In automated test environments, consistency is just as important as accuracy. Even when test programs are perfectly written, unstable hardware interfaces can lead to false failures and yield loss. The ATE test PCB plays a critical role in maintaining stable signal transmission between automated test equipment and the device under test (DUT).
A properly engineered ATE test PCB ensures that test results remain repeatable across thousands—or even millions—of test cycles.
The Role of ATE Test PCB in Production Testing
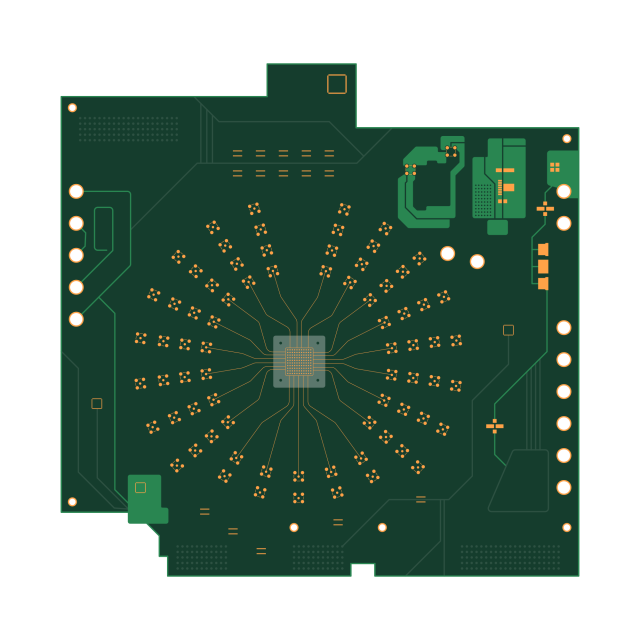
An ATE test PCB acts as the electrical backbone of an automated test system. It distributes power, routes signals, and maintains controlled electrical paths between the tester and DUT.
Unlike functional PCBs, ATE test PCBs must perform reliably under:
-
Continuous mechanical stress
-
Repeated probing or socket insertion
-
High-speed signal switching
-
Long operating hours
Any inconsistency directly affects test accuracy and throughput.
Why Measurement Stability Depends on ATE Test PCB Quality
In high-volume testing, unstable test boards can cause:
-
Intermittent contact resistance
-
Signal skew or reflection
-
Ground bounce and noise coupling
-
False fails or masked defects
A high-quality ATE test PCB minimizes these risks by maintaining consistent electrical characteristics throughout its service life.
Key Electrical Design Considerations
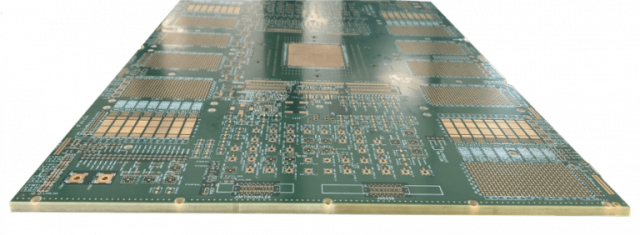
Controlled Impedance for High-Speed Signals
Modern ATE systems test devices at increasingly high speeds. ATE test PCB design must include:
-
Controlled impedance routing
-
Stable reference planes
-
Proper termination strategies
These elements reduce signal distortion and measurement variation.
Power Integrity and Grounding
Clean power delivery is essential. ATE test PCBs require:
-
Low-impedance power planes
-
Robust decoupling strategies
-
Solid grounding structures
Stable power prevents test drift and noise-related failures.
Mechanical and Structural Requirements
ATE test PCBs are subject to frequent mechanical interaction. Designs must prioritize:
-
PCB flatness to ensure uniform contact
-
Reinforced connector and socket regions
-
Durable materials that resist warpage
Mechanical integrity directly impacts long-term test consistency.
Manufacturing Consistency Matters More Than Speed
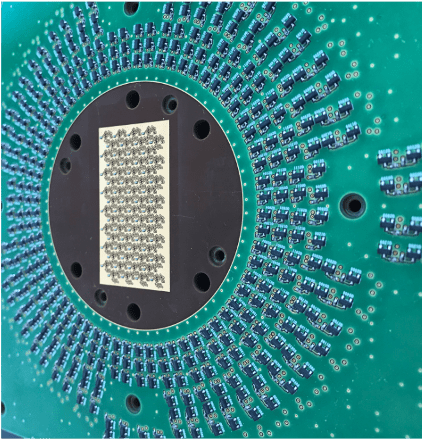
Producing a reliable ATE test PCB requires tight manufacturing control:
-
Consistent laminate properties
-
Uniform copper thickness
-
Precise drilling and plating
-
Accurate layer registration
Variations between boards can lead to inconsistent test results, even with identical test programs.
Material Selection for ATE Test PCBs
Common materials include:
-
High-Tg FR-4 for durability
-
Low-loss laminates for high-speed or RF testing
-
Hybrid stackups for mixed-signal environments
Material stability over time and temperature is more important than extreme electrical performance.
Typical Applications of ATE Test PCBs
ATE test PCBs are widely used in:
-
Semiconductor IC final testing
-
Memory and logic device validation
-
Automotive electronics testing
-
Industrial and consumer electronics mass production
Each application demands repeatable and predictable performance.
Extending the Service Life of ATE Test PCBs
A well-designed ATE test PCB helps reduce:
-
Maintenance frequency
-
Board replacement costs
-
Unexpected test downtime
Longer service life improves overall equipment efficiency (OEE) in production test lines.
Choosing the Right ATE Test PCB Manufacturer
When selecting an ATE test PCB supplier, consider:
-
Experience with production test boards
-
Ability to control impedance and layer consistency
-
Proven quality inspection processes
-
Support for quick revisions and replacement builds
A reliable manufacturer supports stable testing over the full product lifecycle.
Conclusion
An ATE test PCB is more than a simple interface—it is a critical factor in test accuracy, yield stability, and production efficiency. By focusing on electrical consistency, mechanical durability, and manufacturing repeatability, high-quality ATE test PCBs enable reliable automated testing in demanding, high-volume environments.
Selecting the right ATE test PCB partner ensures stable measurements, reduced false failures, and long-term testing success.

