Applications of Factory Automation in PCB Manufacturing
As electronic devices become more compact, powerful, and multifunctional, printed circuit boards (PCBs) must meet increasingly complex performance and reliability requirements. To support this evolution, factory automation has become a fundamental pillar of modern PCB manufacturing. Automated systems not only accelerate production but also improve precision, ensure repeatability, and reduce human error—making them indispensable for high-end electronics, including electric vehicles, telecommunications, industrial control systems, and consumer devices.
Below, we explore how factory automation transforms PCB production, enhances quality, and supports advanced electronic designs.

1. Automated Loading and Precision Positioning
PCB components are small, delicate, and increasingly complex. Proper handling is essential to avoid deformation, damage, or misalignment.
Modern robotic systems equipped with multi-axis servo motors and high-resolution vision systems ensure:
-
Controlled pick-and-place operations
-
Precise component orientation
-
Accurate alignment for each process stage
For industries like EV battery management or wire bonding, these systems are crucial for maintaining micron-level precision.
2. Automated Solder Paste Application

Before components are mounted, solder paste must be applied through metal stencils with exact volume and uniformity.
Automated solder paste printers provide:
-
Highly consistent paste deposition
-
Real-time monitoring of volume and shape
-
Reduced waste through controlled dispensing
This significantly improves solder joint reliability and minimizes process variations.
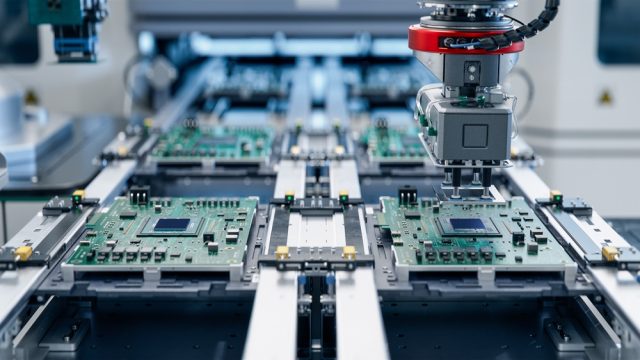
3. High-Speed Automated Component Mounting
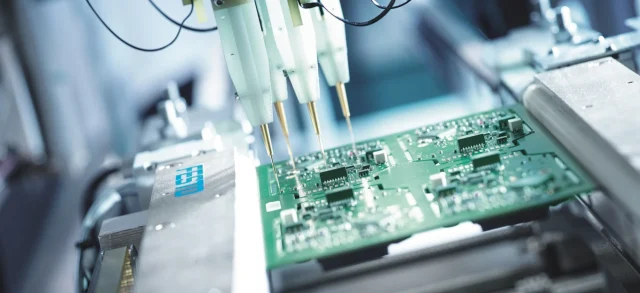
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) machines are the core of modern PCB assembly. With the ability to place tens of thousands of components per hour, SMT automation ensures:
-
Accurate placement of ultra-miniature parts
-
Precise routing of micro-wires and connectors
-
Near-zero placement errors
Automation makes it possible to build dense multilayer PCBs with fine-pitch components that human hands could never handle efficiently.
4. Automated Inspection and Functional Testing
Given the complexity of PCB designs, testing is critical to ensuring performance and reliability.
Automated testing systems include:
-
AOI (Automated Optical Inspection): Detects solder defects, shorts, missing components
-
ICT (In-Circuit Testing): Verifies connectivity, resistance, capacitance
-
Functional Test Systems: Evaluate real operating behavior using advanced software
These systems ensure every PCB leaving production meets strict quality standards.
5. Enabling Advanced Miniaturization
Microelectronics continue to shrink, requiring ultra-precise manufacturing.
Factory automation supports:
-
Micro-dispensing of adhesives and lubricants
-
High-precision wire bonding
-
Better process repeatability for ultra-small geometries
This enables production of micro-PCBs used in wearables, medical devices, and compact industrial sensors.
6. Automated Traceability Throughout Production
Traceability is essential for quality control, risk mitigation, and regulatory compliance.
Automated tracking systems use:
-
Barcodes
-
RFID tags
-
2D laser-etched codes
These systems record:
-
Material batches
-
Equipment used
-
Operator data
-
Process timestamps
This provides full visibility into the production lifecycle and facilitates rapid root-cause analysis.
7. Automated Packaging for Safe Delivery
PCBs are fragile, and improper packaging can lead to ESD damage or mechanical stress during transport.
Automated packaging systems help:
-
Wrap PCBs with ESD-safe materials
-
Sort and stack boards
-
Palletize large batches
This reduces manual handling and protects the PCBs’ structural and functional integrity.
The Growing Importance of Factory Automation
Factory automation continues to evolve, driven by:
-
Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing
-
Robotics, machine vision, and AI
-
Digital twins and simulation tools
-
Predictive maintenance and real-time monitoring
These advancements allow factories to achieve higher efficiency, better quality, and faster throughput—critical for industries facing rising demand for advanced electronics.
Conclusion
Factory automation is not merely an enhancement—it is the backbone of modern PCB manufacturing. Through precise handling, high-speed assembly, real-time monitoring, advanced testing, and reliable traceability, automation supports the development of increasingly sophisticated electronics.
As demand for miniaturized, high-performance PCBs grows, manufacturers adopting advanced automation technologies will be best positioned to deliver superior quality, efficiency, and scalability.

