Rigid-Flex PCB as a System-Level Interconnect Architecture
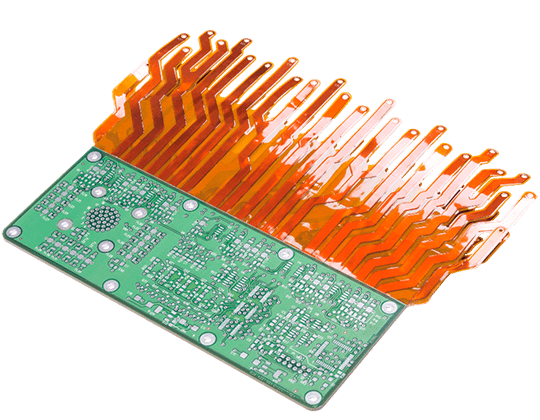
Rigid-Flex PCB technology integrates rigid PCB structures and flexible circuits into a single, unified interconnect platform. Compared with traditional rigid PCB assemblies connected by cables or connectors, a Rigid-Flex PCB significantly reduces interconnect interfaces while improving electrical continuity and mechanical robustness.
In modern electronic systems, Rigid-Flex PCB designs are no longer niche solutions. They have become a core architecture for space-constrained, vibration-sensitive, and high-reliability applications where rigid PCB or flexible PCB alone cannot meet system requirements.
Why Rigid-Flex PCB Is Critical in Compact and High-Reliability Designs
As electronic devices evolve toward higher functional density, smaller form factors, and complex 3D packaging, traditional rigid PCB layouts increasingly suffer from space inefficiency, connector failures, and signal integrity degradation.
Rigid-Flex PCB architecture directly addresses these limitations by allowing rigid PCB sections to be electrically and mechanically connected through flexible PCB layers. This approach eliminates board-to-board connectors, reduces solder joints, and improves overall system reliability.
Key engineering benefits of Rigid-Flex PCB include improved signal integrity, reduced EMI risk, lower assembly weight, enhanced shock resistance, and simplified system integration. For many designs, Rigid-Flex PCB is not just an optimization—it is a necessity.
Core Engineering Challenges in Rigid-Flex PCB Manufacturing
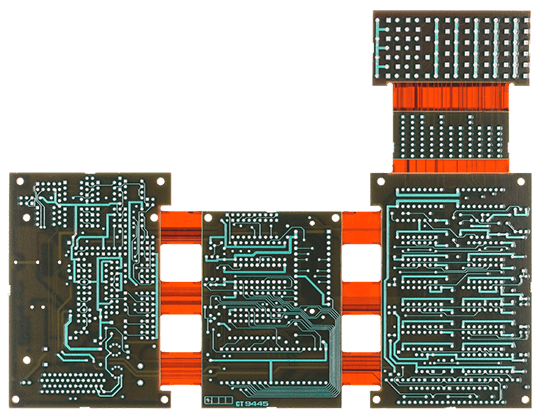
Rigid-Flex PCB manufacturing introduces a higher level of process complexity compared with standard rigid PCB fabrication. The coexistence of rigid and flexible materials creates challenges related to thermal behavior, mechanical stress, and dimensional stability.
Common Rigid-Flex PCB engineering challenges include copper fatigue in flex regions, layer registration accuracy across rigid-flex interfaces, impedance discontinuities during signal transitions, and delamination risks under thermal cycling.
Professional Rigid-Flex PCB fabrication requires precise control of lamination pressure, material flow, copper plating uniformity, and drilling accuracy. Without these controls, long-term Rigid-Flex PCB reliability cannot be guaranteed.
Rigid-Flex PCB Stackup Design and Material Engineering
Rigid-Flex PCB stackup design is a critical determinant of both electrical performance and mechanical durability. A typical Rigid-Flex PCB combines FR-4 or high-Tg rigid cores with polyimide-based flexible layers, carefully arranged to manage stress distribution.
Advanced Rigid-Flex PCB stackups focus on neutral axis optimization to reduce copper strain during bending. Copper thickness in flex layers is tightly controlled to balance flexibility and current-carrying capability, while dielectric thickness is optimized for controlled impedance routing.
A well-engineered Rigid-Flex PCB stackup ensures stable impedance, minimized signal loss, and long-term mechanical endurance under repeated flexing.
Signal Integrity and Controlled Impedance in Rigid-Flex PCB Designs
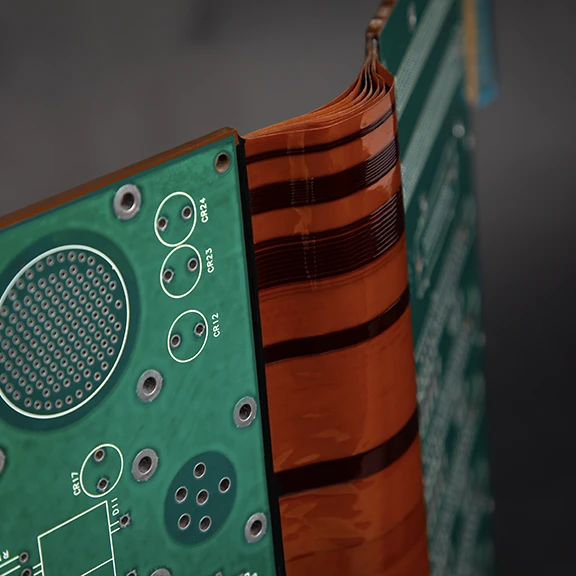
High-speed digital and RF systems place strict demands on signal integrity, making Rigid-Flex PCB impedance control a major design priority. Improper rigid-to-flex transitions can introduce impedance discontinuities, reflections, and phase distortion.
Professional Rigid-Flex PCB engineering ensures smooth impedance continuity by maintaining consistent trace geometry, dielectric properties, and reference plane integrity across rigid and flexible sections. Simulation-driven stackup design and impedance modeling are essential steps in this process.
As data rates and RF frequencies increase, Rigid-Flex PCB solutions provide superior signal stability compared with connector-based rigid PCB assemblies.
Rigid-Flex PCB Assembly and Reliability Validation
Rigid-Flex PCB assembly requires specialized fixtures and process control to protect flexible regions during soldering and handling. Standard PCB assembly methods are insufficient for high-reliability Rigid-Flex PCB products.
Advanced Rigid-Flex PCB assembly includes customized support tooling, optimized reflow profiles, and strict inspection protocols such as AOI and X-ray analysis. Reliability validation often involves dynamic bend testing, thermal cycling, vibration testing, and mechanical stress analysis.
These validation steps ensure that Rigid-Flex PCB assemblies maintain electrical performance and structural integrity throughout the product lifecycle.
Rigid-Flex PCB Applications Across High-End Industries
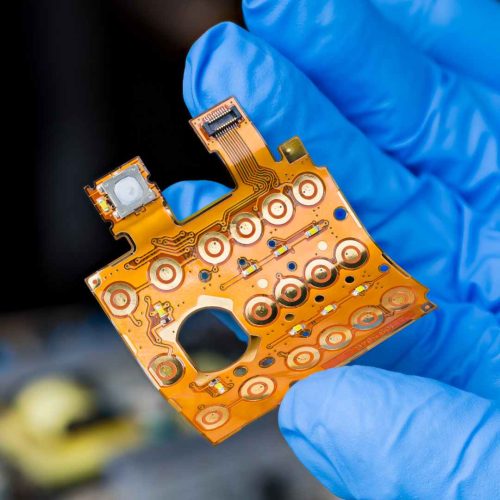

Rigid-Flex PCB technology is widely adopted in industries where performance and reliability are mission-critical. Typical Rigid-Flex PCB applications include aerospace electronics, satellite payloads, medical devices, industrial automation systems, automotive electronics, and compact consumer products.
In each of these sectors, Rigid-Flex PCB enables tighter integration, reduced failure risk, and improved system durability under harsh operating conditions.
KKPCB Expertise in Rigid-Flex PCB Solutions
KKPCB delivers engineering-driven Rigid-Flex PCB fabrication and assembly services, supporting complex multilayer Rigid-Flex PCB designs with controlled impedance, tight tolerances, and high reliability standards.
From early-stage stackup optimization to full-scale Rigid-Flex PCB manufacturing and assembly, KKPCB focuses on process stability, material integrity, and long-term performance. Our Rigid-Flex PCB solutions help customers reduce system complexity, improve reliability, and accelerate product development.

