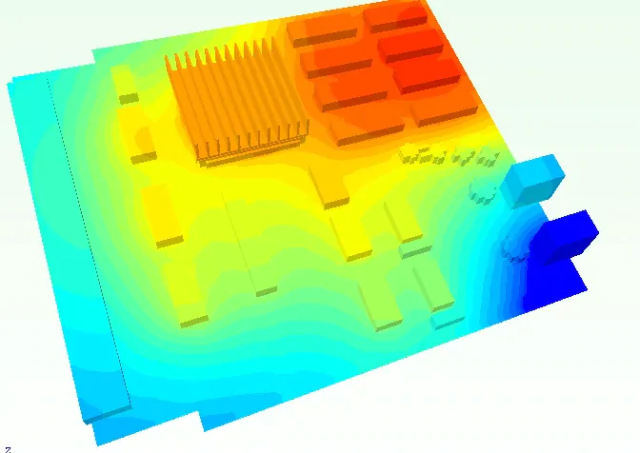
A Thermal Management PCB refers to a printed circuit board specifically engineered to dissipate heat efficiently. It integrates advanced materials, copper structures, and thermal pathways to transfer heat away from sensitive components.
Common types of thermal management PCBs include:
-
Metal Core PCB (MCPCB)
-
Aluminum PCB
-
Copper Core PCB
-
Heavy Copper PCB
-
Thermal Via PCB
-
IMS (Insulated Metal Substrate) PCB
These PCB technologies are widely used in LED lighting, automotive electronics, power supplies, and industrial equipment.
Why Thermal Management Is Critical in PCB Design
Effective PCB heat dissipation ensures:
-
Stable electrical performance
-
Reduced thermal stress on components
-
Improved product reliability
-
Extended operational lifespan
-
Compliance with safety standards
As power density increases in modern devices, thermal management PCB design becomes a core engineering requirement rather than an optional enhancement.
Key Thermal Management PCB Design Strategies
1. Metal Core PCB (MCPCB)
MCPCBs use an aluminum or copper base layer to enhance heat conduction. The metal substrate acts as a heat spreader, transferring heat efficiently away from components. Aluminum PCBs are particularly popular for LED lighting and automotive applications.
2. Thermal Vias and Via Arrays
Thermal vias connect surface-mounted components to internal or backside copper layers. Properly designed via arrays improve vertical heat transfer and reduce localized hot spots.
3. Heavy Copper PCB
Heavy copper PCBs (2 oz to 10 oz copper thickness or more) increase current-carrying capacity and improve heat distribution across the board.
4. Optimized PCB Stackup
Multilayer thermal management PCBs often include internal ground or copper planes dedicated to heat spreading. Proper stackup design enhances both electrical performance and thermal stability.
5. Thermal Interface Materials (TIM)
TIMs improve thermal contact between components and heat sinks, reducing thermal resistance in high-power PCB assemblies.
Materials Used in Thermal Management PCB
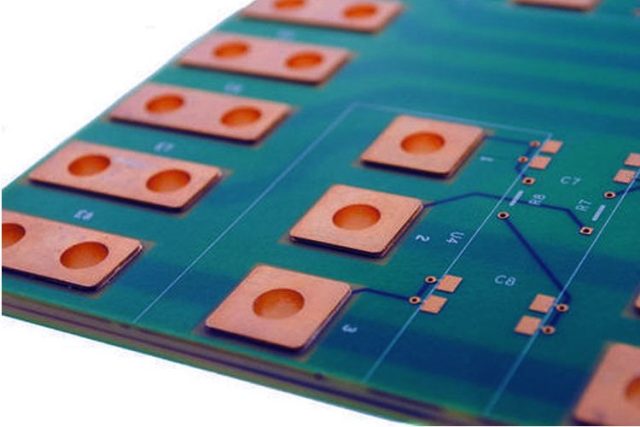
Material selection directly impacts thermal conductivity. Common materials include:
-
Aluminum substrates (high thermal conductivity, cost-effective)
-
Copper cores (excellent heat dissipation, higher cost)
-
Ceramic substrates (AlN, Al₂O₃ for high-frequency and high-temperature applications)
-
High Tg FR-4 for improved thermal endurance
Advanced applications may require low thermal resistance PCB materials to maintain optimal performance in high-temperature environments.
Applications of Thermal Management PCB
Thermal management PCBs are widely used in:
-
LED lighting systems
-
Electric vehicles (EV) power modules
-
Industrial power supplies
-
Telecommunication equipment
-
Renewable energy systems (solar inverters)
-
Medical electronics
-
High-frequency RF amplifiers
In these applications, efficient PCB thermal management ensures stable operation under continuous high-load conditions.
Thermal Simulation and Reliability Testing

Modern PCB design incorporates thermal simulation tools to predict temperature distribution before production. Combined with thermal cycling tests and reliability validation, manufacturers can ensure consistent performance under extreme operating conditions.
Collaboration between PCB designers and manufacturers is essential to optimize thermal management PCB manufacturing and achieve cost-effective heat dissipation solutions.
Conclusion
A well-designed Thermal Management PCB is essential for high-power and high-density electronic systems. By combining metal core technology, thermal vias, heavy copper layers, and optimized stackup design, engineers can significantly improve heat dissipation, enhance product reliability, and extend system lifespan.
As electronic innovation continues to advance, thermal management PCB solutions will remain a cornerstone of next-generation power electronics and high-performance devices.

