In automated semiconductor testing, the performance of a test system is not determined by PCB fabrication alone. ATE PCB Assembly plays a decisive role in ensuring electrical accuracy, mechanical stability, and long-term repeatability throughout the entire test lifecycle.
A production-ready ATE PCB assembly process directly supports higher yield, fewer false failures, and stable high-volume testing.
Why ATE PCB Assembly Is Critical in Production Testing
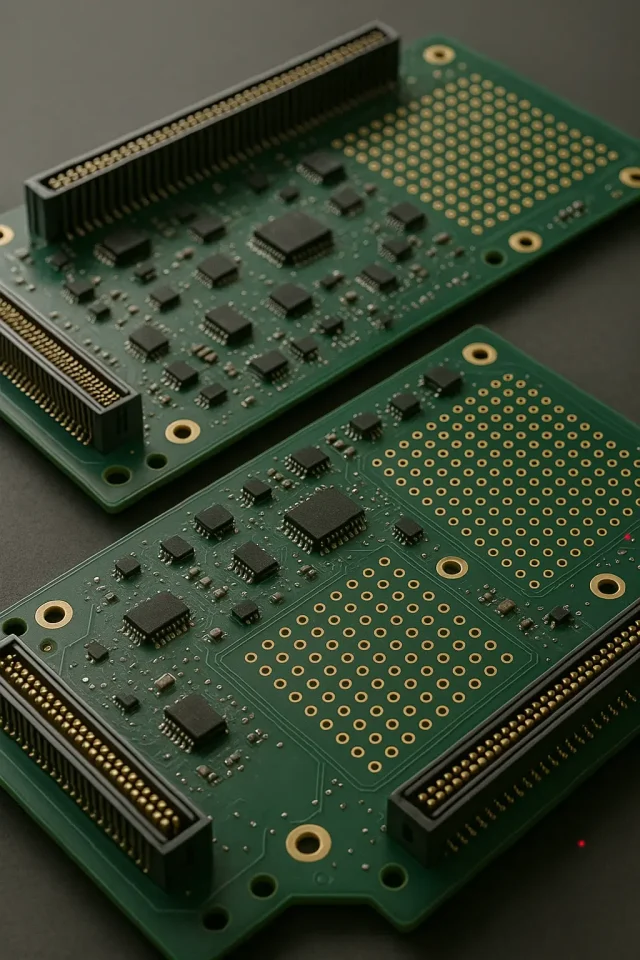
ATE environments operate under demanding conditions:
-
Continuous high-speed signal switching
-
Frequent socket and connector insertions
-
Long-term thermal and mechanical stress
Assembly quality determines whether a test board can maintain stable performance over time.
Assembly Challenges Unique to ATE PCBs
Compared with standard PCB assembly, ATE PCB assembly must address:
-
High-pin-count connectors and sockets
-
Mixed signal, power, and high-current components
-
Tight coplanarity and flatness requirements
These challenges require specialized assembly processes and experience.
Signal Integrity Preservation During Assembly
Even a well-designed PCB can fail if assembled incorrectly. ATE PCB assembly focuses on:
-
Precise placement of high-speed components
-
Controlled solder volume to avoid impedance disturbance
-
Clean reference plane continuity
Proper assembly preserves controlled impedance and signal timing.
Power Integrity and High-Current Assembly Considerations

ATE PCBs often carry multiple voltage domains and high transient currents. Assembly best practices include:
-
Low-resistance solder joints
-
Reinforced power connector mounting
-
Proper thermal relief design
Stable power delivery ensures reliable test results.
Mechanical Robustness for Repeated Test Cycles
ATE PCB assemblies must withstand:
-
Thousands of insertions and removals
-
High mechanical stress at connector interfaces
-
Continuous operation over long periods
Mechanical reinforcement and precise alignment are essential.
Assembly Process Control and Inspection
High-quality ATE PCB assembly includes:
-
Automated optical inspection (AOI)
-
X-ray inspection for BGA and hidden joints
-
Functional and continuity testing
These controls reduce early failures and improve consistency.
Integration with Sockets, Probe Interfaces, and Load Boards
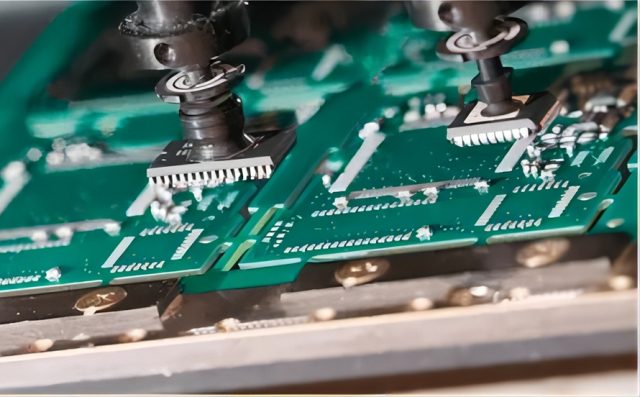
ATE PCB assembly often involves:
-
Test sockets and contactors
-
Probe card or load board interfaces
-
Customized mechanical fixtures
Accurate integration ensures stable electrical contact and repeatable testing.
Applications of ATE PCB Assembly
ATE PCB assemblies are widely used in:
-
Semiconductor production test systems
-
IC functional and parametric testing
-
Reliability and burn-in test platforms
-
High-speed memory and logic device testing
Each application depends on consistent assembly quality.
Choosing an ATE PCB Assembly Partner

When selecting an ATE PCB assembly supplier, consider:
-
Experience with semiconductor test hardware
-
Capability for high-pin-count and complex assemblies
-
Process control and inspection standards
-
Support from prototype to volume production
A reliable partner reduces test downtime and long-term cost.
Conclusion
ATE PCB Assembly is a critical factor in achieving stable, repeatable, and production-ready automated testing. Through precise component placement, robust mechanical integration, and strict quality control, professional ATE PCB assembly supports reliable semiconductor testing across the entire product lifecycle.
Partnering with an experienced ATE PCB assembly manufacturer ensures consistent performance from engineering validation to mass production.

