With the rapid development of today’s electronics industry, electronic products are becoming smaller, lighter, and more complex. To meet this demand, engineers have adopted Surface Mount Technology (SMT) — an advanced PCB assembly method that allows components to be mounted directly onto the surface of the printed circuit board.
If you’ve ever looked at the intricate boards inside smartphones, computers, or automotive electronics and wondered how those tiny parts are attached, the answer is simple: SMT PCB assembly.
What Is SMT PCB Assembly?
SMT PCB assembly (Surface Mount Technology PCB Assembly) refers to the process of directly mounting SMD components onto the surface of a PCB.
This differs from Plated Through-Hole (PTH) assembly, where component pins are inserted into holes before soldering. SMT technology offers higher speed, smaller component size, and better reliability — making it the dominant PCB manufacturing method for modern electronics.
8 Key Steps in the SMT PCB Assembly Process
1. Incoming Material Inspection
The SMT process starts with incoming material inspection. All components, PCBs, and materials are checked to ensure they meet the specifications in the Bill of Materials (BOM). The PCB surface must be flat, clean, and oxidation-free, while all SMD components must match the correct footprint and dimensions.
2. Pre-SMT Assembly Preparation
Before production begins, engineers prepare everything required for the SMT manufacturing process:
Solder stencil fabrication
Baking PCBs and BGA chips
Preparing pick-and-place files
Setting up feeders
Proper preparation ensures accuracy and efficiency in the SMT production line.
3. Solder Paste Printing
This is the foundation of SMT assembly quality. Using a laser-cut stainless-steel stencil, solder paste is applied to the PCB pads. The quality of solder paste printing directly affects solder joints and yield rate.
At KKPCB, we use premium lead-free solder paste, stored at 0–10°C and thoroughly mixed before application to ensure perfect viscosity and adhesion.
4. Component Placement (Pick & Place)
Once solder paste is applied, a high-speed SMT machine (such as Yamaha) automatically places the SMD components onto the PCB with micron-level accuracy.
For prototype PCB assembly, components may come in trays or loose packaging, while for mass SMT manufacturing, they’re usually in reels. After initial placement, engineers perform first-article inspection (FAI) to verify accuracy before mass production.
5. Reflow Soldering
After placement, the PCB enters a reflow oven where solder paste melts and solidifies, bonding components permanently.
Although vapor phase soldering is suitable for prototypes or sensitive components, reflow soldering is the most common method in SMT mass production.
At KKPCB, we use a 10-zone reflow oven in a nitrogen environment to ensure optimal temperature profiling and strong solder joints.
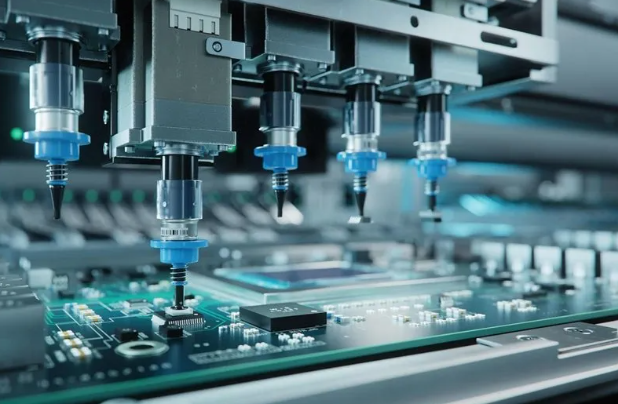
6. AOI (Automated Optical Inspection)
Quality assurance is critical. After soldering, each board undergoes 100% AOI inspection. Multiple cameras capture high-resolution images to detect missing, misaligned, or wrong components.
Without AOI, SMT assembly quality cannot be guaranteed. This step ensures consistent accuracy across all PCB assemblies.
7. Visual Inspection
Even after AOI, manual visual inspection is performed to identify cosmetic defects such as scratches, solder splashes, or color variations. Though time-consuming, it ensures every PCB assembly meets our cosmetic and mechanical standards.
8. Final Quality Inspection & Testing
Finally, QC engineers conduct final quality inspection — checking the assembled PCBs against design drawings
and engineering notes. This ensures that every surface mount PCB is accurately produced and ready for functional testing or next-stage assembly.
The SMT PCB assembly process plays a vital role in modern electronics manufacturing, offering high speed, precision, and reliability. From solder paste printing to reflow soldering and AOI inspection, each step ensures that every PCB assembly meets international quality standards.
Whether for consumer electronics, automotive, telecommunication, or medical devices, SMT manufacturing continues to power the innovation behind every modern electronic product.

